List of content you will read in this article:
If you're a Linux user, especially one who prefers Ubuntu Linux , you may have encountered the frustrating "Unable to Locate Package" error at some point during software installation. This cryptic error message can leave you scratching your head and wondering how to resolve it. Fear not, as in this guide, we'll walk you through the steps to troubleshoot and fix this common issue. The "Unable to Locate Package" error typically occurs when the system cannot find the software package you're trying to install. In this article, we'll demystify this error and provide you with a comprehensive set of solutions to resolve it.
👉 Want to dive deeper into Ubuntu and understand its key features, advantages, and disadvantages? Explore our comprehensive guide on "What is Ubuntu" to gain a better insight! 🚀
Why the "Unable to Locate Package" Error Strikes?
Before we delve into the solutions for fixing the "Unable to Locate Package" error, it's crucial to understand why this error might rear its head in the first place. Several common reasons can lead to this issue, and identifying the underlying cause is the first step toward resolving it.
Outdated Package Lists
One of the most common causes of this error is outdated package lists. Ubuntu relies on repositories to fetch and install software packages. If your local package lists are not up to date, Ubuntu won't be able to locate the packages you're trying to install.
Typo in Package Name
A simple typo or incorrect package name provided in the terminal can lead to an error. Ubuntu is case-sensitive, so ensure that you've entered the package name correctly.
Missing Repository
If the software you're trying to install is not available in the repositories enabled on your system, you'll encounter this error. Sometimes, you may need to add additional repositories to access certain packages.
Internet Connection Issues:
A stable internet connection is essential for Ubuntu to fetch packages from repositories. If your connection is slow or intermittent, it may cause this error.
Repository Key Issues
Ubuntu uses GPG keys to verify the authenticity of packages from repositories. If there's an issue with the key or it's missing, you may face this error.
Repository Maintenance
Occasionally, repositories undergo maintenance, making packages temporarily unavailable. This can lead to errors as well.
Understanding the root cause of the "Unable to Locate Package" error is vital, as it will help you choose the appropriate solution.
Fixing Ubuntu's "Unable to Locate Package" Error
Now that we've explored the reasons behind the "Unable to Locate Package" error in Ubuntu, let's dive into the step-by-step methods to resolve this frustrating issue. Depending on the root cause of the error, you may need to follow one or more of these solutions.
Update Package Lists
- Open the Terminal: Launch the Terminal application on your Ubuntu system. You can do this by searching for "Terminal" in the Applications menu.
- Update Package Lists: Run the following command to update your local package lists:
sudo apt update
This command will refresh the list of available packages, ensuring that Ubuntu can locate the package you want to install.
- Retry Installation: After the update is complete, try installing the package again using the `sudo apt install` command. If the outdated package list was the culprit, this should resolve the error.
👉 "Ready to explore more Ubuntu updates? Check out our comprehensive guide on 'How to Update Ubuntu' for step-by-step instructions and expert tips! 🚀"
Check Package Name
- Double-Check Spelling: Ensure that you've correctly spelled the package name in the terminal. Remember that Ubuntu is case-sensitive, so even a minor typo can trigger the error.
- Use Autocompletion: To avoid typing errors, you can use the Tab key for auto-completion. Simply start typing the package name, press Tab, and Ubuntu will complete it for you.
- Search for the Package: If you're unsure about the package name, you can search for it using the `apt search` command:
apt search package_name
Replace `package_name` with the name of the package you're looking for. This will list available packages matching your search criteria.
Add Missing Repositories
- Identify the Repository: Determine which repository contains the package you need. You can often find this information on the official website of the software or in the documentation.
- Add the Repository: Use the `add-apt-repository` command to add the missing repository. Replace `repository_url` with the actual URL of the repository:
sudo add-apt-repository repository_url
- Update and Install: After adding the repository, update your package lists again with `sudo apt update` and then try installing the package as usual.
Check Internet Connection
- Verify Connection: Ensure that your internet connection is stable. You can do this by opening a web browser and visiting a website.
- Check Proxy Settings: If you're behind a proxy, make sure your proxy settings are configured correctly in Ubuntu. Incorrect proxy settings can hinder package retrieval.
Address Repository Key Issues
- Retrieve Missing Keys: If you suspect a missing or outdated GPG key is causing the error, you can attempt to retrieve it. First, identify the missing key using the error message, and then run the following command to fetch it:
sudo apt-key adv --recv-keys --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com key_id
Replace `key_id` with the actual key ID mentioned in the error message.
- Update and Install: After fetching the missing key, update your package lists with `sudo apt update` and then proceed to install the package.
Wait for Repository Maintenance
If you've ruled out all other possibilities and suspect that repository maintenance might be causing the issue, the best course of action is to wait. Repository maintenance is typically temporary, and the packages should become available again once it's completed.
Update packages and repository cache
Keeping your Ubuntu system's package lists and cache up-to-date is crucial to avoid the "E: Unable to Locate Package" error. Outdated information can lead to confusion when searching for software. But why do updates matter: Imagine a library with a constantly changing catalog. An outdated catalog wouldn't reflect new books or changes in location. Similarly, outdated package lists wouldn't show newly added software or updates for existing ones.
To ensure your system has the latest information, run the following commands in your terminal:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
Use code with caution.
- sudo apt update: This refreshes the list of available packages from the configured repositories.
- sudo apt upgrade -y: This upgrades all currently installed packages to their latest versions (the -y flag assumes "yes" to prompts).
Benefits of Updated Packages:
- Access to New Software: Updated package lists allow you to discover and install newly released software in Ubuntu.
- Improved Functionality: Updates often include bug fixes and security patches, ensuring smoother and safer operation of your system.
What if the Error Persists?
If the error persists after updating, explore other solutions covered in this guide or search online resources for further troubleshooting specific to the package you're trying to install.
Check the availability of the package for the Ubuntu version
If the previous solutions haven't solved the "E: Unable to Locate Package Ubuntu" error, it's possible the package isn't compatible with your specific Ubuntu server version.
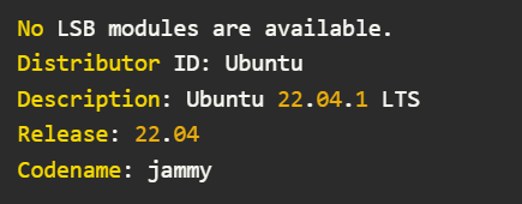
The first step is to determine your Ubuntu version. Open a terminal and run:
lsb_release -a
This will display details like:
Searching for the Package
- Visit the official Ubuntu Packages Search
- Scroll down to the search section.
- Enter the package name in the "Keyword" field.
- Select your Ubuntu version's codename from the "Distribution" menu. Leave "Section" set to "any".
- Click "Search".

The results will show if the package exists for your Ubuntu version. If it does, note the repository it belongs to (e.g., "main", "universe", "multiverse").
Troubleshooting Missing Repositories
If the package resides in "universe" or "multiverse" but you encounter the error again, these repositories might not be enabled on your system.
To enable them, run:
sudo add-apt-repository universe multiverse
Update the package cache:
sudo apt update
Outdated Software and Alternative Methods
In some cases, software might not be actively maintained for newer Ubuntu versions. Here are alternative ways:
- Third-Party repositories (PPAs): If the software has an official PPA (Personal Package Archive), you can add it to your system to install the package. However, use PPAs with caution, as they come from external sources.
- DEB files and snap packages: The Ubuntu Packages search may also suggest DEB files or Snap packages as alternatives. While these methods can work, they require additional steps and might not be as secure or well-maintained as official repositories.
This comprehensive approach should help you determine package availability and explore alternative installation methods if needed. Remember to prioritize official repositories whenever possible for a secure and streamlined experience.
Check the activation of the Ubuntu version
The "E: Unable to Locate Package Ubuntu" error can sometimes arise due to an unsupported Ubuntu version. Here's how to check your version's support status:
Regular vs. Long-Term Support (LTS)
There are two main Ubuntu release types:
- Regular Releases: Receive updates for nine months.
- Long-Term Support (LTS) Releases: Receive updates for five years.
Checking Support Status
It's crucial to ensure your Ubuntu version is still within its active support period. Open a terminal and run:
hwe-support-status --verbose
The output will show one of two messages:
“Your system is supported until [date].": This indicates your version is currently supported and receiving updates.
"Your system has reached end-of-life.": This means your version is no longer supported, and installing new packages might lead to errors.
Note 1: If your version has reached its end-of-life, it's highly recommended to upgrade to a supported version. Upgrading ensures access to security patches, bug fixes, and the latest software.
Note 2: The `hwe-support-status` command might not be available on all Ubuntu versions. You can find alternative methods to check support status online.
Note 3: Upgrading to a newer version is generally recommended, even if your current version is still in support. This ensures you benefit from the latest features and security improvements.
Fix the repository
The "E: Unable to Locate Package" error can sometimes be caused by issues with your system's source list configuration. Let's see how this works:
Imagine a library with a catalog listing the available books and their locations. Similarly, Ubuntu's `/etc/apt/sources.list` file acts as a source list, directing your system to online repositories where software packages reside.
Verifying Source Repositories:
- Open a terminal and run `sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list` (replace `nano` with your preferred text editor if needed).
- Look for lines starting with `deb` or `deb-src`. These represent repositories containing software packages.
- Crucially, if these lines are commented out with a `#` symbol, your system won't be able to locate packages.
Uncommenting Repositories (if necessary):
- If the repository lines are commented out, remove the `#` symbol to activate them.
- Save the changes and exit the text editor.
- Run `sudo apt update` to refresh the package list based on the enabled repositories.
The example might look like this:

After uncommenting, it would look like this (with active repositories):
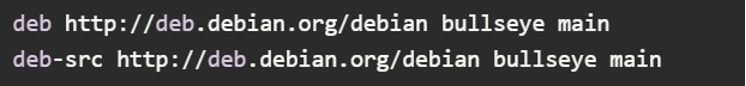
Note: Remember, commenting out unnecessary repositories is fine, but ensuring at least one active repository is crucial for successful package installation.
By understanding the source list and verifying its configuration, you can effectively troubleshoot the "E: Unable to Locate Package Ubuntu" error and access the software you need.
How to fix unable to locate package git?
This guide addresses the common "E: Unable to Locate Package" error you might encounter on Ubuntu, Debian, and Kali Linux. The solutions provided here can help you resolve issues related to specific packages like `sudo`, `git`, `net-tools`, `yum`, and `wget`.
Why these errors occur?
Several factors can lead to this error message:
- Typos: Double-check the package name for any spelling mistakes. Linux is case-sensitive, so "Git" is different from "git".
- Outdated package lists: Outdated information about available packages can cause confusion.
- Missing repositories: The package you seek might not be present in the repositories configured on your system.
- Unsupported package: In rare cases, the package might not be compatible with your specific Linux version.
What are the solutions?
- Ensure you've typed the package name correctly, including proper capitalization.
- Run the following command in your terminal to update the list of available packages:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
Note: This command is specific to Ubuntu and Debian. Use `sudo dnf upgrade` for Kali.
- If the package belongs to a non-default repository (e.g., universe or multiverse in Ubuntu/Debian), you might need to enable it. Consult your distribution's documentation for specific instructions.
- In rare cases, the package might not be in the official repositories for your version. Consider these options:
Third-Party Repositories (PPAs): Use PPAs with caution as they come from external sources.
DEB or Snap Packages: The official Ubuntu packages search might suggest alternative installation methods.
Examples:
- Unable to locate package sudo: This usually indicates a typo. The correct package name is `sudo`.
- Unable to locate package git: Ensure your repositories are up-to-date and `git` is available in the default repositories for your Linux distribution.
- Unable to locate package net-tools: `net-tools` might be replaced with a different package name in newer versions. You can search for alternatives that provide similar functionality.
- Unable to locate package yum: `yum` is the package manager for Red Hat-based distributions (e.g., CentOS, Fedora). Ubuntu/Debian use `apt`.
- Unable to locate package wget: Update your package lists and ensure `wget` is included in the default repositories.
How do I find the location of a package in Linux?
While installed software can sometimes reside in various locations, here's how to effectively track them down on Linux systems:
System-wide binaries: These are typically found in directories like:
/usr/bin
/sbin (for system administration tools)
User-specific binaries: These might be located in:
/home/<username>/bin (replace <username> with your actual username)
Finding Specific Packages
Several methods can help you pinpoint the exact location of an installed package. These methods include:
Method 1.`which` command: This command displays the full path to the first executable file found in your system's search path that matches the specified filename.
which <package_name>
(Replace `<package_name>` with the actual package name)
Example:
which firefox
This might return something like:
/usr/bin/firefox
Method 2. `whereis` command: This command provides more comprehensive information about an installed package, including the location of its binary, source code (if available), and manual page (if applicable).
whereis <package_name>
Example:
whereis git
This might return something like:
git: /usr/bin/git /usr/share/man/man1/git.1.gz
Method 3. `dpkg` command (Debian/Ubuntu): For Debian-based systems like Ubuntu, you can use `dpkg` to list the files installed by a specific package.
dpkg -L <package_name>
Example:
dpkg -L net-tools
This will display a detailed list of all files installed by the `net-tools` package.
Note: Remember that these are just some of the common methods. The specific approach might vary depending on your Linux distribution and package manager.
Final Words
In this comprehensive guide, we've explored the various reasons behind this error, ranging from outdated package lists to missing repositories and internet connection issues. We've provided you with a range of effective methods to address each of these issues, ensuring that you have a solution at your fingertips, regardless of the underlying cause.
By keeping your package lists up to date, double-checking package names, adding missing repositories, verifying your internet connection, addressing repository key issues, and being patient during repository maintenance, you can navigate the world of Ubuntu software installation with confidence.

Hello, everyone, my name is Lisa. I'm a passionate electrical engineering student with a keen interest in technology. I'm fascinated by the intersection of engineering principles and technological advancements, and I'm eager to contribute to the field by applying my knowledge and skills to solve real-world problems.