List of content you will read in this article:
What is CDN, why is it worth dealing with, how much it costs and what benefit we will have ... are some of the most frequent questions we hear lately in a technology that is now economically accessible and should exist on most websites.
What is CDN?
A CDN (Content Delivery Network) is essentially a group of servers – divided into different countries around the world – that work together to deliver content online. A CDN allows you to quickly transfer the items needed to load content online, including HTML pages, CSS and JavaScript files, stylesheets, images, and videos.
The popularity of CDN services is increasing nowadays as the majority of online traffic is served via CDN. More well-known companies such as Facebook, Netflix, and Amazon have done the same. In fact, a properly configured CDN will protect your website from hacking or DDOS.
The CDN is not, however, a hosting service, as your blog should be hosted somewhere before the CDN service can work and connect. CDN is an extra feature that will increase the speed of your blog quite a bit, providing your visitors with a faster and more enjoyable experience.
How does a CDN work?
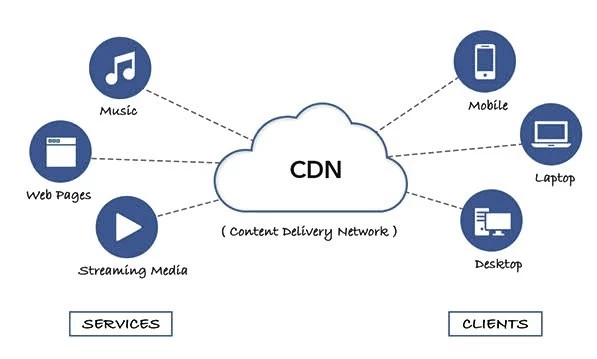
CDN is a network of servers around the world and undertakes to serve the data of your website (usually the ones that are heavier and do not change often, such as images, CSS, and JavaScript code) to each visitor from the loop closest to it. For example, a visitor to our website from America will load the website from a server in America while a visitor from Greece will load the website from a Greek server. As a result, we have very fast times for all visitors regardless of where they are.
In essence, a website is hosted only on a server in the country of origin but at the same time on a Greek server for Greeks, on an English server for English, on an American server for Americans, etc.
At the same time, due to the fact that the website loads from the CDN and not from our own server, it results in the server itself that hosted our website having much fewer requests and therefore needing much fewer resources to serve the website. As a result, this has to load more quickly our server and website, as there are our own resources to serve significantly fewer requests.
Benefits of CDN service
There are several things you can take advantage of from a CDN service, bearing in mind how your SEO ranking will increase, but you'll see why below.
- Increases the speed of page loading: When you have a CDN service, it means that every visitor who visits your blog will put it from the nearest server. As a result, Google will see a higher score on the speed of your website and you'll see your ranking increase.
- It will reduce the bandwidth on your server: Bandwidth is obviously one of the things that worry bloggers the more people visit your blog, the more bandwidth increases. In most sharing hosting packages, bandwidth is often quite limited, and to make sure you don't reach it and you won't have to pay more for a larger server, with a CDN service you will save enough of your precious bandwidth.
- Greater security: In addition to the fact that a CDN service can increase your security from DDOS attacks if your server falls until you solve the problem your website will remain open with the temporary cache that is left over.
- Minify code: If you've heard the word "minify" before but are terrified because it concerns your blog code, then with a CDN service the case is just a click away to activate the minify in all your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files.
So since you now know some of the key benefits of a CDN service, it's time to find the right one for you that meets your needs.
Cloudflare – The best free CDN
Cloudflare is one of the largest companies in the whole world and probably the most popular CDN service available. It provides an excellent free package for those interested in testing its service and some subscription packages for those who want to take advantage of more features, faster speed, and more tools available.
While the free package is frankly excellent, in fact, the difference between the free package and the cheapest one that costs $20 a month, is the day after night. At $20 a month the speed increases dramatically above, there is a firewall, automatic mobile optimization, automatic TCP optimization, and most importantly of all, compression and optimization of photos – things that are not provided in the free service package.
Essentially, with the free package you will receive protection from DDOS attacks and speed enhancement through the servers provided by the company, but in a limited number as only subscribers enjoy all servers, while free users are limited to only some of them. With the free package, you will also be able to minify your most important files and you will see the speed of your blog go up in scores from websites such as GTMetrix, Pingdom, and Google PageSpeed Insights.
The CDN (Content Delivery Network) is essentially a group of servers – divided into different countries around the world – that work together to deliver content online. A CDN allows you to quickly transfer the items needed to load content online, including HTML pages, JavaScript files, stylesheets, images, and videos.
To link your blog to CloudFlare, you will first need to change the nameservers of your domain name to those given to you by the service and then either install its WordPress plugin for better cache setting or add it to the plugin cache you are already using.
Types of CDN
-
Commercial CDN: This type of CDN is provided by third-party companies, such as Amazon Web Services, Cloudflare, or Akamai. Commercial CDNs typically offer global coverage, advanced caching and optimization techniques, and 24/7 customer support. They are suitable for businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large enterprises.
-
Peer-to-peer CDN: This type of CDN uses a distributed network of computers to share content. Users who access the content also contribute to the network by sharing the content with other users. Peer-to-peer CDNs are often used for large file downloads, such as software updates or video streaming. Examples of peer-to-peer CDNs include BitTorrent and Swarmify.
-
Private CDN: This type of CDN is built and maintained by a single organization for its own use. Private CDNs are typically used by large businesses or organizations that require high levels of security or control over their content delivery. Private CDNs can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud, and can be customized to meet the specific needs of the organization.
Do You need a CDN for Your Website and how Much will it Cost You?
All websites that have potential customers or visitors who are from different countries from the country where the website is hosted can benefit from the CDN. For example, a tour desk or hotel that has visitors from all over the world will have the greatest benefit from a CDN service.
Examples of maximum benefit are catering, tourism, vehicle rental, e-shops, transport, technical services, logistics, etc. At the same time, it is an optimal solution even for companies that have purely visitors from the country the website is hosted, but the website is hosted on servers abroad.
Indicatively without going into great detail, a website with about 100-200 visitors per day and with data per page 3-10MB will cost about three to five United States dollars per month. Of course, in calculating the cost, the optimization of each website plays a role in order to use a cache where necessary, making the necessary minifications, etc in order to drop, even more, the cost of CDN.
The cost of a CDN is solely related to the amount of data that will be transferred over its network. That is, the more traffic a site has, the more information will be transferred, so we will have a higher cost. However, the cost of a CDN is very low in relation to the benefits it offers. A feature of CDN costs is the variable cost/GB ratio, as the more GB transferred, the lower the cost of transport and hosting.
Factors to Consider while Choosing a CDN
-
Cost: The cost of a CDN can vary widely depending on the provider, the amount of traffic or bandwidth used, and the level of service required. Some CDNs offer pay-as-you-go pricing models, while others require a monthly or yearly subscription. Businesses should consider their budget and projected traffic volumes when choosing a CDN.
-
Geographic coverage: The geographic coverage of a CDN is important for ensuring fast and reliable content delivery to users around the world. Businesses should choose a CDN with a large number of servers located in strategic locations to minimize latency and improve user experience.
-
Features and capabilities: Different CDNs offer different features and capabilities, such as advanced caching and optimization techniques, SSL support, mobile optimization, and security features. Businesses should choose a CDN that offers the features and capabilities that best match their website's needs.
-
Reliability and support: Reliability and support are critical factors when choosing a CDN. A reliable CDN should offer high uptime and fast content delivery, with minimal downtime or performance issues. In addition, the CDN provider should offer 24/7 customer support and be responsive to any issues or concerns that arise. Regenerate response
Conclusion
We consider that in our days when the cost of a CDN is inversely proportional to the benefits it offers us, CDN is a necessary service for websites that want to have a professional presence and image on the Internet.
