List of content you will read in this article:
While there are plenty of DNS servers, both free and paid, available for anyone to use, in certain situations it is better to have your own. Its installation, however, can be more complex than you may think. In this tutorial, we are going to discuss the installation of DNS servers in Windows Server 2012, 2016, and 2019.
What is DNS?
In simple terms, DNS or Domain Name Server is like an internet address book. While you browse information on the web, you type different domain names, such as abc.com or xyz.com. Right? Furthermore, the web browser interacts with the help of IP (Internet Protocol) addresses.
The DNS translates the domain names to the IP addresses so that the web browsers can access the internet resources. Every device connected with the internet has a unique IP address. The devices use these IP addresses of other devices to exchange information. The DNS servers discard the requirement of remembering such complicated numbers, such as 192.168.1.1. Or there are even more complex addresses like 2111.bc00.2789.1::c567:s9a2.
Moving on, here are some insights about the features of the Window Servers!
Windows Server 2019 is power-packed with several features, standing first in the lane of other windows servers, namely, windows server 2012 and 2016!
Features of Windows Server 2019:
- Windows Admin center
- Storage Migration Services
- HCI and WSSD
- System Insights
In the same way earlier, as compared to Windows server 2012, Windows Server 2016, was clearly a more updated and powerful addition.
Here are some of the features:
- Addition of more DNS policies
- Improvised support of Windows Powershell
- Root hints IPv6
- Support for unknown record
- Addition of RRP
How to Install a DNS Server on Windows?
Let us begin our core topic to understand the process of installing a DNS server. Before that, here are some prerequisites.
Prerequisites
- Server with Windows Server 2012,2016,2019 (as per your requirements)
- Pre-installed DNS server role
If you do not have a pre-installed DNS server role, follow these steps!
Installing DNS server role
Now, let us start the process of installation:
- Click on the Server Manager and move on to Local server.
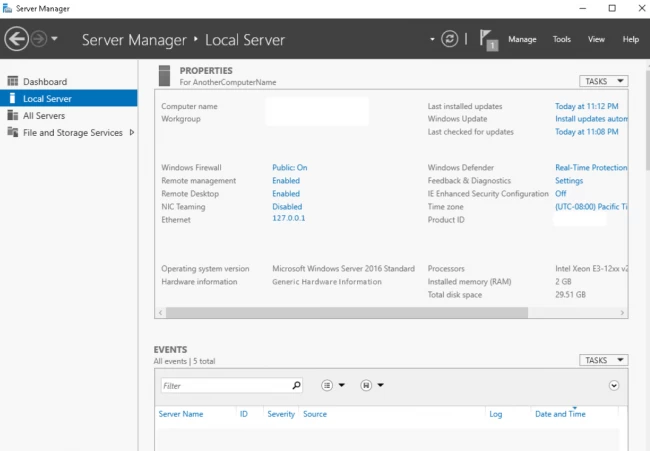
- Tap on Manage, as you can see the very first option that says, Add roles and features, click on it.
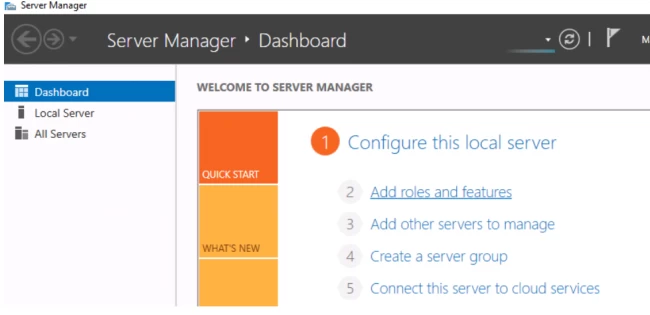
- Read the information and the data in front of you for a better understanding and then click on next.
- Click on the first option, Role-based or feature-based installation, and move on to the next page.

- Next up, from the server pool, you have to choose your desired server for the DNS server role.
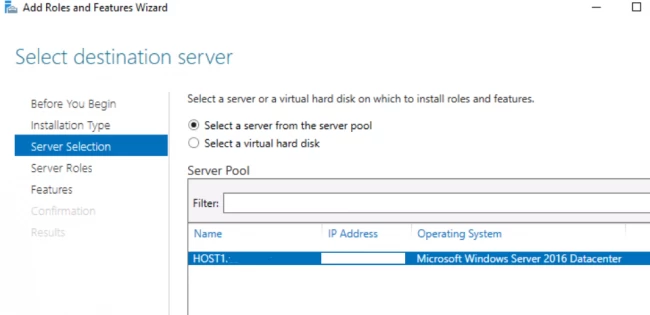
- Then select the DNS server role. You will encounter a pop-up window asking you to install some additional tools for the DNS server. If you wish to install the tools, check your requirements and accordingly take the step.
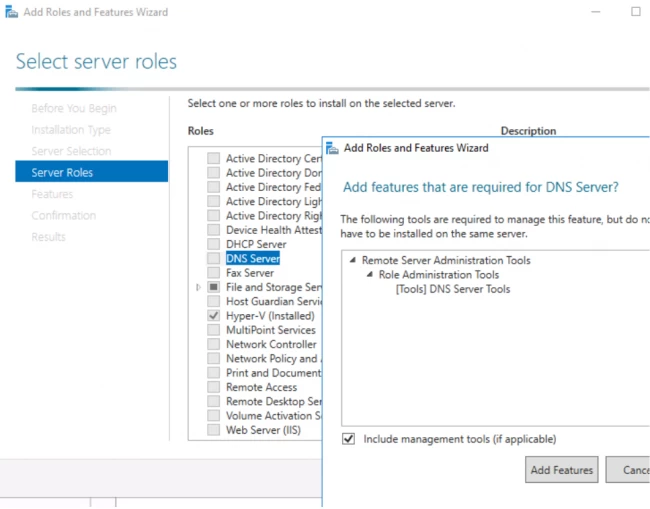
- Now, you will see a checklist. Tick off the option DNS server. By default, the option of file and storage services is checked. Tap on next.
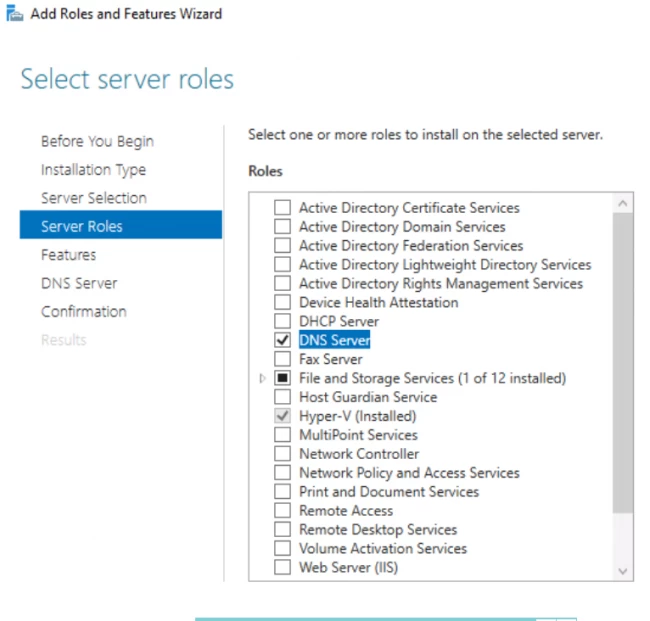
- The next window shows you some additional features for your DNS server. Read them carefully, add them if required.
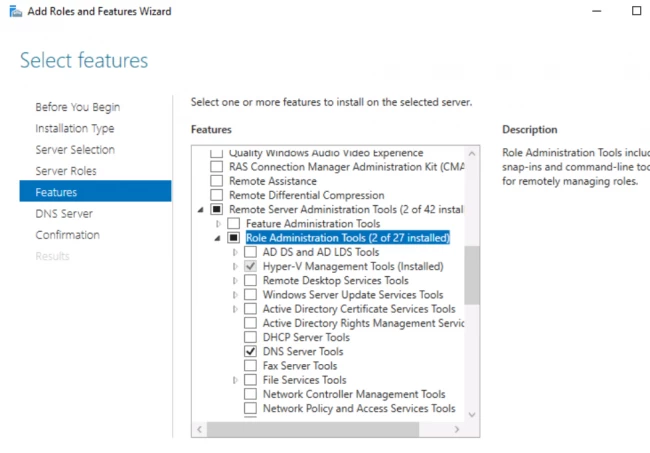
- The next window is again an informational slide. Read and click Next.
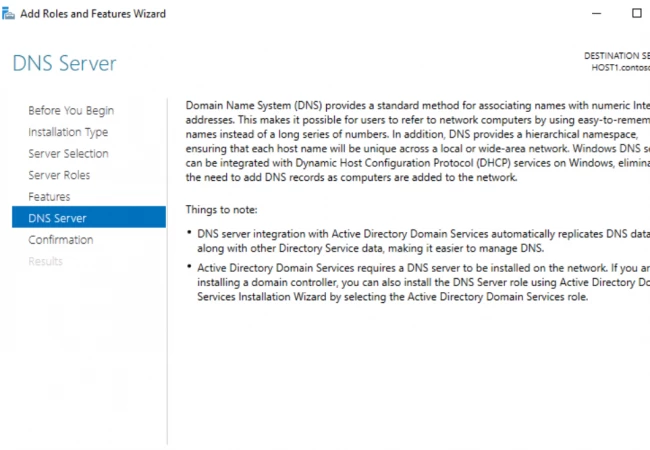
- That's it! The last window asks for your confirmation and takes you back to the Server Manager.
Bravo! You have successfully installed the DNS Server role in your system. Now, go to your Server Manager. You can see a box representing the DNS role!
Well, now that you have installed the DNS server role, let us tread forward. Here is a guide to making your work easy regarding the installation of the DNS server in Windows Server 2012.
Install the DNS server in Windows Server
To configure the DNS server, follow these steps:
- Open the Server Manager and click ‘Tools’. Then hit the DNS option.
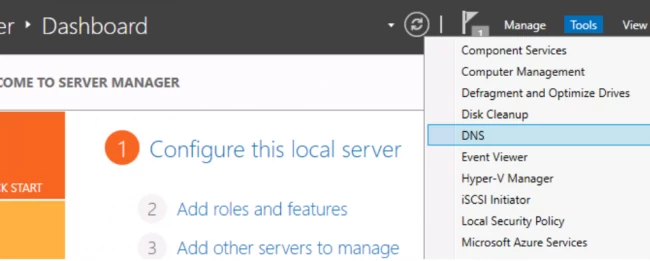
- Now, the configuration of the zones is pending.
Zones are simply the distinct portions of a domain namespace. Furthermore, click on the DNS server, then on the Action menu. Click on Configure a DNS Server and the DNS Server wizard pops up. The wizard shows you three options, namely,
- Create forward and reverse lookup zones
- Create a forward lookup zone
- Configure root hints only
You need to select one option. Now, to sort your ambiguities, let us explain these pointers one by one.
- Forward and reverse lookup zone: This option takes an IP address and resolves it into a domain name.
- Forward lookup zone: This option is the exact opposite of the forward and reverse lookup zones. It helps you to take a domain name and then resolve it into an IP address.
- Root hints only: This option allows you to have the IP addresses of the DNS servers where records can be easily acquired.
Now, click on the option that suits you the best, and hit next. After that, enter the zone name. Move on and click next. Let us tread forward.
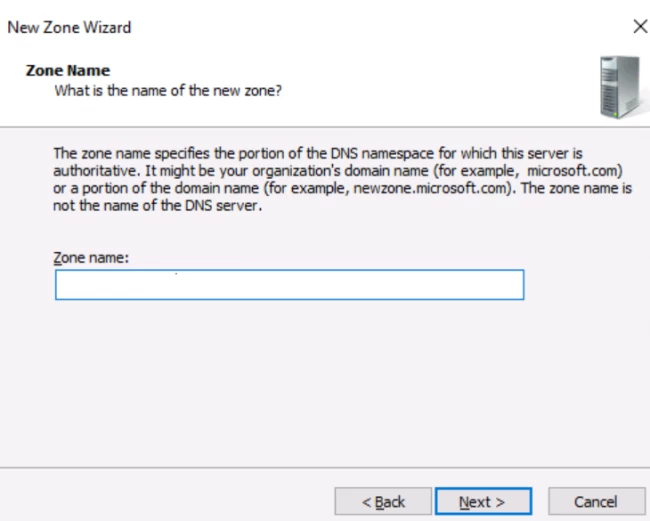
- Right Click on the Forward lookup zone and click on the first option, the ‘New zone’ option.
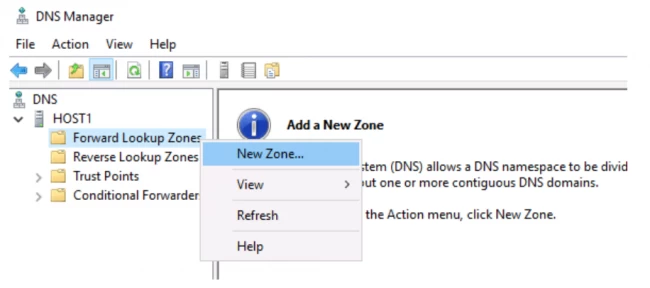
- Now, you have to select the kind of DNS you want to have. Now, there are three options on the screen. Primary zone, Secondary zone, and Stub zone.
The location of the Primary zone is in your server, whereas the Secondary zone resides on some other server. If your requirement is not related to handling large networks, then simply go for the Primary zone. Now, click on next and type any desired name for your zone file.
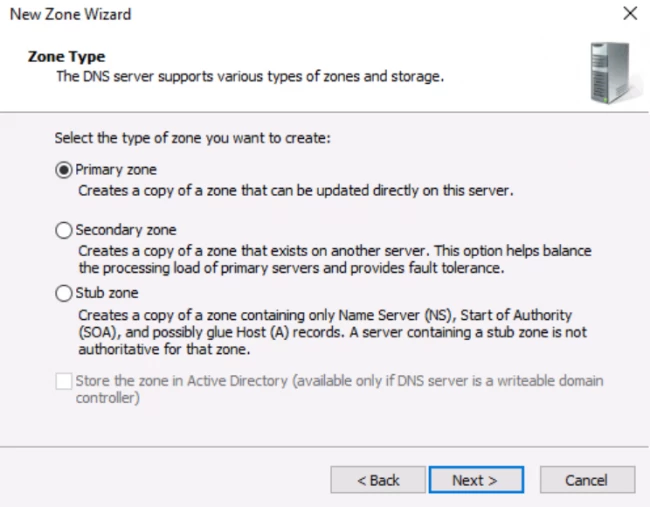
- The wizard box of the new zone file appears and asks you to select an option related to dynamic updates.
Now, you have to make a selection regarding how your server will respond to the Dynamic updates. You will see several options. Options like, allow only secure dynamic updates and then, do not allow dynamic updates. Here, choose the first option if you want integration between the DNS and the Active directory. If not, then opt for the latter option.
- Simply click next and hit finish.
Great! You have successfully created the forward zone. Now, to set up the zone, you have to complete another task. You need to add DNS records. There are numerous DNS records. Here's a glimpse of some of them:
- A-record
- MX
- NS
- CNAME-record
- Now, click on your zone name file and hit the option,’ New host (A or AAAA)’.
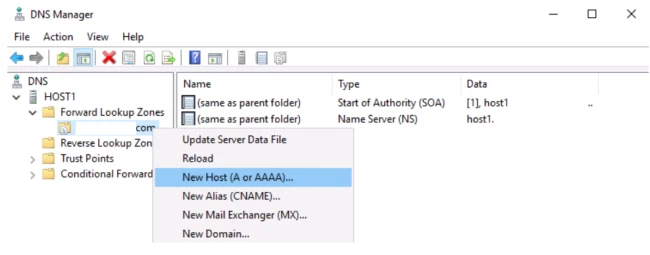
- Enter the asked details in the next window and tap on Add host.
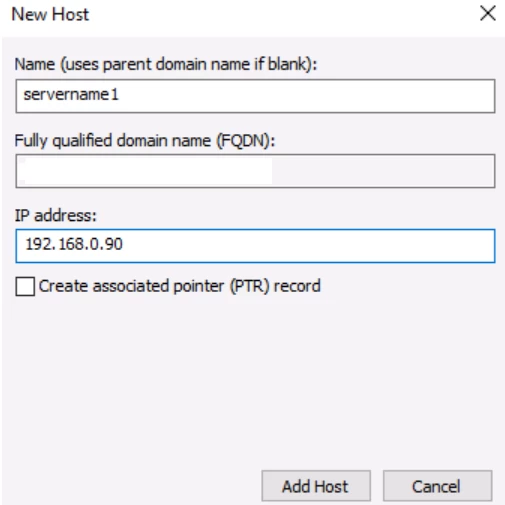
The host is now created.
Now, using PowerShell, create a record. The next step is to allocate a file name for storing your DNS records. The zone name that you entered previously with a .dns extension, is by default the filename.
When you go to the DNS server window, you will see that a host has been created. Now, choose the reverse lookup zone and click on add new zone again. Keep following the steps as done in the case of forward lookup zone till you click the option of Primary zone.
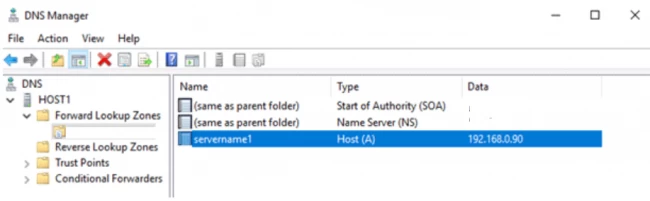
Now here you have to enter the kind of IP address. Choose IPv4 and click next.
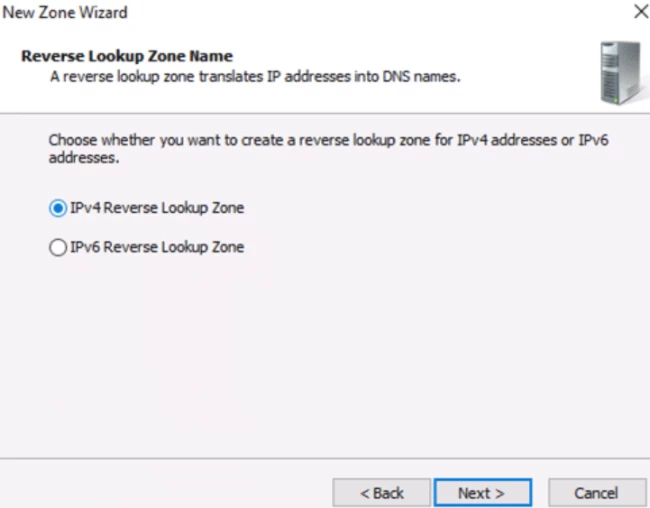
In the next window, type the first three parts of your IP address and hit next.
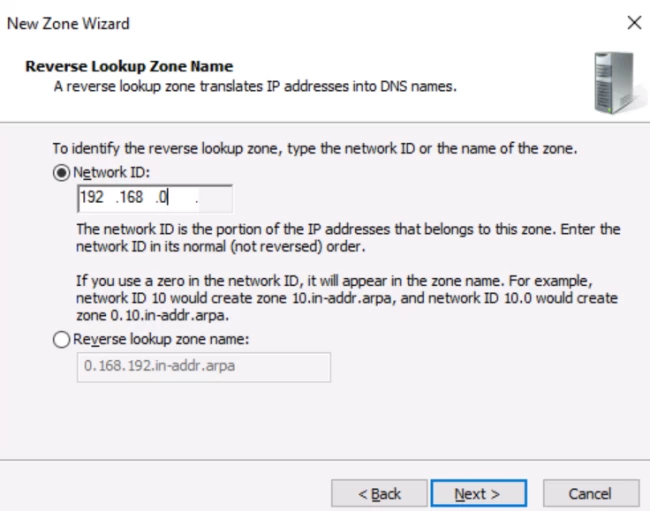
Again, click next.
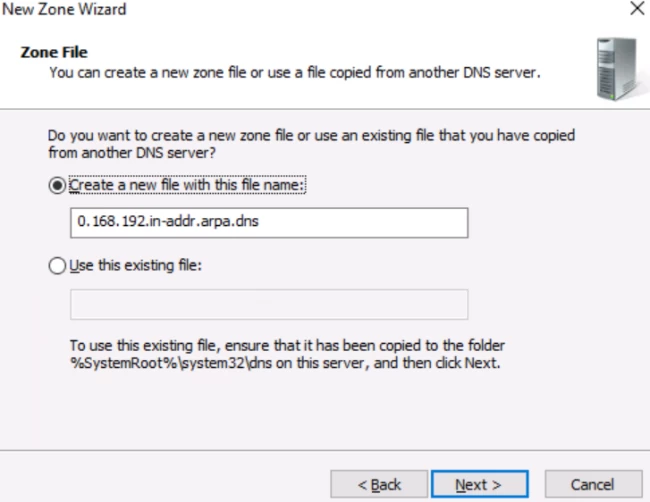
Again click on Do not allow dynamic updates and hit next.
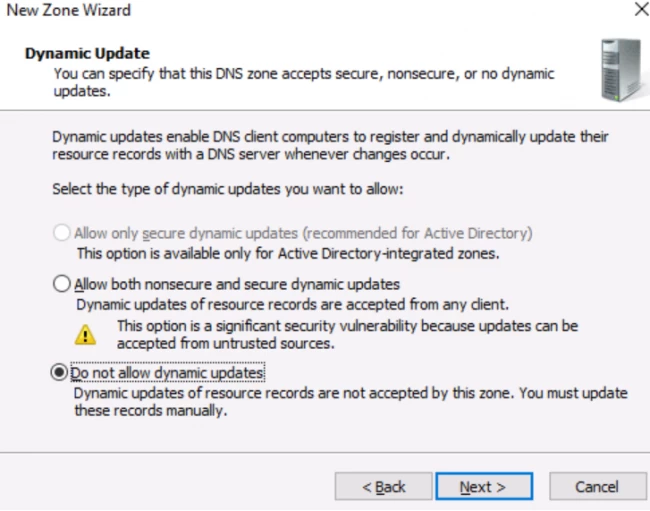
The next window is the last window. Hit finish.
The next popup is regarding the configuration of the forwarders. Forwarders are DNS servers to which the server sends queries when it itself can’t answer them.
To complete the configuration, click on the properties.
Click next, and add the desired address where you want to divert the requests.
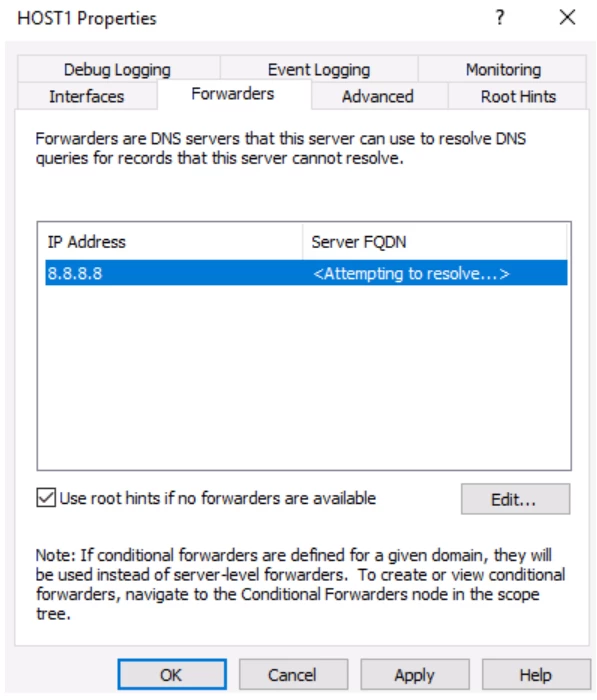
And that’s it, you’re done.
Conclusion
If you have precisely followed all the steps outlined in this article, the DNS server has been successfully installed in the Windows Server. We hope that this article assisted you to accomplish your goal in the best way possible. If you run into any problems during the installation process, have any questions or suggestions, please leave a comment in the comment section below.
