List of content you will read in this article:
In the Linux Operating System, you cannot execute any command without proper permission. Every file and directory has some permission or privilege (read, write, or execute) associated with them. If you are not authorized to access the file or directory, executing any command (instruction that carries a legal duty to obey) on that will result in a “permission denied” error in Linux. This prevalent common can only be resolved by getting the proper access to that file and directory. In this article, we will help you with how to fix the permission denied errors in Linux and what type of error this is with the help of various Linux commands.
What is Linux Permission Denied Error?
This type of error will occur whenever you run a command for which you do not have the execute permission. Similarly, you cannot perform read or write actions if you do not have read or write permission for any file or directory. These Linux permissions are the primary reason behind the security of Linux, as they will help in protecting the data from unauthorized access.
- Read (r): This permission allows users to view the content of a file or directory. For instance, with read permission, you can read the contents of a text file or list the files in a directory.
- Write (w): Write permission enables users to modify the contents of a file or create new files within a directory. Without written permission, you can't make changes to a file or add new files to a directory.
- Execute (x): Execute permission is specifically for files that contain executable code, such as shell scripts or binary executables. Having execute permission allows users to run these files as programs.
These permissions can be set for three categories of users:
- Owner (u): The user who owns the file or directory.
- Group (g): A specific group of users to which the file or directory belongs.
- Others (o): All other users who are not the owner or part of the group.
In addition to these basic permissions, Linux also supports more advanced features like the setuid, setgid, and sticky bit, which can influence how permissions work for certain files and directories.
So, if you want to solve a Linux permission denied error, you can check your privileges for the specific file or folder using the following command.
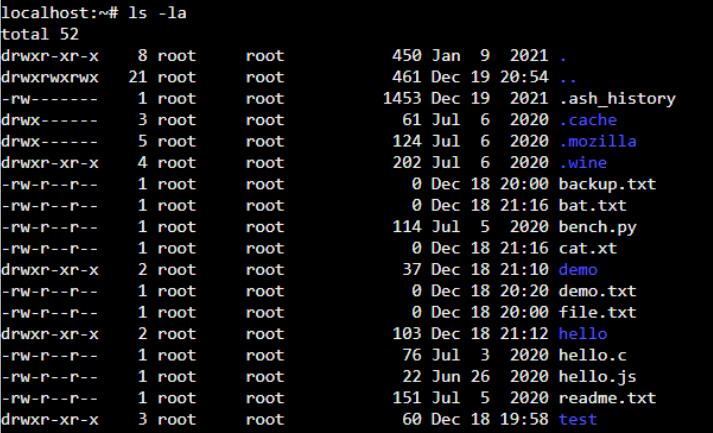
ls -la
ls command will display the long listing of all files and folders along with the permission, as shown below.
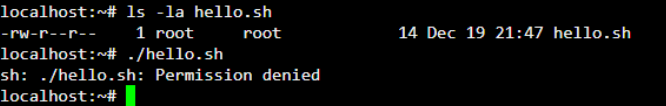
As shown below, we have created a shell script “hello.sh” without the execute permission. On executing “hello.sh”, you will get a permission denied linux error.
Common Scenarios Leading to "Bash Permission Denied" Errors
"Permission Denied" errors in Linux can occur in various scenarios, often due to the stringent security measures in place. Understanding these common situations where users encounter these errors is crucial for effective troubleshooting and prevention. Here are some typical scenarios:
Software Installation and Updates
When attempting to install or update software packages using package managers like apt or yum, users may encounter "Permission Denied" errors. This can happen if they lack the necessary privileges to modify system files or directories where packages are installed.
System Configuration and Maintenance
Modifying system configuration files, such as those in the /etc directory, often requires root or sudo privileges. Users may face "Permission Denied" errors when attempting to edit these critical files without the necessary access.
Accessing Shared Directories
In a networked environment, accessing shared directories or files on remote servers may result in "Permission Denied" errors if the user does not have the required permissions granted by the remote system.
User Home Directory
Users may encounter permission issues when attempting to perform actions within their own home directories. This could include creating, deleting, or modifying files and directories.
Executing Shell Scripts
Running shell scripts or executable files that lack execute permissions can trigger "Permission Denied" errors. Users must ensure the script has the appropriate execute permissions.
File Ownership Changes
When attempting to change the ownership of files or directories, users may encounter issues if they don't have the necessary permissions to perform the ownership transfer.
Basics To Fix Permission Denied Error in Linux?
To solve this error, you need to add the correct permissions to the file to execute. However, you need to be a “root” user or have sudo access to change the permission. For changing the permission, Linux offers a chmod command. The chmod stands for change mod. This command has a simple syntax, as shown below.
chmod flags permissions filename
- Flags are the additional options that users can set.
- Permissions can either be read, written, or executed in the file. You can represent them in symbolic form (r, w, and x) or octal numbers.
- The Filename specifies the file’s name for changing the permissions.
Representation of permissions
Below is the symbolic and octal representation of the user’s permissions while executing the “chmod” command. First, we will understand the representation before using it.
Symbolic Representation
chmod u=rwx,g=r,o=r file
where:
- u=rwx sets permissions for the user who owns the file:
- r specifies read permissions.
- w specifies write permissions.
- x specifies execute permissions.
- g=r sets permissions for the group associated with the file:
- g stands for "group".
- r means the group members can only read the file.
- o=r sets permissions for others (everyone else who is not the file owner or part of the group):
- o stands for "others".
- r means these users can only read the file.
Octal Representation
chmod 744 file
where:
- 7 (first digit) is for the user (owner) and represents rwx (read, write, execute), a sum of:
- 4 for read.
- 2 for write.
- 1 for execute.
- Totaling 7, granting full permissions to the owner.
- 4 (second digit) is for the group and represents r-- (read only), meaning:
- 4 for read.
- Group members do not have write or execute permissions.
- 4 (third digit) is for others and also represents r-- (read only), indicating:
- 4 for read.
- All other users do not have write or execute permissions.
In octal representation, each digit is a sum of its constituent permissions (4 for read, 2 for write, 1 for execute), and 0 means no permissions are set. The first digit sets permissions for the user, the second for the group, and the third for others.
How to Solve Linux Permission Denied?
Now, we are aware of the error, as shown below.
Giving the appropriate permission to the user will solve the problem. Thus, we are giving the execute permission to the user to run the “hello.sh” shell script. Execute the below command to provide execute permission.
chmod +x hello.sh

Now, we can see the change in the permission of the “hello.sh” script file. The above command provides the execute permission to the file. As you can see, the root user can make the required changes. If we execute the shell script, we should not get the error. Let’s try by running the below command.
./hello.sh
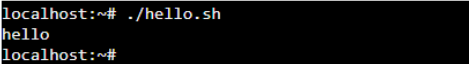
After executing the “hello.sh”, we get the output that displays the “hello.” Changing permission has solved the problem of bash permission being denied.
Troubleshooting Tips
Diagnosing the root cause of "Permission Denied" errors is essential for resolving them. Here are some troubleshooting tips to help you pinpoint the issue:
- Check Error Messages: Pay close attention to the specific error messages. They often provide valuable information about the nature of the permission problem and the affected file or directory.
- Review Log Files: Examine system logs, such as /var/log/syslog or /var/log/auth.log to identify relevant log entries related to the permission issue. Logs may provide additional context.
- Verify File Permissions: Use the ls -l command to inspect the permissions of the file or directory in question. Ensure that the permissions are set correctly.
- Ownership Matters: Confirm the ownership of the file or directory. Verify if the user attempting the action has ownership or belongs to the group that has access.
- Use sudo or su: When dealing with system-level files or administrative tasks, consider using sudo or su to gain temporary elevated privileges.
- Check Disk Space: Sometimes, "Permission Denied" errors can occur due to insufficient disk space. Check available disk space using the df command.
- Network and Remote Access: If accessing files or directories over a network, ensure that network configurations, such as NFS or Samba, are correctly set up, and you have proper access permissions on the remote server.
Conclusion
If you are a regular Linux user, you might have faced the “permission denied” error while executing various commands. This might be due to the incorrect privileges to run that command. Only a root user or user with sudo access can change the permissions for the file or directory you want to access or execute. If you are the correct user to make the required permission changes, you can run the “chmod” command and add the desired permission.
This is all about how you can solve/fix permission-denied errors in Linux with the help of the above-listed commands/methods. If you think there are other alternatives to achieve the goal, you can put them down via the comment box. Also, you can buy a Linux VPS server to run and test the above-listed commands.
![How to fix permission denied error in Linux? [Solutions]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/permission-denied-linux327-main.webp)
I'm fascinated by the IT world and how the 1's and 0's work. While I venture into the world of Technology, I try to share what I know in the simplest way with you. Not a fan of coffee, a travel addict, and a self-accredited 'master chef'.