List of content you will read in this article:
- 1. What is a MAC Address?
- 2. Format & Notation of a MAC Address
- 3. Types of MAC Addresses
- 4. What does a MAC address look like?
- 5. Why care about MAC addresses?
- 6. How to find a MAC address?
- 7. Ways to change MAC Addresses in Windows
- 8. Can a device have more than one mac address?
- 9. MAC VS IP Addresses
- 10. What is MAC Cloning?
- 11. Advantages of MAC Address
- 12. Disadvantages of MAC Address
- 13. Why Should the MAC Address Be Unique in the LAN Network?
- 14. Conclusion
- 15. FAQ
Computer networks formed with various devices need a unique network adapter that comes with a MAC address. A single network adapter from a particular network is given this address to receive a worldwide unique identification number. Even if the network circulates various network adapters like Ethernet or Bluetooth, they will still receive a different unique number. As MAC addresses are assigned right after manufacturing single pieces of hardware, they are also known as physical or hardware addresses.
An important note here is -device addresses are not the same as MAC addresses because devices come with several network adapters, and they are not given one unique identification number. A MAC address is a 48-bit hardware recognition number assigned to a particular device on one single network in technical terms. In written form, they follow two significant formats, and the first half of it always is used to identify the corporation that is manufacturing the hardware. You can present the addresses in the following manner/syntax:
AA:AA:AA:SS:SS:SS
AAAA-AASS-SSSS
The first six digits represent the organization, called an Organizational Unique Identifier or an OUI. Some of the well-known OUIs are given below as an example:
CC:46:D6- Cisco
3C:5A:B4- Google
3C:D9:2B- Hewlett Packard
00:A0:C9- Intel Corporation
What is a MAC Address?
In technical terms, a MAC address is defined as a long address consisting of 48 bits, and it follows a hexadecimal format. This format uses base-16 to identify individual numbers of the address. By implementing this method, there is no possibility of having two same MAC addresses because the number of combinations present in forming a 12-digit address is usually in hundreds of trillions. This address is the sublayer of Data-link, and can actively participate in the network connections of a device. The standard followed to formulate this address is based on the IEEE authority committee, and they also are responsible for assigning a unique MAC prefix to every registered vendor.
What is a MAC address used for?
It is a network adapter's hardware address, such as the Ethernet card in a computer or the Wi-Fi module in a smartphone. A MAC address serves the following major functions:
- Device Identification: MAC addresses are used to identify devices on a network in a unique way. No two devices should have the same MAC address, which aids in device identification.
- Data Link Layer Communication: For example, in Ethernet networks, the MAC address is used to route data frames between devices on the same local network.
- Switching and Routing: MAC addresses allow switches to forward data exclusively to devices that have the correct MAC address. This aids in the effective transmission of data inside a network.
- Security: MAC addresses are used by some network security features to regulate network access. MAC address filtering, for example, can be used to allow or disallow specific devices from connecting to a network.
Note: While MAC addresses are required for local network communication, they are often not visible outside of the local network. When sending data over the internet, the source and destination IP addresses are used to route the data, and MAC addresses are normally not transmitted outside of the local network.
How MAC addresses get assigned?
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) oversees the assignment of MAC addresses through its Registration Authority (RA). The process involves the following steps:
OUI (Organizationally Unique Identifier) assignment
The first three bytes of a MAC address, known as the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI), are assigned to specific manufacturers or organizations. The IEEE assigns OUIs to organizations upon request. An OUI uniquely identifies the manufacturer or organization that produced the network device.
Extension identifier assignment
The remaining three bytes of the MAC address, known as the extension identifier, are assigned by the manufacturer or organization that owns the OUI. They can be assigned in any way the organization chooses, as long as the resulting MAC address remains globally unique.
Note: The responsibility for ensuring global uniqueness of MAC addresses lies with the manufacturers or vendors who obtain OUIs. This helps prevent conflicts and ensures that MAC addresses are globally unique, facilitating proper functioning of networks.
Format & Notation of a MAC Address
MAC addresses usually form the same format and notation to help networks interact instantly. The address consists of 12 digits, and while assigning the numbers of prefixes, we follow Colon-Hexadecimal notation. In any MAC address, the first six digits represent the organization that manufactured the device, and it is called OUI. The left side of the address is given for the manufacturer to assign an OUI number, and the right-hand side of the address represents the Network Interface Controller. An organization identifier is mainly to understand the origins of the device, and it helps us understand its compatibility. Some of the well-known IT companies have the following OUIs:
CC:46:D6- Cisco
3C:5A:B4- Google
3C:D9:2B- Hewlett Packard
00:9A:CD- Huawei Technologies.
Some other notations also include periods and hyphens separated, but it is important to align them with the operating system. In the case of Linux, it follows colon notation, and Cisco systems use period notation.
Types of MAC Addresses
Even in-network devices' unique identifiers, there are multiple categories, and each has its specific functions and functionality. Three main types of MAC addresses can be attached to a network: Unicast, Multicast, and Broadcast.
1. Unicast
A unicast MAC address represents multiple NIC ports present in the network or aimed at only a specific NIC. For the network controller, this is an in-built component and helps only a certain number of ports. When one single port is given a MAC address and transmits the frame to another single destination device, then that type of MAC address is called unicast.
2. Multicast
In the case of a unicast MAC address, we have seen that the packets are transmitted on an Ethernet network to only fixed receivers. Still, when we come to multicast, the members can be changed from time to time. As they are changing, we need to deploy multiple MAC addresses at the data layer, represented in the most significant octet.
3. Broadcast
In a way, we can say that broadcast is an extension of multicast MAC address because the frames reach every computer that is associated with that LAN segment. That is why the destination address has all bits as one. The devices that involve broadcast MAC addresses plan to send data to every receiver present in the network.
What does a MAC address look like?
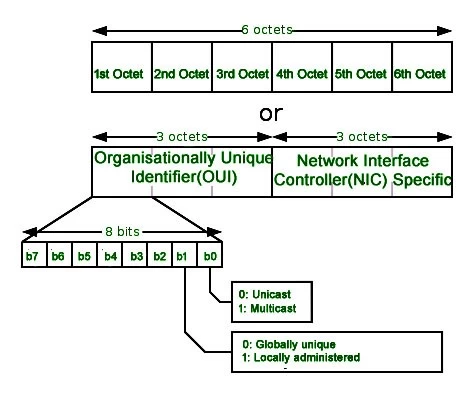
- Any MAC address associated with a network adapter comes with six outlets, and they are divided into three outlets with eight bits each.
- The first one is called OUI, and it is for recognizing which company manufactured the physical hardware components.
- Once you are done with the 24-bit number, you will see three pairs of digits that help us understand the device interface or network interface.
- The next three octets contain eight bits, and they are four main parts encoded with different information.
- First Part (receiver): The first set of digits helps us figure out whether the address is associated with a group or individual. This set is short of I/G, so it is called a unicast address if it is equal to zero. If the value is equal to 1, then it is multicast, and if it is neither of those two values, then the MAC address belongs to broadcast.
- Second Part( Registry): The second set of digits is to determine global and local validity. This one is called U/L. If the value is zero, then it is universal, and if it is equal to one, the address is locally administered.
- Third Part( Identification of Manufacturer): From the 3rd bit to the 24th, we consider the organizationally unique identifier introduced by IEEE.
- Fourth Part( Adapter Identifier): From the 25th bit to 48th, we retrieve a unique number called hardware identifier, and it is assigned to help us find the right network adapter.
Why care about MAC addresses?
We always mention the importance of IP addresses, but we tend to forget that IP and MAC addresses complement real-world applications like network routing and device identification. MAC address serves as an essential element in the seven-layer network communication model made by the Internal Organization for Standardization(ISO). They take the backup layer two, first introduced by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The second layer taken by MAC address is again divided into two sublayers called media access control and logical link control. These sublayers take care of the transmission process, and they give all the necessary tools to sustain a physical connection.
The second most important application of MAC addresses comes with its ability to filter wireless networks. If a user tries to engage with a device with a dynamic IP address, the MAC address can prevent strangers/attackers from gaining access to the network. The routers are designed in a particular fashion where they only have one specific MAC address, so system owners can still identify their devices.
People often misunderstand that MAC addresses have nothing to do with packet transfers because there is no hierarchy. However, there are different protocols for proper authentication of packets processed through Ethernets.
Data recovery is another important application of any MAC address, and it retrieves the data by using two possible modes called Quick and Deep scan. These methods are deployed using metadata present in the file system. In the deep scan case, the system breaks down multiple levels to reach the binary stage. Most of these methods are present in both Mac and Windows computers.
How to find a MAC address?
The older versions used to display MAC addresses using Winnipeg and ipconfig. In Windows, the operating system takes control of the MAC addresses to support the dial-up connections. Some of them even use virtual adapters to lower the use of hardware and increase software implementation. If you want to find your MAC address with little to no effort, you need to access the command line locally and remotely.
For Windows Computers
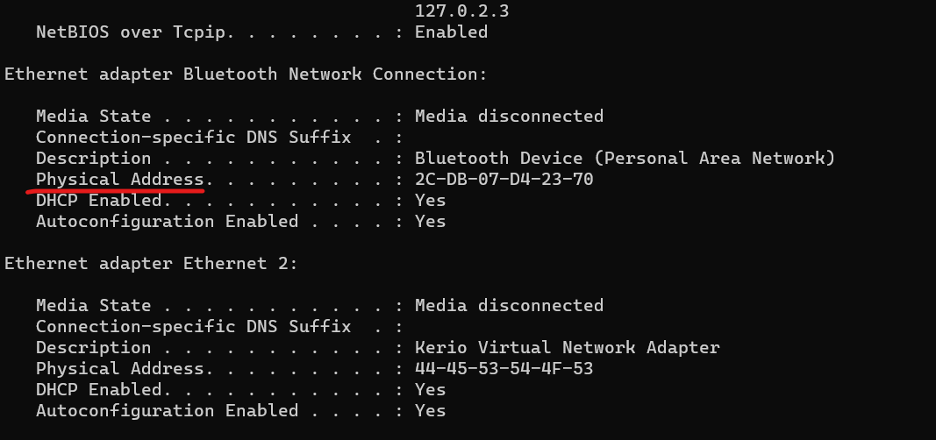
- Open the Command Prompt.
- Type the command `ipconfig /all` and press Enter.
- Look for the "Physical Address" under the network adapter you are using; this is your MAC address.
For Mac Computers
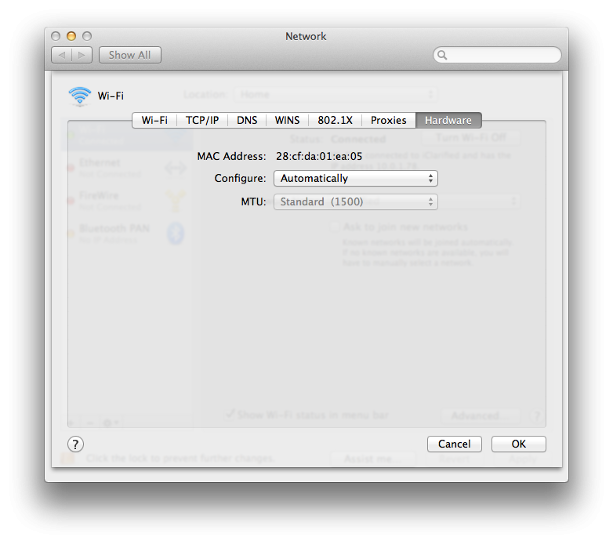
- Go to the Apple menu and select "System Preferences."

- Click on "Network."
- Select the active network connection on the left.
- Click on "Advanced."
- Go to the "Hardware" tab; the MAC address is the "Ethernet ID."
For Roku Players
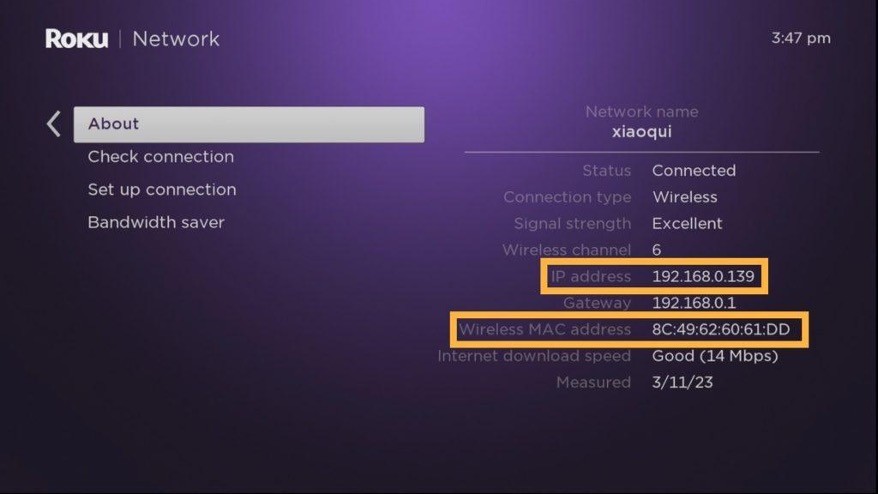
- From the Roku home screen, go to "Settings."
- Select "System" and then "About."
- The MAC address will be listed in front of "Wireless MAC Address" or "Wired MAC Address."
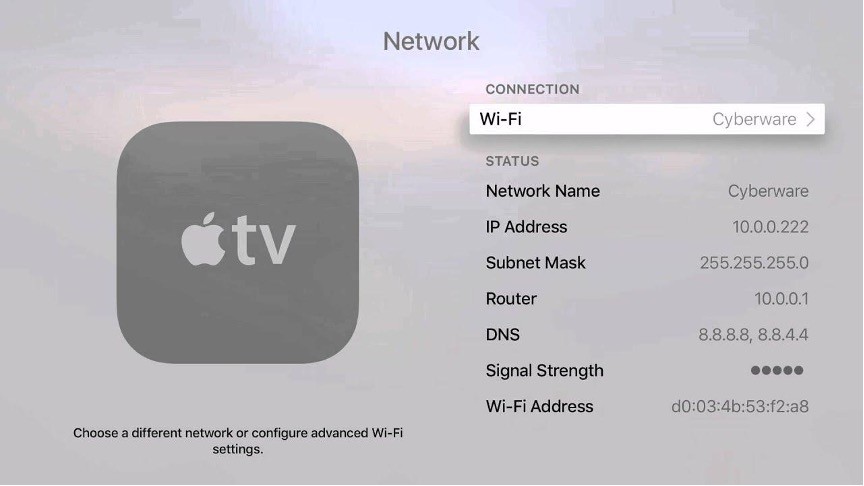
For Apple TVs
- Go to "Settings."
- Select "General" and then "About."
- The MAC address is listed as the "Wi-Fi Address."
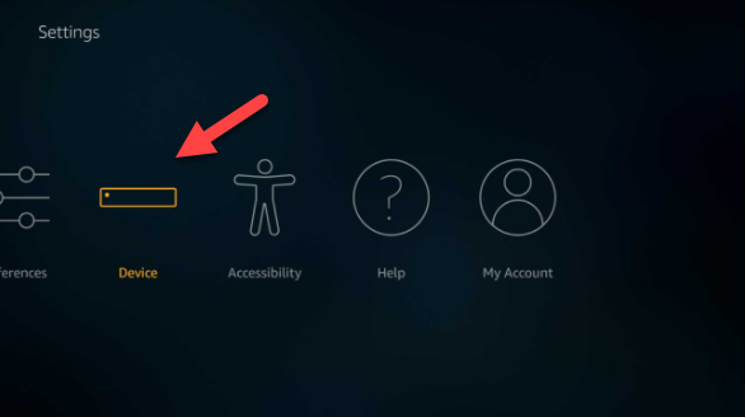
For Amazon Fire TV
- Navigate to "Settings."
- Select "Device" or "My Fire TV."
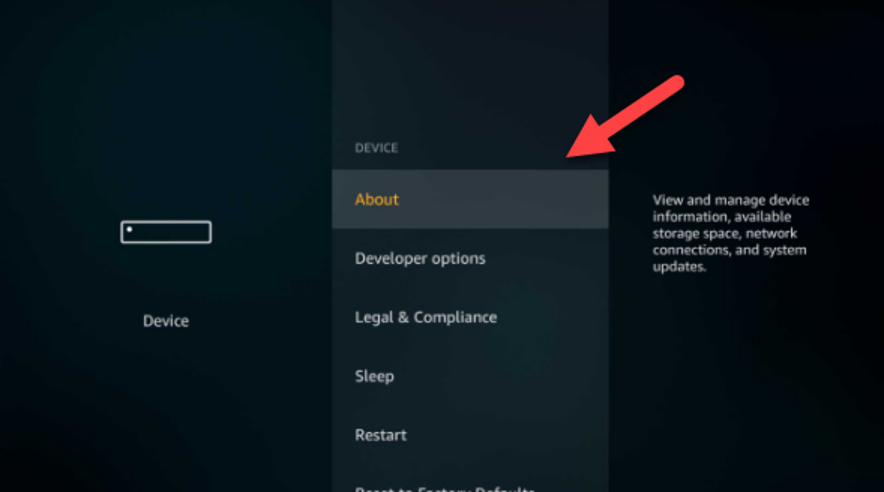
- Choose "About."
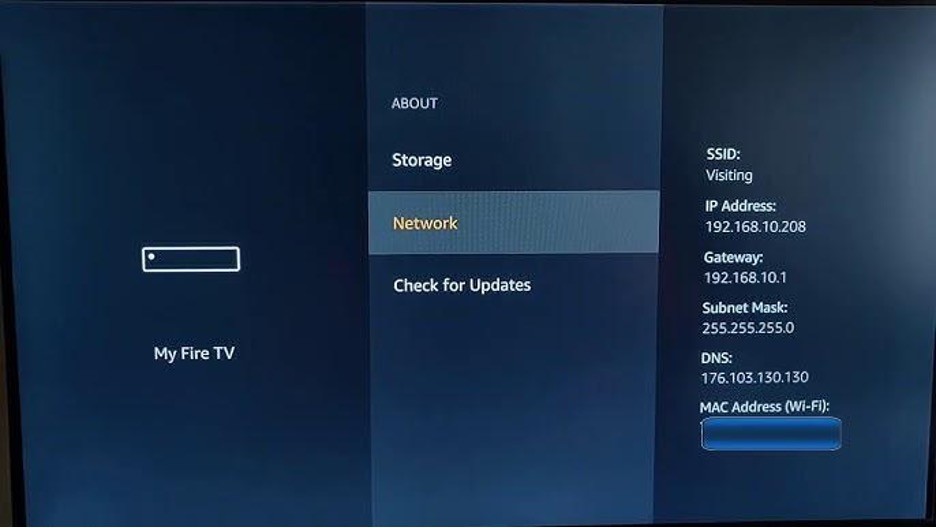
- The MAC address is listed under "MAC Address."
For Smart TVs
The procedure differs depending on the manufacturer and model. It is usually found in the network or settings menu. Specific instructions can be found in your TV's user manual or support documentation.
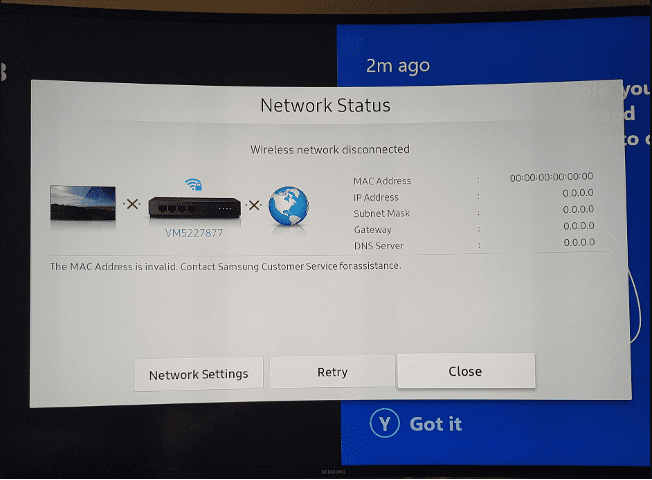
For Nintendo Switch
- From the home menu, go to "System Settings."
- Scroll down and select "Internet."
- The MAC address is listed under "System MAC Address."
For Playstation 3 (PS3)
- From the main menu, go to "Settings."
- Choose "System Settings" and then "System Information."
- The MAC address is listed as the "MAC Address (LAN Cable)."
.png)
For Playstation 4 (PS4)
- Navigate to "Settings."
-01.jpg)
- Go to "Network" and then " View Connection Status."
-02.jpg)
- The MAC address is listed as the "MAC Address (LAN Cable)."
-03.jpg)
For Playstation 5 (PS5)
- From the Home Screen, choose "Settings."
-01.jpg)
- Select "System" and then "Console Information."
-02.jpg)
- Now, you can see the MAC address.
-03.jpg)
For Xbox 360
- From the dashboard, go to "My Xbox."
- Select "System Settings."
- Choose "Network Settings" and then "Configure Network."
- Click the Additional Settings button.
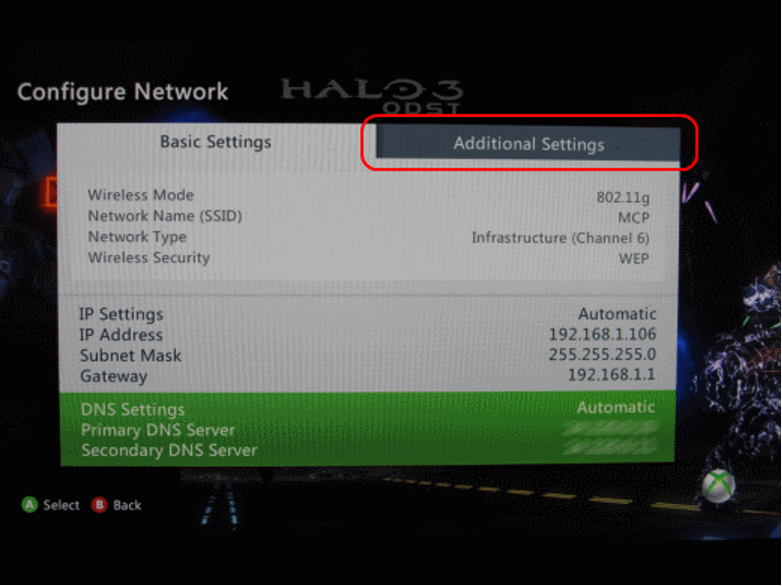
- Scroll down to Advanced Settings.
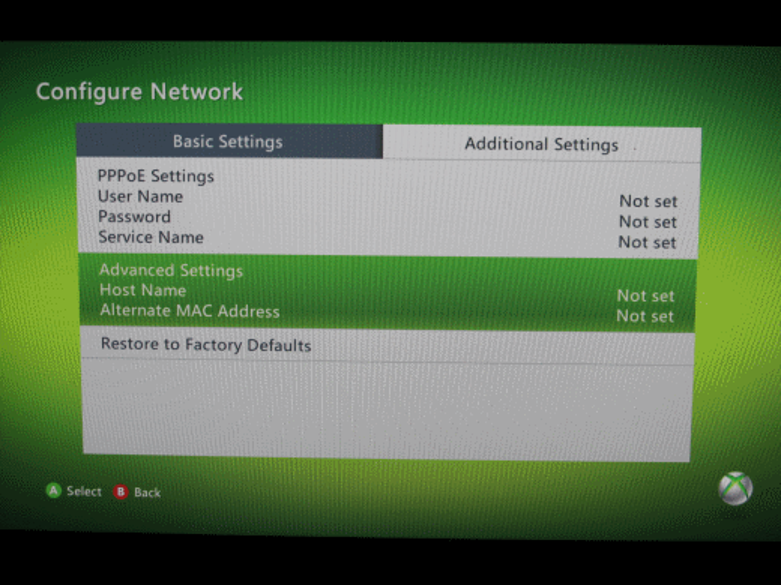
- The MAC address appears in the "Wireless MAC" section.
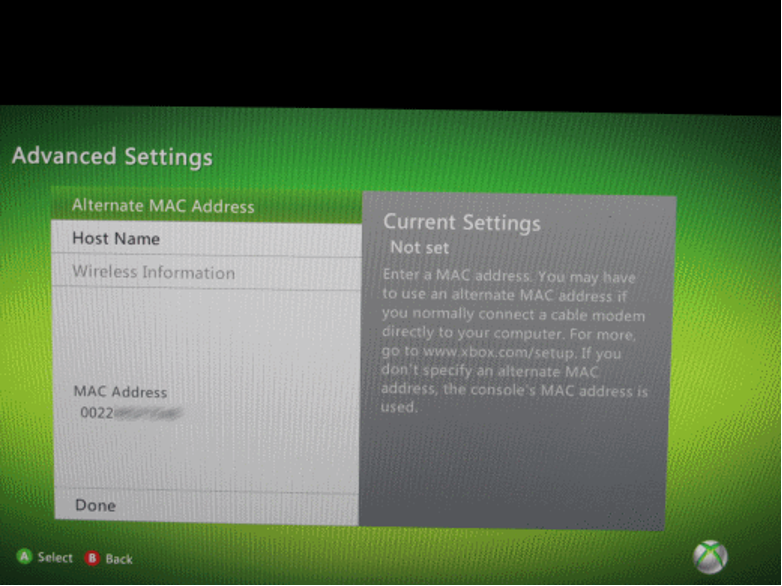
For Xbox One
- Go to "Settings."
- Select "Network."
- Choose "Advanced Settings."
- On the right side of the screen, the MAC address will be presented next to MAC.
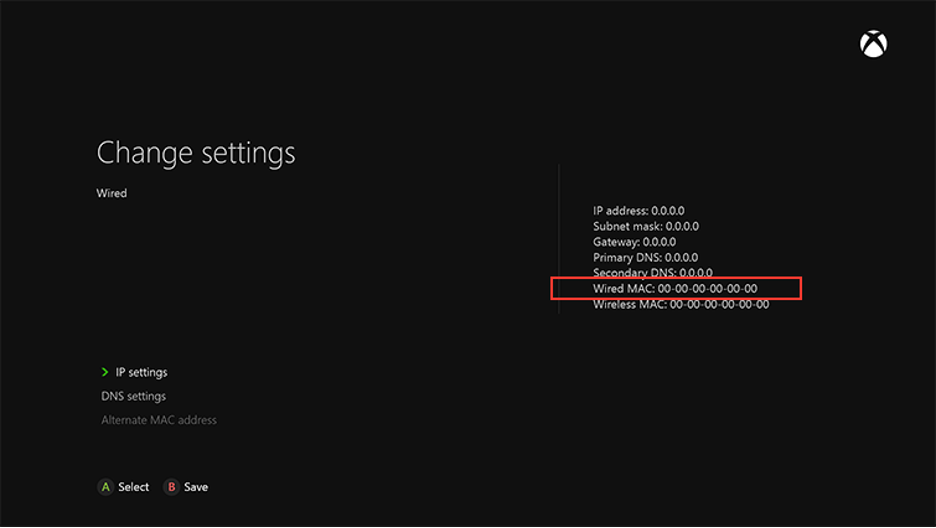
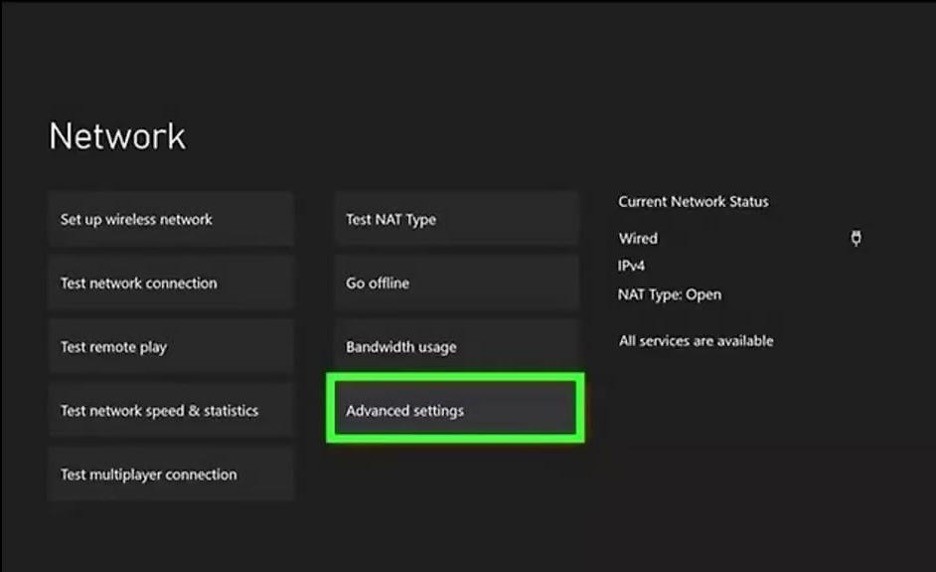
For Xbox Series X/S
- Press the “Xbox button” on the Xbox controller.
- Select “Settings” from the “Profile & System” menu.
- Select “Network Settings” from the “General” menu.
- Choose “Advanced Settings”.
- The wireless MAC address will be presented under “Wireless MAC” in the “IP Settings” menu.
Note: Remember that these are basic principles, and there may be minor differences depending on software upgrades or device models.
Ways to change MAC Addresses in Windows
Using Device Manager
One can use the device manager given in the Windows OS to track down the address and change it accordingly. After you open the device manager window, you should click right next to the arrow to view the list's content.
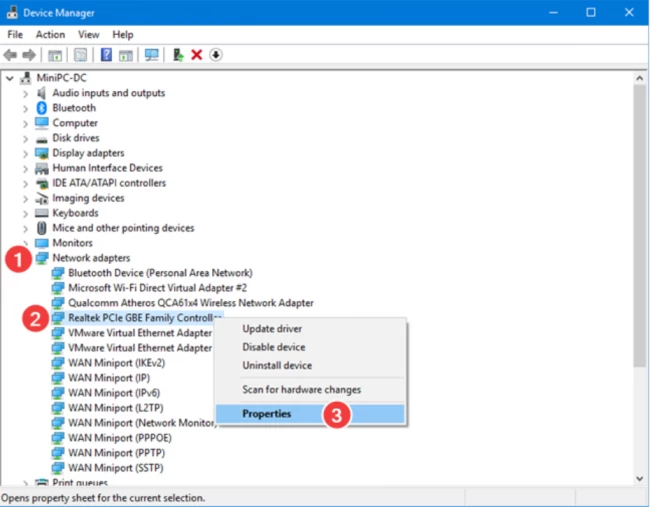
Once you find the Network Adapters option, you are supposed to long tap for the network card you are willing to chance. Now that you have the desired network card, give a right-click and select properties. In the properties window, select the advanced category and input the new address value.
Using Control Panel
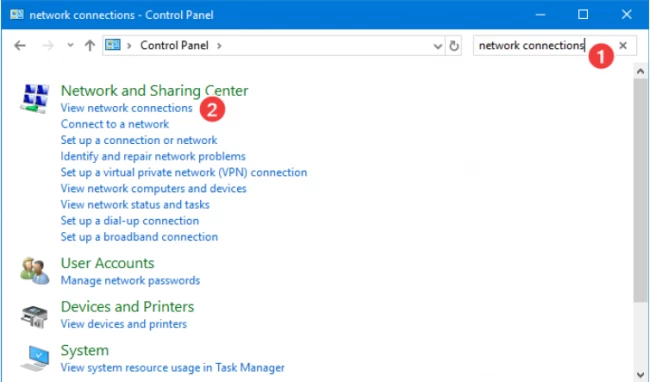
When we are using the control panel to change the MAC address, we must go to the “network connections” and click the first option available on the list.
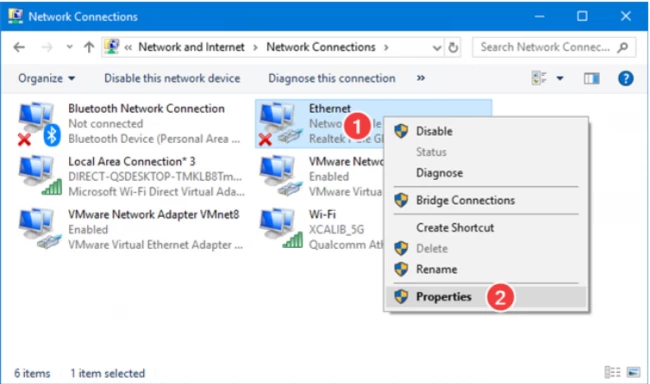
After clicking “view network connections”, you will see different Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Ethernet, and VMware network options. In those available connections, you are supposed to right-click on Ethernet and choose properties at the bottom.
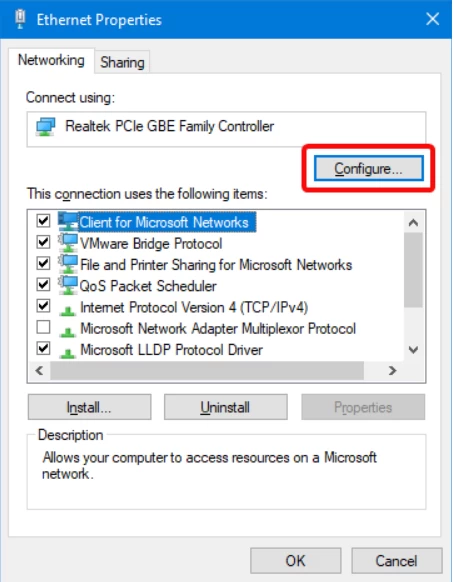
An Ethernet properties window will pop-up, and you need to select the configure button that is highlighted in the picture below:
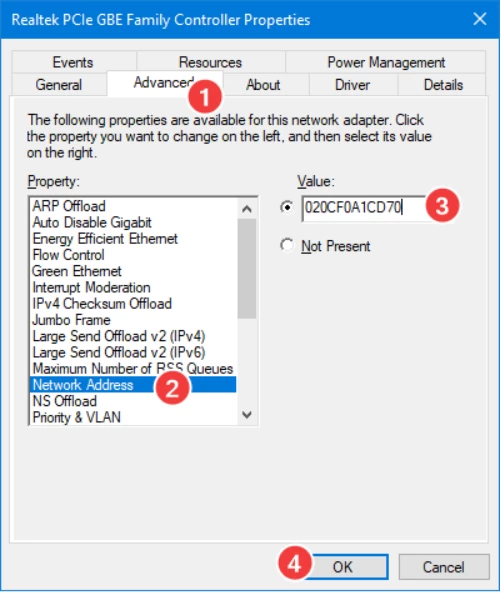
Go to the advanced tab and select New Network Address. In the value box, enter the new MAC address and press the OK button.
Using Command Prompt
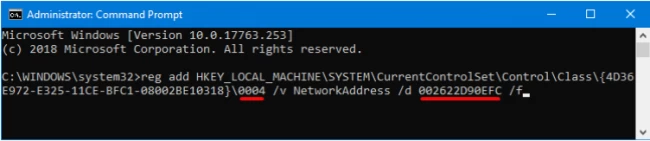
Command prompt or Powershell is one of the fastest ways to change MAC addresses. It is done by writing a few command lines and storing them in the form of a script. After you store it, you need to run the same procedure to change the addresses repeatedly. The first step in this method involves opening the command line programs as an administrator. It entirely depends on the type of app you prefer to deploy on your system.
Right before you proceed with the execution process, you need to change two main things associated with your network card and the new MAC address. You can use the Registry editor to find out the information on the first string, and you can change the values of the second string.
Can a device have more than one mac address?
Yes, a device can have many MAC addresses, but each one is usually associated with a single network interface. Devices with numerous network interfaces, such as a computer that supports both cable Ethernet and wireless Wi-Fi, will have a separate MAC address for each interface. Here are some examples of common instances in which a device may have several MAC addresses:
- Multiple Network Interfaces: A computer with both wired and wireless network adapters will have a unique MAC address for each adapter.
- Virtualization: In virtualized environments, virtual machines (VMs) running on a single physical device may each have their own virtual network interface card (vNIC) with a unique MAC address.
- Network Adapters: Some devices may have additional network adapters or interfaces, each with its own MAC address. This can include USB Ethernet adapters, Bluetooth interfaces, etc.
- Network Interface Cards (NIC) Replacement: If a network interface card is replaced or upgraded, the new card will have its own MAC address.
MAC VS IP Addresses
Here we explore some major differences between MAC and IP address :
|
MAC Address |
IP Address |
|
The MAC address is assigned to the Network Interface controller to take care of data transmission via Ethernet or Wi-Fi portals. |
Network routers are assigned to a unique IP address to increase anonymity. If it is in a private network, then it is not possible to display it on the system’s screen. |
|
These addresses are in the color or shape form present as a mailbox in our home. |
In the case of an IP address, it is the postal address assigned to our house. |
|
To help acquire MAC addresses, we use a protocol called Address Resolution. |
Here, it is called Reverse Address Resolution. |
|
Manufacturers are responsible for assigning unique identifiers called MAC addresses. |
For IP addresses, the local networks help in finding out the location of the device. |
|
As it is a second layer in the OSI module, it is assigned a lower level in any model of networking. |
IP addresses are given a higher level in the OSI networking model. |
|
MAC addresses handling data recovery and filtering to avoid cyber attackers. |
IP addresses cannot handle any filtering tasks, and the system relies only on MAC addresses. |
|
There is no possibility of hiding a MAC address. |
One can easily find ways to hide their IP addresses. |
|
MAC addresses are related to only interface layers and have no interconnected layers present. |
The IP address is software-oriented, so it appears in an Open Systems Interconnections model. |
Reason to Have Both IP and MAC Addresses
There are some reasons why both IP and MAC addresses are used:
MAC addresses for local network communication
MAC addresses, situated at the data link layer of the network stack, are assigned to network interface cards (NICs) to uniquely identify each NIC within a local network. Primarily utilized for local network communication, especially in LANs, MAC addresses play a key role in directing packets at the data link layer when devices within the same network need to communicate.
IP addresses for network routing
IP addresses function at the network layer of the network stack, providing unique identification for devices on a network. They facilitate communication between devices across diverse networks, allowing routing of packets over the internet or wide area networks (WANs). IP addresses establish a logical addressing framework, enabling devices to be identified and communicated on a broader scale.
Address resolution
In the address resolution process, IP and MAC addresses collaborate, facilitated by the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). ARP resolves an IP address to its corresponding MAC address within a local network. When a device intends to send a packet locally, it consults its ARP cache or broadcasts an ARP request to identify the MAC address associated with the destination device's IP address. This mapping ensures accurate packet delivery within the local network.
Flexibility and scalability
IP addresses offer abstraction and flexibility, enabling hierarchical organization and global scalability of networks. Unlike MAC addresses, which are linked to specific network interfaces, IP addresses can be assigned to devices irrespective of their physical location or interface. This flexibility permits devices to seamlessly connect to diverse networks and migrate between them without requiring changes to their IP addresses.
What is MAC Cloning?
MAC cloning, also known as MAC address cloning, is a technique in which a device clones another network-enabled device's Media Access Control (MAC) address. In instances where Internet Service Providers (ISPs) authenticate devices based on their MAC addresses, MAC cloning is routinely utilized. When replacing routers or modems, users can use MAC cloning to keep a recognized identity with the ISP without reconfiguring.
Advantages of MAC Address
In computer networks, MAC (Media Access Control) addresses have various advantages:
- Uniqueness: This uniqueness ensures that no two network devices on the same network have the same MAC address. It allows for accurate identification and addressing of individual devices on a network.
- Data Link Layer Addressing: This addressing scheme is essential for local network communication, as it allows devices to send and receive data within a LAN (Local Area Network) without needing to go through routing processes.
- Hardware-Based Identification: They are typically hardcoded into the hardware of the NIC and cannot be easily changed. This aspect provides a reliable and persistent identifier for a network device.
- Address Resolution: ARP resolves IP addresses to their corresponding MAC addresses on a local network. This process is crucial for devices to communicate with each other within the same network segment.
- Layer 2 Security: For example, some network switches support MAC address filtering, which allows administrators to define a list of allowed MAC addresses that can access the network. This feature can help prevent unauthorized devices from connecting to the network.
- Device Tracking: Network administrators can monitor and track devices on a network based on their MAC addresses. This information can be useful for inventory management, troubleshooting, and security purposes.
Disadvantages of MAC Address
While MAC (Media Access Control) addresses have their advantages, they also come with some limitations and disadvantages:
- Limited to Local Networks: They are not designed for global addressing or routing, which means they cannot be used for communication between devices on different networks or over the internet.
- Lack of Flexibility: This lack of flexibility can be a challenge in certain scenarios, such as when a device needs to change its network interface or move to a different network.
- Inefficiency in Scaling: With the growth of networks and the proliferation of devices, managing and maintaining unique MAC addresses for every device becomes increasingly complex and challenging.
- Limited Security Features: MAC addresses can be spoofed or cloned, allowing unauthorized devices to masquerade as legitimate ones.
- Incompatibility between Different Network Technologies: Different network technologies may have different addressing schemes, making it difficult to directly communicate between devices with different types of MAC addresses.
- Lack of Hierarchical Structure: This absence makes it challenging to efficiently route and manage network traffic based on MAC addresses alone.
Why Should the MAC Address Be Unique in the LAN Network?
In a LAN network, the uniqueness of MAC addresses is critical to ensuring proper and efficient communication. Because MAC addresses function as data link layer hardware identifiers, each device on the local network must have a unique MAC address. This uniqueness minimizes network conflicts and misunderstanding, allowing devices to be precisely identified and improving data frame routing. It ensures that when devices communicate within the same network, data is sent only to the intended receiver, avoiding any ambiguity or interference that could occur if many devices shared the same MAC address.
Conclusion
That brings us to the end of the article, and we hope you grasped all the information related to MAC addresses. Some of the key pointers to remember are MAC address identification, real-life use cases, and ways to change MAC addresses on different platforms. Cloning of MAC addresses and using cable modems are some other important aspects of computer networking. These values associated with MAC addresses serve as a key function to many network protocols, and each type of address supports different broadband viewing instances and applications.

I'm fascinated by the IT world and how the 1's and 0's work. While I venture into the world of Technology, I try to share what I know in the simplest way with you. Not a fan of coffee, a travel addict, and a self-accredited 'master chef'.