List of content you will read in this article:
Mastering Kali RDP (Microsoft WBT Server) in the dynamic realm of cybersecurity opens doors to unparalleled efficiency. This comprehensive guide dives into setting up and optimizing remote desktop solutions on Kali Linux, including XFCE, VNC, and SSH. Whether connecting to Windows machines or enabling Linux RDP, our step-by-step approach ensures you navigate the complexities seamlessly. From the first paragraph, discover the power of Kali RDP, empowering you to excel in penetration testing and cybersecurity tasks.
How To Establish Remote Access To Kali Linux – Native Solution
When it comes to remotely accessing Kali Linux (Kernel Auditing LInux), the native solution provides a seamless and efficient way to connect. Follow these steps to set up remote access effortlessly.
Ensure SSH Service is Running
Before diving into the remote desktop setup, make sure the SSH (Secure Shell) service is up and running on your Kali Linux machine. SSH serves as the foundation for secure communication between devices.
To confirm if SSH is active, open a terminal and enter the following command:
service ssh status
If the service is not running, start it using:
service ssh start
Update and Upgrade Kali Linux
Keeping your Kali Linux system updated is crucial for security and compatibility. Execute the following commands to update and upgrade your system:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade -y
Install and Configure XRDP
XRDP (X Remote Desktop Protocol) is the key component for enabling remote desktop functionality on Kali Linux. Install XRDP using the following command:
sudo apt install xrdp -y
Once installed, start the XRDP service and set it to run on boot:
sudo service xrdp start
sudo update-rc.d xrdp enable
Configure Firewall Settings
To ensure smooth remote desktop access, configure your firewall to allow connections on the default RDP port (3389). Use the following commands:
sudo ufw allow 3389/tcp
sudo ufw reload
Connect to Kali Linux Remotely
With everything set up, you can connect to your Kali Linux machine remotely using an RDP client. Enter the IP address of your Kali system, and you'll be prompted to enter your credentials.
Enjoy the convenience of managing your Kali Linux environment remotely, enhancing your efficiency and flexibility in cybersecurity tasks.
Setting up RDP with XFCE
Enhancing the remote desktop experience on Kali Linux often involves choosing a suitable desktop environment. XFCE, known for its lightweight and user-friendly nature, can be seamlessly integrated with RDP.
Install XFCE Desktop Environment
Begin by installing the XFCE desktop environment using the following command:
sudo apt install xfce4
Configure XRDP to Use XFCE
After XFCE is installed, configure XRDP to use it as the default desktop environment. Open the XRDP configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/xrdp/xrdp.ini
Locate the `[xrdp1]` section and change the `port=-1` to `port=ask-1`. Save the changes and exit the editor.
Restart XRDP Service
Restart the XRDP service to apply the configuration changes:
sudo service xrdp restart
Now, when you connect to Kali Linux via RDP, you'll be prompted to choose the desktop environment. Select "XFCE Session" to initiate the remote connection with the XFCE desktop.
Remote Desktop (GUI) access to Kali
While the command-line interface is powerful, having graphical user interface (GUI) access to Kali Linux through a remote desktop can significantly enhance user interaction. Let's explore how to achieve GUI access to Kali Linux using RDP.
- Launch Remote Desktop Connection on the Windows system.
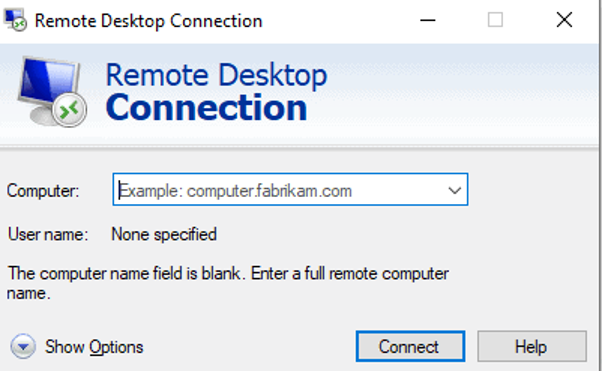
- Input the IP address of the Kali machine and click on the "Connect" button.
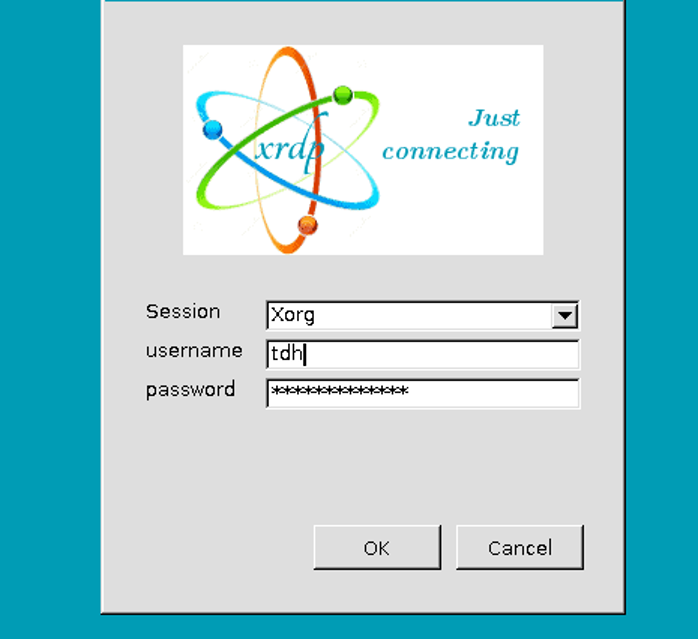
- Close the Xorg session and, after entering the necessary credentials, click "OK" to conclude the process.
How to Set Up RDP for Windows Remote Machines
Collaboration in cybersecurity often involves managing various systems, including Windows machines. Setting up RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) for Windows remote machines allows seamless connectivity. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to configure Kali Linux Remote Desktop Windows 10.
Enable Remote Desktop on Windows
On the Windows machine, navigate to "Settings" > "System" > "Remote Desktop." Enable Remote Desktop and note down the system's IP address.
Install Remmina (Optional)
For an optimal RDP experience, install Remmina on your Kali Linux machine. Use the following command:
sudo apt install remmina
Open Remmina and Add Connection
Open Remmina, click on "Create a new connection," choose "RDP" as the protocol, and enter the Windows machine's IP address and login credentials.
Connect to Windows Remote Machine
Click "Connect," and Remmina will establish an RDP connection to the Windows machine. Enjoy seamless remote access from your Kali Linux environment.
VNC for Kali Remote Desktop
VNC (Virtual Network Computing) provides an alternative method for remote desktop access on Kali Linux. Explore how to set up VNC for Kali Remote Desktop for a versatile and user-friendly experience.
Install VNC Server
Install a VNC server on your Kali Linux machine. For example, using TightVNC:
sudo apt install tightvncserver
Start VNC Server
Start the VNC server using the following command:
tightvncserver
Set up a VNC password when prompted.
Install VNC Viewer on Local Machine
On your local machine, install a VNC viewer. RealVNC or TigerVNC are popular choices.
Connect to Kali Linux via VNC
Open the VNC viewer, and enter the Kali Linux IP address followed by the VNC server display number (e.g., `192.168.1.2:1`). Enter the VNC password when prompted.
Terminal Access Using SSH
While remote desktop solutions provide graphical access, terminal access using SSH remains a fundamental aspect of Kali Linux. Here's a guide on utilizing SSH for efficient and secure terminal access.
Install OpenSSH Server
Ensure the OpenSSH server is installed on your Kali Linux machine:
sudo apt install openssh-server
Start SSH Service
If not started automatically, initiate the SSH service:
sudo service ssh start
Connect via SSH
On your local machine, open a terminal and use the following command to connect to your Kali Linux machine:
ssh username@kali-linux-ip
Replace `username` with your Kali Linux username and `kali-linux-ip` with the actual IP address.
Final Words
In conclusion, navigating the intricate landscape of Kali RDP opens a gateway to unparalleled flexibility and efficiency in the realm of cybersecurity. From configuring remote desktop solutions like XFCE and VNC to establishing connections with Windows machines through RDP, Kali Linux offers various options tailored to diverse user preferences. Terminal access via SSH remains a steadfast foundation, blending the power of the command line with the robustness of Kali's tools. Embracing these remote access methodologies not only streamlines penetration testing tasks but also underscores the adaptability of Kali Linux RDP to meet the dynamic demands of cybersecurity professionals. As we wrap up this exploration, remember that the journey doesn't end here—continuously fine-tune and secure your Kali RDP setup to stay at the forefront of cutting-edge cybersecurity practices.

Hello, everyone, my name is Lisa. I'm a passionate electrical engineering student with a keen interest in technology. I'm fascinated by the intersection of engineering principles and technological advancements, and I'm eager to contribute to the field by applying my knowledge and skills to solve real-world problems.