List of content you will read in this article:
If you ever heard the word "Internet Protocol," you probably know the importance of IP in the internet world. So IP or Internet Protocol is a set of rules that works to route and address data packets. These packets can travel across networks and reach the appropriate destination.
There are two major types of IPs, the first one is IPv4, and the second one is IPv6 because they are widely used protocols worldwide. However, IPv6 has almost vanished IPv4 due to its excellent compatibility. So this blog will completely focus on an introduction to IPv6 and everything about this internet protocol.
What is IPv6?
The full form of IPv6 is Internet Protocol version 6, but many people also call it Internet Protocol (IP)'s next generation. This IP is developed for advancement in technology and replacing IPv4, but many internet services still have IPv4 in their system. Every computing machine, smartphone, IoT sensor, automation component, etc., requires a numerical IP address for communicating with other devices.

IPv6 was developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to deal with the long-anticipated problem of IPv4 address exhaustion. Throughout this article, we will familiarize ourselves with the concept of IPv6.
History Behind IPv6
After IPv4’s development in the early 80s, the available IPv4 address pool began to shrink rapidly as the demand for addresses exponentially increased with the Internet. Outlined below are the major points that played a key role in the birth of IPv6:
- The Internet has grown exponentially, and the address space allowed by IPv4 is saturating. There is a requirement to have a protocol that can satisfy the needs of future Internet addresses expected to grow unexpectedly.
- IPv4 on its own does not provide any security features. Data has to be encrypted with some other security applications before being sent on the Internet.
- Data prioritization in IPv4 is not up to date. Though IPv4 has a few bits reserved for Type of Service or Quality of Service, they do not provide much functionality.
- IPv4 enabled clients can be configured manually, or they need some address configuration mechanism. It does not have a mechanism to configure a device to have a globally unique IP address.

Taking pre-cognizance of the situation that might arise, IETF, in 1994, initiated the development of an addressing protocol to replace IPv4. The progress of IPv6 can be tracked using the RFC published:
- 1998 – RFC 2460 – Basic Protocol
- 2003 – RFC 2553 – Basic Socket API
- 2003 – RFC 3315 – DHCPv6
- 2004 – RFC 3775 – Mobile IPv6
- 2004 – RFC 3697 – Flow Label Specification
- 2006 – RFC 4291 – Address architecture (revision)
- 2006 – RFC 4294 – Node requirement
On June 06, 2012, some of the Internet giants chose to put their Servers on IPv6. Presently they are using the Dual-Stack mechanism to implement IPv6 parallel with IPv4.
Why Only Consider Using IPv6 Now?
IPv6 is widely considered due to its compatibility. Getting from IPv6 only system to an IPv4 system will not work as there is no backward compatibility built into it. However, older hardware can be upgraded with new firmware.
The problem is moving to purely IPv6 equipment or dual-stack gear, which can work on both protocols by the ISPs is super expensive back in the day, but now this is being implemented. Some of the main IPv6 features are as follows:
- Support addresses that are 128 bits long.
- Integrated with IPsec (Internet Protocol Security), which authenticates and encrypts the data sent.
- Allows the host to send fragment packets instead of the router.
- Does not require a DHCP (Domain Host Control Protocol) or manual configurations.
- Uses the host’s address resource codes from the DNS to map the IPv6 addresses.
- Stateless Auto-reconfiguration of Hosts allows IPv6 hosts to configure when connected to a routed IPv6 network automatically.
- More efficient routing
- Ipv6 supports auto-configuration, which corrects most of the flaws from IPv4 while integrated with the security features.
As we have mentioned above, IPv4 used to provide the services previously because it uses a 32-bit addressing scheme for supporting almost 4.3 billion devices. But now, the increased number of smartphones, computers, and laptops requires more addresses. Hence, IPv6 is developed that uses 128-bit addresses for supporting almost 340 trillion devices.
Issues with IPv6
There is no secret that IPv6 is as famous as IPv4. IPv6 implementations are comparatively new for the system. So software that is used to create systems for IPv4 hasn’t tested IPv6 appropriately. Hence, it can create issues, and they have to resolve them as quickly as possible for correct working. There are various groups that are doing complete testing of IPv6, but many IT equipment manufacturers already sold products with IPv6 vulnerabilities.
PS: Here's how you can set up IPv6 successfully on your Windows VPS.
IPv4 and IPv6
Ipv4 was developed in the late 70s, and it was the first non-experimental version on the internet. The total number of addresses allocated by IPv4 is 232, which is about 4 billion unique addresses. IPv6 theoretically allows 2128 addresses (3.4*1038), but the actual number is smaller as multiple ranges are reserved for special use or completely excluded from use.

IPv6 replaces IPv4 32 bit address with a 128-bit address, resulting in many addresses. IPv6 addresses are represented as eight groups comprising four hexadecimal digits while colons separate groups.
2003:0DB8:0000:12A4:D354:0008:0417:420B
Two decimal digits represent an example for IPv4 addresses in four groups which are separated by full stops.
198.168.34.65
The main reasons behind IPv4 being alone so far are reusing the same IP addresses and NAT. Network address translation (NAT) converts the private IPs to public IPs, which are unique. All the overlapping private IPs are behind unique public IPs.
Internet Protocol version 6 is a new addressing protocol designed to incorporate all the possible requirements of the future internet known to us as Internet version 2. Like its predecessor, IPv4, this protocol works on the Network Layer (Layer-3) of the OSI model. Along with its offering of an enormous amount of logical address space, this protocol has great features which address the shortcomings of IPv4.
IPv4 has proven itself as a robust routable addressing protocol and has served us for decades on its best-effort-delivery mechanism. It was designed in the early ’80s and did not get any major change afterwards. At the time of its birth, internet access was limited only to a few universities for their research and the Department of Defense. IPv4 is 32 bits long and offers around 4,294,967,296 (232) addresses. This address space was considered more than enough at the time.
Why There is No IPv5
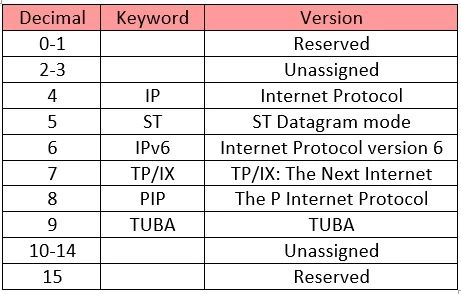
Until recently, Internet Protocol has been recognized as IPv4 only. Versions 0 to 3 were used while the protocol was itself under development and experimental process. So, we can assume lots of background activities remain active before putting a protocol into production. Similarly, protocol version 5 was used while experimenting with the stream protocol for the Internet.
It is known to us as Internet Stream Protocol which used Internet Protocol number 5 to encapsulate its datagram. It was never brought into public use. Here is a table of IP versions and how they are used:
Conclusion
So it was the complete information IPv6 and why it is so much popular among IT equipment companies. As we have mentioned earlier, IPv6 offers more compatibility than IPv4, but it has some vulnerabilities. If you like our blog, then you can visit our website, which has a huge list of informative blogs and guides.
In case you are looking for IPV6 VPS Server and want to use IPV6 features, you can use MonoVM VPS servers. Apart from IPv6 services, we also offer multiple services like VPS hosting, Web hosting, dedicated server, and many more.
