List of content you will read in this article:
There are many different database services out there and MySQL is one of the more popular ones. It is a part of some of the most used stacks out there such as LAMP (i.e. Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP), WAMP (i.e. Windows, Apache, mysql, PHP), and MAMP (i.e. macOS, Apache, MySQL, PHP). By definition, it is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) with a client-server model. Here, We will go through MySQL reset root password.
🔐 "Ready to fortify your online security? Learn more about the importance of password strength in our comprehensive guide: 'How to Choose a Strong Password'." 🔐
How to Change MySQL User Root Password in Linux
Step 1: Log in as MySQL User
The journey to fortifying your MySQL database begins with logging in as the MySQL user. This step ensures that you have the necessary permissions to execute the forthcoming operations seamlessly. Open your terminal and enter the following command:
mysql -u root -p
You'll be prompted to enter the current password for the root user.
Step 2: Stop the MySQL Server
Before making any changes to the MySQL User Root Password, it's essential to halt the MySQL server. This ensures that no ongoing processes interfere with the modification. Execute the following command to stop the server:
sudo service mysql stop
Step 3: Create a Password File
Now, it's time to create a password file that will store the new MySQL User Root Password securely. Choose a location for the file and create it using a text editor like nano or vim. For instance:
sudo nano /var/mysql-password
Enter the new password in the file, save, and exit.
👉 Ready to become a Nano Text Editor pro? Dive deeper into advanced Nano commands and techniques by exploring our comprehensive guide on "How to Use Nano Text Editor"! 🚀
📥 Download our comprehensive "VIM Cheat Sheet PDF" for lightning-fast coding! 🚀
Step 4: Apply the Changes
Apply the changes to update the MySQL User Root Password. Use the following command, replacing 'path/to/password/file' with the actual path to your password file:
sudo mysqld_safe --init-file=path/to/password/file
Step 5: Restart the Server
With the password updated, it's time to restart the MySQL server. Ensure a smooth restart by executing the following command:
sudo service mysql start
Step 6: Log in and Clean Up
Now that the MySQL server is up and running with the new password, log in to confirm the changes:
mysql -u root -p
Enter the updated password when prompted. Once logged in, it's good practice to clean up the password file to maintain security:
sudo rm /var/mysql-password
How to Reset MySQL Root Password in Windows
Resetting the MySQL root password in Windows is a straightforward process. This tutorial outlines the steps using Windows 11, applicable also for Windows 10.
Step 1: Log in as Administrator
Access the Windows machine as an administrator for the necessary system-level modification rights.
Step 2: Stop MySQL server
- Press Win+R, type services.msc, and press Enter.
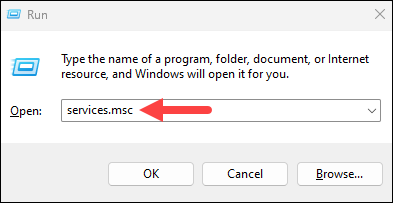
- Locate MySQL service, right-click, and select Stop.
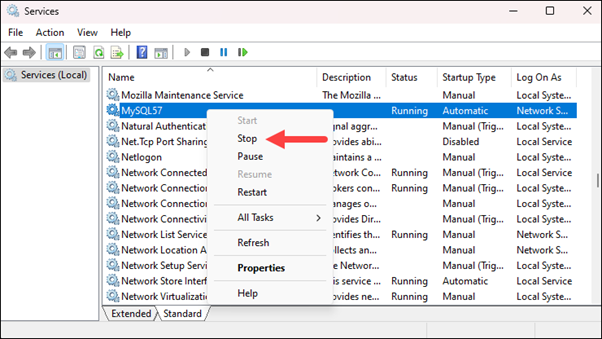
Step 3: Create Password File
Create a password file (mysql-init.txt) with the new password using Notepad:
- Press the Windows key, search for Notepad, and press Enter.
- Add the line:
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'NewPassword'; (Replace 'NewPassword' with your chosen password).
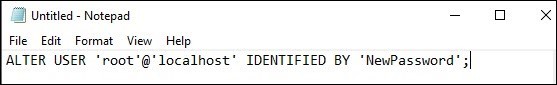
- Save the file to the root of your hard drive (C:).
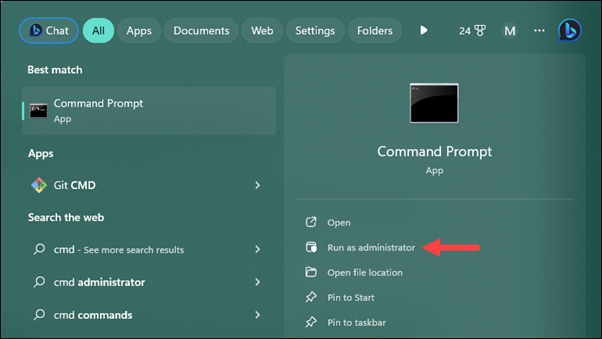
Step 4: Open Command Prompt
Press the Windows key, type cmd, and select Run as administrator.
Step 5: Add New Parameters and Restart Server
- Navigate to MySQL directory in Command Prompt using:
cd "C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.7\bin"
- Adjust version as needed.
- Depending on installation method:
- For ZIP archive installation, run:
mysqld --init-file=C:\\mysql-init.txt
In the command, you need to include the --defaults-file option, followed by the path to the configuration file. To obtain the file path, right-click the MySQL service in the services list and choose Properties.
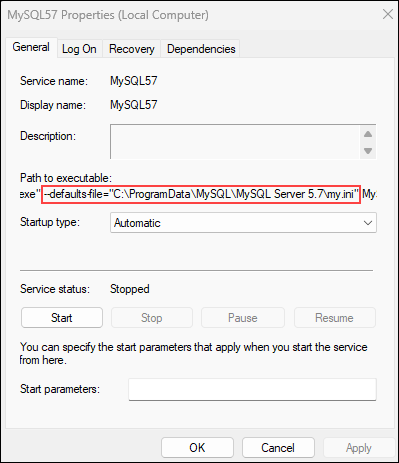
- For MySQL Installation Wizard, use:
mysqld --defaults-file="C:\\ProgramData\\MySQL\\MySQL Server 5.7\\my.ini" --init-file=C:\\mysql-init.txt
- Restart MySQL service from Services list by right-clicking and selecting Start.
🔗 "Looking for more MySQL tips and tricks? Check out our comprehensive MySQL Cheat Sheet for a quick reference to all your database needs! 📊📚"
Step 6: Clean up
Log into MySQL with the new password. After confirming the change, delete the C:\mysql-init.txt file.
Conclusion
Successfully resetting the MySQL root password is a vital skill for database administrators and anyone managing a MySQL server. This guide aimed to provide clear, step-by-step instructions on how to reset the MySQL root password, a task that is essential for maintaining the security and integrity of your database. Remember, regularly updating your MySQL root password and following best security practices can help protect your database from unauthorized access. By following the procedures outlined, you can ensure that your MySQL database remains secure, and you retain full control over its access.
