OpenSSL is one of the most widely used cryptographic libraries in the world, powering SSL/TLS certificates, secure data transmission, and countless security tools. Whether you're a developer, system administrator, cybersecurity professional, or a beginner securing your first Windows workstation, knowing how to install OpenSSL on Windows is essential.
However, installing OpenSSL on Windows is not as straightforward as installing it on Linux. Windows does not include OpenSSL by default, there are multiple builds to choose from, and misconfiguring paths can lead to "command not recognized" errors. This guide solves all of that; step-by-step, visuals included.
We’ll also walk you through:
- OpenSSL Windows download options
- Windows OpenSSL setup guide
- How to configure OpenSSL Windows environment variables
- How to verify your installation
- Basic OpenSSL commands Windows users should know
- Troubleshooting common installation issues
- Updating and uninstalling OpenSSL safely
If you’re new to SSL/TLS or certificates, you can also check out our related guides such as What is SSL and TLS vs SSL.
Why Install OpenSSL on Windows?
OpenSSL enables you to:
- Generate private keys and CSRs
- Create self-signed certificates
- Test SSL/TLS configurations
- Encrypt/decrypt files
- Validate certificates and certificate chains
- Sign and verify data
OpenSSL Installation Methods on Windows
Below is a quick comparison of the main approaches you can use before diving deeper into the actual Windows OpenSSL setup guide.
|
Method |
Difficulty |
Best For |
Pros |
Cons |
|
Precompiled Installer (e.g., SLProweb) |
Easy |
Most users |
Quick, GUI-based, stable |
Might not always include latest version |
|
Package Managers (Chocolatey, Scoop) |
Easy–Medium |
Developers, sysadmins |
Auto-updates, fast installs |
Requires package manager setup |
|
Build from Source |
Hard |
Advanced users |
Full customization, latest release |
Time-consuming |
|
WSL / Cygwin |
Medium |
Linux users on Windows |
Native Linux OpenSSL |
Not Windows-native |
What Is OpenSSL and Why Use It on Windows?
OpenSSL is an open-source toolkit that implements essential cryptographic functions such as:
- RSA, AES, SHA hashing
- SSL/TLS protocols
- Certificate generation
- Key management
- Secure network communication
It’s an essential tool if you work with HTTPS, servers, VPNs, or secure file encryption. Installing OpenSSL on Windows gives you access to the same powerful command-line tools available on Linux. By the way, you can check tutorials for installing SSL in real-world environments like How to Install SSL on VPS or How to Install a Free SSL on a Shared Web Host.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Before you install OpenSSL on Windows, ensure your system meets the following requirements.
Supported Windows Versions
OpenSSL runs on:
- Windows 11
- Windows 10
- Windows Server 2016, 2019, 2022
Older versions may work but are not recommended.
System Requirements
- 64-bit Windows (recommended)
- 100–300 MB of free disk space
- Internet access for download or package manager installation
- Administrator privileges
Additional Recommended Tools
OpenSSL sometimes requires:
- Visual C++ Redistributable (VC++ 2015–2022)
- Perl (only for building from source)
- Git (for source builds)
How to Download OpenSSL for Windows (Safest Options)
There are several ways to perform an OpenSSL Windows download, but not all sources are equally secure.
1. Official OpenSSL Source Code
Best for: users compiling from source
Source: openssl.org
2. Precompiled Binaries for Windows
Recommended for most readers.
Trusted providers:
- SLProweb (Installer-based, stable)
- The Indy Project (DLL-focused)
3. Windows Package Managers
If you prefer automation:
- Chocolatey
- Scoop
These provide seamless updates and clean installs.
4. WSL or Cygwin
For developers who prefer Linux-style environments.
Windows OpenSSL Setup Guide (Step-by-Step Installation)
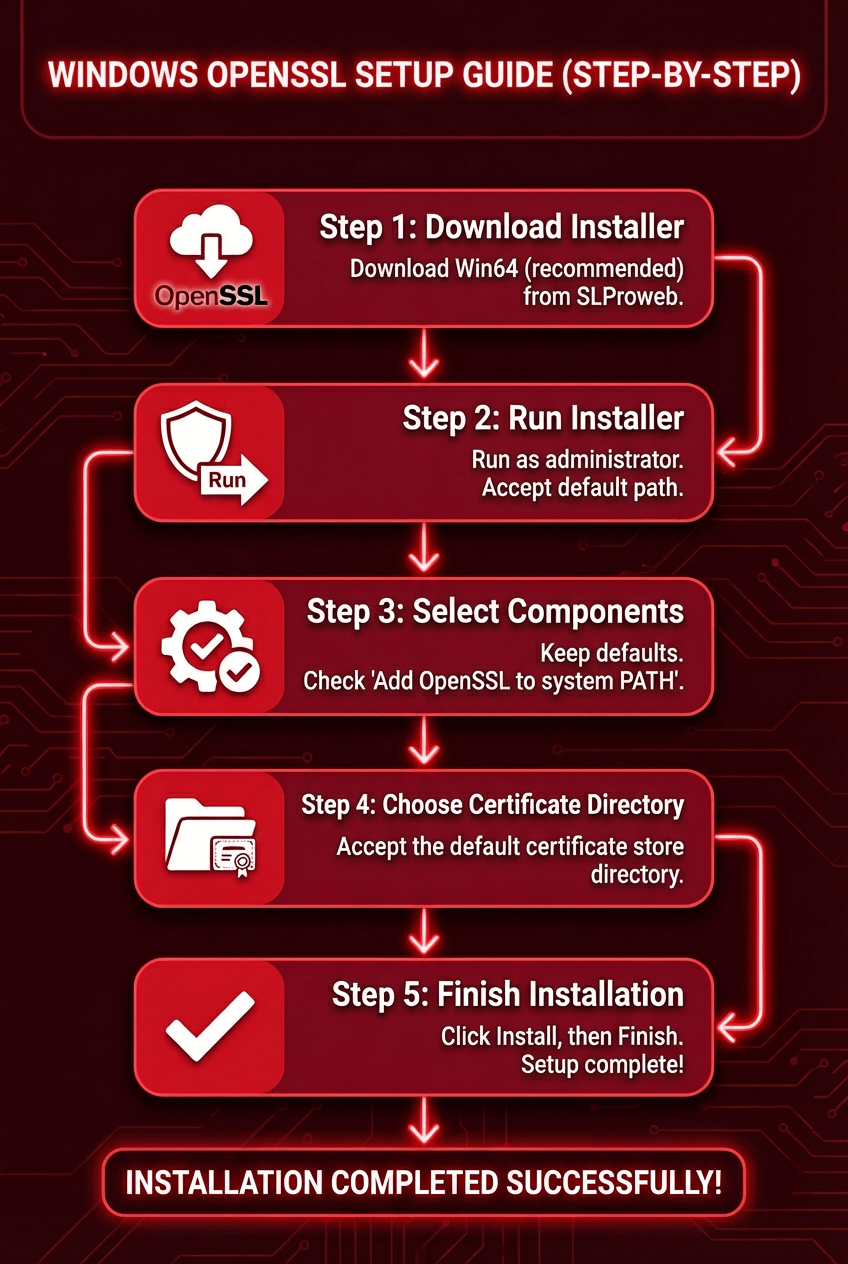
Below is the most reliable method: installing OpenSSL with a GUI installer on Windows.
Step 1: Download OpenSSL Installer
1. Visit the SLProweb OpenSSL download page.
2. Choose the correct version
- Win64 OpenSSL (recommended)
- Win32 OpenSSL (only for legacy systems)
3. Download the .exe installer.
Step 2: Run the Installer
- Right-click the downloaded file.
- Select Run as administrator.
- Accept the license agreement.
Choose your installation directory (default is fine):
C:\Program Files\OpenSSL-Win64
Step 3: Select Components
Keep default settings unless you know you need advanced components.
Check the option:
✔ Add OpenSSL to the system PATH (if available)
This prevents PATH issues later.
Step 4: Choose the OpenSSL Directory for Certificates
You can use the default directory for OpenSSL’s certificate store.
Step 5: Finish Installation
Click Install, wait for completion, and then click Finish.
Congratulations, you’ve completed the basic portion of the Windows OpenSSL setup guide.
Setting OpenSSL Windows Environment Variables
If the installer did not automatically configure PATH, you must set the OpenSSL Windows environment variables manually.
This step is essential — otherwise, you’ll get the error:
'openssl' is not recognized as an internal or external command
Here’s how to fix it.
Step 1: Open Environment Variables
Press Windows + R
Type:
sysdm.cpl
Go to Advanced → Environment Variables
Step 2: Edit System PATH
Under System Variables:
- Find Path
- Click Edit → New
- Add the full path to your OpenSSL bin directory:
C:\Program Files\OpenSSL-Win64\bin
Click OK on all windows to save.
Step 3: Restart Command Prompt
Close and reopen CMD or PowerShell.
Your environment is now fully configured.
Verifying Your OpenSSL Installation
To confirm everything is working:
Run the version command
openssl version
If installed correctly, you should see something like:
OpenSSL 3.2.1 07 Feb 2025
Check OpenSSL directory
where openssl
This ensures your PATH is set properly.
If both commands work, your install OpenSSL on Windows process is complete — and you’re ready to run OpenSSL commands Windows users rely on daily.
Basic OpenSSL Commands to Get Started (For Windows Users)
Now that you’ve completed the install OpenSSL on Windows process and configured your Windows OpenSSL environment variables, you can begin using OpenSSL for practical cryptographic tasks.
Here are the most essential OpenSSL commands Windows users need on a daily basis.
1. Check Your OpenSSL Version
Use this command to confirm your installation:
openssl version -a
This displays:
- OpenSSL version
- Build date
- Platform
- Configuration directory
2. Generate a Private Key
Generate a 2048-bit RSA private key
openssl genrsa -out private.key 2048
Generate a 4096-bit key (recommended for best security)
openssl genrsa -out private.key 4096
3. Create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
A CSR is required if you plan to install an SSL certificate on a website.
openssl req -new -key private.key -out request.csr
The command will ask you for:
- Country
- State
- City
- Organization
- Common Name (your domain)
4. Generate a Self-Signed Certificate
Useful for testing servers locally.
openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key private.key -sha256 -days 365 -out certificate.crt
5. Convert Certificate Formats (PEM, PFX, DER)
Convert PEM → PFX
openssl pkcs12 -export -out certificate.pfx -inkey private.key -in certificate.crt
Convert DER → PEM
openssl x509 -inform DER -in certificate.der -out certificate.pem
6. Check Certificate Information
openssl x509 -in certificate.crt -text -noout
7. Verify a Certificate and Private Key Match
openssl x509 -noout -modulus -in certificate.crt | openssl md5
openssl rsa -noout -modulus -in private.key | openssl md5
If both hashes match, they belong together.
Troubleshooting Common OpenSSL Installation Issues on Windows

Even after a successful install OpenSSL on Windows, you might run into common errors. Below are the most frequent problems users encounter and how to resolve them.
1. “openssl is not recognized as an internal or external command”
Cause:
The PATH variable is incorrect.
Fix:
Add this to your System PATH:
C:\Program Files\OpenSSL-Win64\bin
Restart CMD or PowerShell.
2. Missing DLL Errors (e.g., “libssl-3-x64.dll not found”)
Cause:
Incomplete installation or missing Visual C++ dependencies.
Fix:
- Reinstall the latest Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable 2015–2022
- Reinstall OpenSSL
- Ensure DLLs exist inside the bin directory
3. “Unable to load config info from openssl.cnf”
Cause:
OpenSSL cannot locate its config file.
Fix:
Add this environment variable manually:
OPENSSL_CONF = C:\Program Files\OpenSSL-Win64\bin\openssl.cfg
If your config filename differs, use that instead.
4. OpenSSL Version Not Updating After Installation
Cause:
Old OpenSSL path still exists earlier in PATH.
Fix:
Go to:
System Environment Variables → PATH
Remove old entries such as:
C:\OpenSSL-Win32\bin
5. Permissions Issues
If you see errors related to writing files:
- Run CMD/PowerShell as Administrator
- Ensure the directory isn’t read-only
Updating OpenSSL on Windows
Unlike Linux, OpenSSL does not update automatically on Windows.
You must update manually, but it’s easy.
Step-by-Step: Update OpenSSL on Windows
1. Download the Latest Build
Perform a new OpenSSL Windows download from a trusted provider.
2. Uninstall the Old Version
Go to:
Control Panel > Programs and Features
Uninstall:
OpenSSL-Win64 or OpenSSL-Win32
3. Install the New Version
Follow the same steps from the Windows OpenSSL setup guide.
4. Verify Version
Run:
openssl version
How to Uninstall OpenSSL on Windows?
If you need to remove OpenSSL entirely, follow this:
1. Uninstall via Control Panel
Navigate to:
Programs and Features → OpenSSL → Uninstall
2. Remove Environment Variables
Remove:
C:\Program Files\OpenSSL-Win64\bin
from:
System → Advanced System Settings → Environment Variables → PATH
3. Delete Remaining Files
Remove leftover folders:
C:\Program Files\OpenSSL-Win64
C:\OpenSSL
Conclusion: Your Complete Windows OpenSSL Setup Guide
You now have everything you need to confidently install OpenSSL on Windows, configure your Windows OpenSSL environment variables, and begin using essential OpenSSL commands Windows professionals rely on.
This guide covered:
- OpenSSL Windows download options
- Full Windows OpenSSL setup guide (step-by-step)
- Environment variables configuration
- Verification commands
- Basic usage examples
- Troubleshooting
- Updating and uninstalling OpenSSL
- FAQ and best practices
Whether you're generating CSRs, securing servers, or learning cryptography, OpenSSL is an essential tool that works flawlessly on Windows when set up correctly.
If you plan to secure a live website, remember; you can always Buy SSL Certification through MonoVM for maximum security and global trust.

I'm fascinated by the IT world and how the 1's and 0's work. While I venture into the world of Technology, I try to share what I know in the simplest way with you. Not a fan of coffee, a travel addict, and a self-accredited 'master chef'.