List of content you will read in this article:
An administrative user is windows default user who has all the rights and permissions over all the resources in the machine. You can use this user to manage permissions and roles for other users. In this article, we will be going through the Windows administrator, how you can configure its credentials, and the functions an administrative user can do.
Administrative user
An administrator account is a login ID with elevated privileges on a system that can be used to manage the system by installing software, applying patches, managing users, starting and stopping services, and so on.
The built-in administrator account on the Windows operating system is called "Administrator." In contrast, other common names for built-in administrator IDs include "root" on Unix and Linux systems and "sa" (short for system administrator) on SQL Server databases. There is no reason for administrator accounts to have default names. It is a common practice in many organisations to rename the built-in administrator account to a different name to make it more difficult to attack them via password guessing and other similar attack methods.
The administrative user has complete control over the permissions associated with various resources on your machine.
User Account Control
Windows users have to deal with User Account Control (UAC) whenever they try to do things that require administrative privileges. This includes a prompt that appears where we need to click "Yes" if you are an administrative user. In contrast, we need to enter administrative credentials if you are not an administrative user. User Account Control prompts are annoying, but they are also beneficial when it comes to security. It allows you to have one administrator account on your machine, but that privilege isn't automatically applied to every new process you start.
The fewer processes running on your system that can cause long-term damage, the better it is. Almost nothing you do on your computer requires Administrator privileges. At least with UAC, a programme must explicitly request full system access before it's granted.
Change administrative Password
You need to be on an administrative account before following the steps. Open the Settings app and go to Accounts > Sign-in options. Select Password> Change to add a new password for the administrative account. The same steps work when you wish to change the Password.
Change administrator name (using CLI)
You might need to change the administrative account's name in some cases. To accomplish this, type the following command after opening the command prompt in privileged mode:
wmic useraccount where name='Administrator' rename 'NewName'
Change administrator name (using GUI)
The below steps will work in Windows Home.
- Press Win+R and type netplwiz in the dialogue box.
- Double click on the administrator account, and you will get a new dialogue box where you can enter the new name for your account.
Enable/ Disable administrative account (using CLI)
To enable the admin account, open the command prompt in privileged mode and type:
net user administrator /active:yes
To disable the admin account, open the command prompt in privileged mode and type:
net user administrator /active:no
Enable/ Disable administrative account (using GUI)
- By pressing Win + R, you can bring up the Run window.
- Enter lusrmgr.msc in the input field and click OK in the dialogue box. This brings up the Local Users and Groups window.
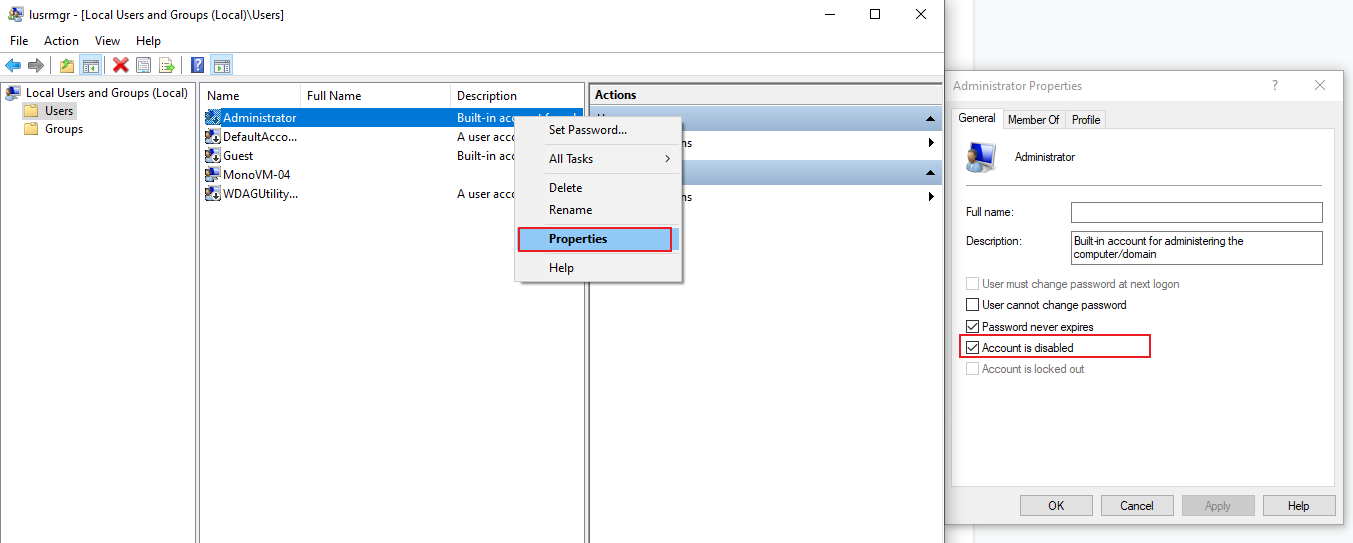
- Click Users in the window's left pane, then right-click Administrator and select Properties.
- You should see an option saying the account is disabled under the General tab.
- Uncheck this box, click OK, and then close the window. To disable the user, check this option.
Conclusion
This article went through the introduction, User Account Control, and configuration related to the administrative user in Windows. We saw how an administrative user handles all the permissions associated with all the users in the machine and can even create and delete other users. We also have the option to change the administrative user's credentials either through GUI or CLI.
People also read:

I'm fascinated by the IT world and how the 1's and 0's work. While I venture into the world of Technology, I try to share what I know in the simplest way with you. Not a fan of coffee, a travel addict, and a self-accredited 'master chef'.