List of content you will read in this article:
It is not a secret that technology has been advancing at a rate previously unseen. All the performance numbers of all the hardware components we use today have risen annually in an exponential manner. Nevertheless, just like how in the automotive industry, packing a vehicle with pure horsepower won't win you the race, in the IT world, performance improvements are not simply due to better hardware. Countless incredibly genius solutions can cause even old outdated hardware to outperform the "latest and greatest" market. Today we will focus on one such solution: Redundant Array of Independent Disks (i.e., RAID) Technology.
What is RAID?
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks and is a technology created to provide a level of fault tolerance and improved server machine performance. Fault tolerance means that the machine would continue operation if a hard disk were to fail. The level of fault tolerance and performance benefits you receive from your RAID array depends on how it is set up and whether you are using hardware RAID controllers or software RAID solutions.
RAID works by connecting two or more (the minimum amount depends on the RAID configuration used) hard drives and striping, mirroring them, or both. Striping is the process of writing data across multiple disks, meaning the disk I/O is significantly improved. On the other hand, disk mirroring causes the data to be copied simultaneously from one disk to another, creating a mirror.
Different RAID configurations utilize these two technologies to create custom ratios between data redundancy and performance improvements. Monovm uses RAID10 configuration for VPS(What is VPS?) Hosting is the most secure and fast RAID configuration.
Hardware vs. Software RAID
Software RAID allows you to set up a RAID array without using a dedicated hardware RAID controller while providing similar functionality. It comes at a price, though; the performance benefits gained from software RAID are not nearly as great as those you could get when using a specialized hardware solution.
Another major issue with software RAID is the fact that it is software. Therefore there will be no data redundancy during boot time, as the software has not launched yet. Despite that, RAID capability is inherent in the operating system. Windows has had built-in support for RAID since Windows 7 (Pro and Ultimate editions). It allows you to split a single disk into two partitions: one to boot from and another for data storage. Then you can have the data partition mirrored.
Hardware RAID typically uses a discreet hardware controller. However, ROC (i.e., RAID-on-Chip) is also widely used in the IT world. In ROC solutions, the RAID processor, memory controller, host interface, I/O interfaces for hard disk drive connections, and sometimes even the memory are all integrated into one single chip, which can be integrated into the motherboard and offers hardware RAID capabilities.
Types of RAID Arrays
These are the most used RAID configurations
|
Features |
RAID 0 |
RAID 1 |
RAID 5 |
RAID 6 |
RAID 10 |
|
Minimum # of drives |
2 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
4 |
|
Data Protection |
No Protection |
Single-drive failure |
Single-drive failure |
Two-drive failure |
Up to one disk failure in each sub-array |
|
Read Performance |
High |
High |
High |
High |
High |
|
Write Performance |
High |
Medium |
Low |
Low |
Medium |
|
Capacity Utilization |
100% |
50% |
67%-94% |
50%-88% |
50% |
Different RAID configurations
What is RAID 0?
This RAID array is used purely to increase server performance and does not provide any data redundancy, thus providing 100% capacity utilization. In this RAID, system data split into multiple blocks, which are writing beyond all drivers in a specific array. It provides excellent input and output performance through multiple disks.
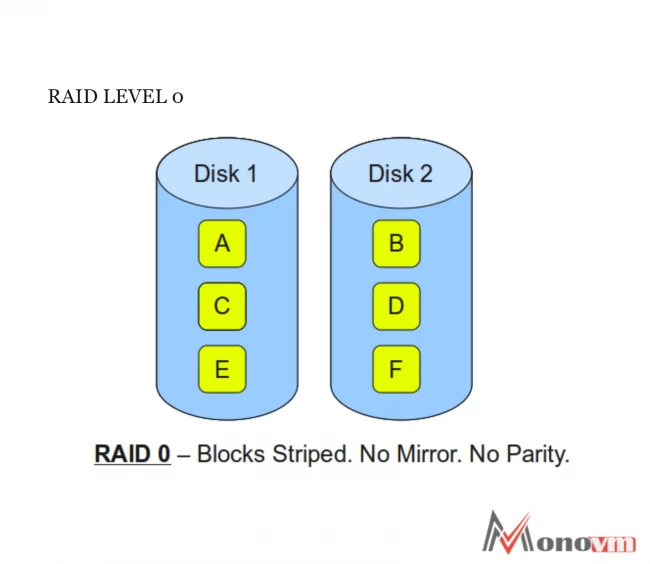
This performance can be improved further through different controllers, ideally single control per disk. RAID 0 is best for the non-critical storage of data required to be read or written at a higher speed.
What is RAID 1?
This RAID array does not do any striping but uses the second drive purely for data mirroring. All of the data gets stored twice by writing them to mirror drive (drive's set) and data drive (data drive's set). In case the drive fails, then the controller can easily work to use either the mirror drive or the data drive for continuous operation and data recovery. Hence, a user will require at least two drives for the RAID 1 array.
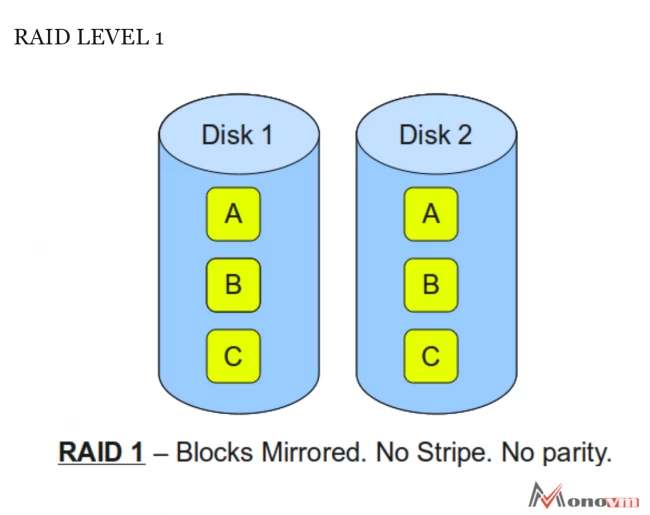
RAID 1 is best for mission-critical storage like it is ideal for accounting systems. This RAID 1 is also best for small servers in which users will use only two data drives.
What is RAID 5?
Data parity is striped across three or more disks, so data is recreated from this distributed data and parity block if one has an error. This means that the drives in this array are hot-swappable.
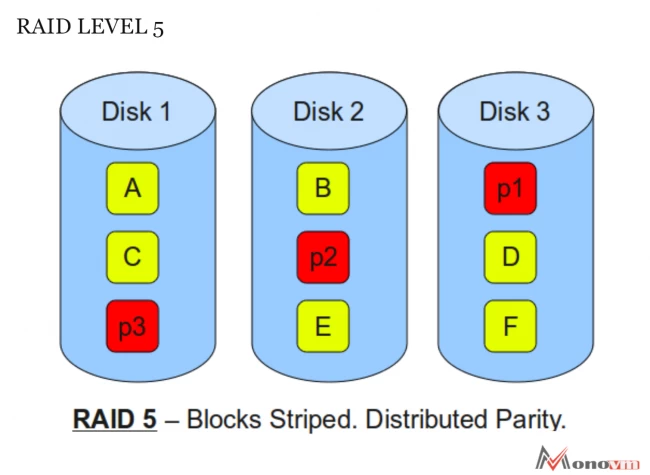
RAID 5 is one of the most common and secured RAID levels that needs at least three drivers, but it can easily work with upto 16. In RAID 5, all of the data blocks are scripted beyond the drive, and on one specific drive, a parity checksum of the block data is written. RAID 5 is ideal for a comprehensive system to combine efficient storage with great security and amazing performance.
What is RAID 6?
Similar to RAID 5, but with one more parity block, meaning that two drives can fail and the server will still be operational. RAID 6 is almost similar to RAID 5, but all of the parity data are written to two different drives. So it needs at least four drivers and can easily withstand two drives dying simultaneously.
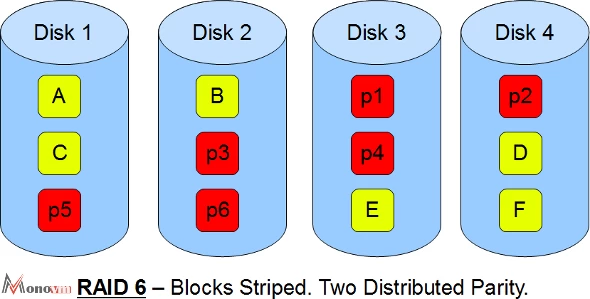
RAID 6 is an ideal all-around system that combines efficient storage with great security and appropriate performance. This RAID is best for is preferable on RAID 5 in file and application servers which use various large drives for the data storage.
What is RAID 10 (1+0)
It is a combination of RAID 1 and RAID 0, often called RAID 1+0. This is the most optimal solution as it combines data striping and data mirroring to provide the best performance and data redundancy. Unlike the rest of RAID arrays, it requires a minimum of 4 hard disks.
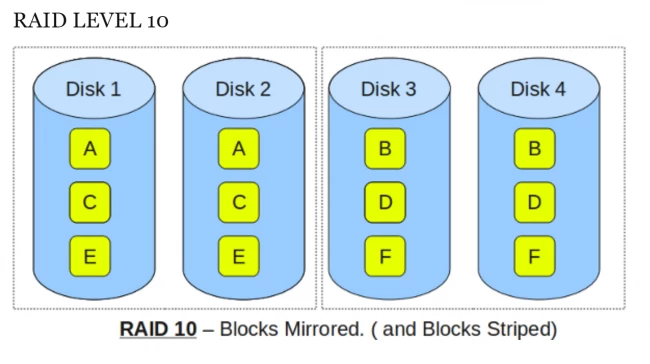
RAID 10 offers amazing security by mirroring data on the secondary drive while using striping beyond every set of drives for speeding up data transfers.
Conclusion
So it was complete information on what RAID is and every single aspect of this technology. We hope that you have understood everything about this particular topic, and if you like our blog, then please do visit our official website as we have a huge list of informative blogs. Apart from it, we also provide multiple services: DNS server, dedicated server, VPS hosting, web hosting, and so on.
