List of content you will read in this article:
If you are a proud owner of a remote Linux server or VPS, you probably know that in order to access it via the internet, you will need to use SSH. Although having a strong and secure password is the only cybersecurity step the majority of remote server users take, additional layers of security are always recommended. One important security measure we suggest you implement is changing the SSH port. Today, we will provide you with a detailed step-by-step tutorial on how to do just that on CentOS.
What is SSH?
The full form of SSH is Secure Shell daemon. It is a network protocol used for performing secure remote logins for Linux systems using a secure channel from an unsecured network with the help of robust cryptography. By default, SSH listens on port 22, so it is good to change the default SSH port in order to add extra security, thus decreasing the risk of an automated attack.
How to Change SSH Port on CentOS 6
The default port number is TCP port # 22, however, you can set the port number of the server according to your requirements. Here’s a detailed tutorial on how to do so on CentOS 6.
Step 1: First of all, you will have to open the SSH configuration file to change the port, thus, execute the following command in the terminal:
/etc/ssh/sshd_config
Step 2: After executing the aforementioned command, execute one of these commands:
Port PortNumberHere
Or
ListenAddress IPv4Address:Port
ListenAddress IPv6Address:Port
ListenAddress Hostname:Port
If you have not specified a port, the SSHD, by default, then it will work on the previously specified addresses and port options. You can also allow multiple listenaddress and options in sshd_config.
Step 3: To run SSH on a non-standard port # 2022 using Port option, use the following command:
# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Step 4: Now, edit to set the port to 2022 and save the file to successfully make the changes:
Port 2022
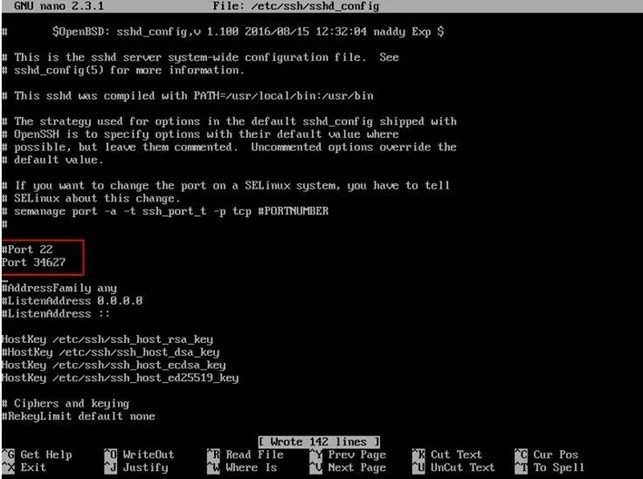
If you want to run SSH on a non-standard port # 2022 using the port option, then try ListenAddress as follows:
## bind sshd to two IP address on a non-standard port ##
ListenAddress 192.168.1.5:2022
ListenAddress 203.1.2.3:2022
Once you use the command successfully, save and close the file.
Remember, you need to update the following items before you restart the system to apply the changes:
- SELinux configuration
- Firewall settings
- fail2ban settings
Update SELinux configuration
If you are using SELinux, add TCP port # 2022 to port contexts for OpenSSH server:
# semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp 2022
Update Firewall Settings
Step 1: Update firewall settings so that users can log in using TCP # 2022. To do so, use the following command to edit, /etc/sysconfig/iptables and open SSHD port 2022:
# vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables
Step 2: After that, edit the values as follows:
## delete or comment out port 22 line ##
## -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
## open port 2022
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 2022 -j ACCEPT
Once you edit the values, save and close the file.
Step 3: If you are an IPv6 user, edit the /etc/sysconfig/ip6tables file as well, so temporally, stop the firewall by typing:
# service iptables stop
# service ip6tables stop
Fail2ban settings
Fail2ban scan all of the log files and ban the IPs with any malicious actions, password failures, SSH logins, exploitations, etc., use it to update the rules.
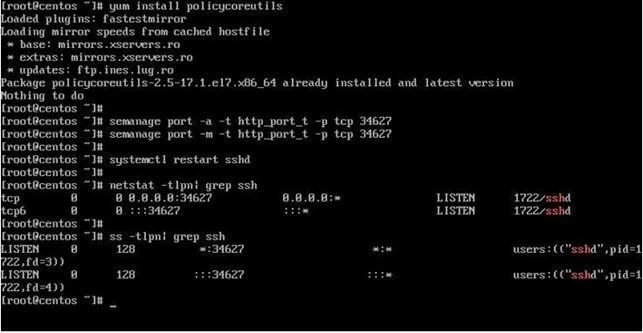
Step 1: Type the following command to restart SSHD services:
# service sshd reload
Step 2: Verify new port settings with this netstat command:
# netstat -tulpn | grep sshd
Step 3: Now, use the following commands to restart the firewall in CentOS:
# service iptables start
For IPv6:
# service ip6tables start
Step 4: Connect to SSH server on port # 2022 using SSH command:
ssh -p PortNumberHere user@server-name-here
ssh -p PortNumberHere user@server-name-here commandNameHere
ssh -p 2022 XYZ@192.168.1.5
ssh -p 2022 XYZ@192.168.1.5 df
To connect to an SSH server on port # 2022 using scp command type:
scp -P PortNumberHere source user@server-name-here:/path/to/dest
scp -P 2022 resume.pdf XYZ@nas01:/backups/personal/XYZ/files/
To connect to an SSH server on port # 2022 using sftp command type:
sftp -P PortNumberHere user@server-name-here
sftp -P 2022 XYZ@192.168.1.5
To connect to SSH server on port # 2022 using rsync command type:
Change SSH port number with rsync command:
sync -av -e 'ssh -p PORT-NUMBER-HERE' source user@server-name
So, to backup /home/XYZ to server1.XYZ.net.in at port number 2022, enter:
rsync -av -e 'ssh -p 2022' /home/XYZ/ backupop@server1.XYZ.net.i
How to change SSH port on CentOS 7
In this section, we will give you a brief guide on how to change the SSH port on CentOS 7. It is simple; however, you have to follow every step to eliminate the chances of occurring errors.
Step 1: First, open /etc/ssh/sshd_config and search for the following Port 229 and make sure to choose an unused/not-well-known port (at least >1023).
Step 2: To open a port on firewallD, use the following command:
firewall-cmd --add-port YOUR_PORT_HERE/tcp
SELinux Configuration
Configure SELinux to behave with the new port by typing the following command:
semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp YOUR_PORT_HERE
Fail2Ban Settings
Step 1: Open /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf and search for the following section to configure Fail2Ban:
[sshd]
# To use more aggressive sshd filter (inclusive sshd-ddos failregex):
#filter = sshd-aggressive
port = ssh
logpath = %(sshd_log)s
backend = %(sshd_backend)s
Step 2: Now, change the values of the port to the actual port by using the following commands. This example shows port 7222:
[sshd]
# To use a more aggressive sshd filter (inclusive sshd-ddos failregex):
#filter = sshd-aggressive
port = 7222
logpath = %(sshd_log)s
backend = %(sshd_backend)s
After the execution of these commands, Fail2Ban will not be able to close the appropriate port.
Step 3: Now, type the following commands to test the new configurations:
systemctl restart sshd
systemctl restart fail2ban
You can also try to connect via SSH to the server with the new port:
ssh USERNAME@YOUR_IP/HOSTNAME -p YOUR_NEW_PORT
Once you complete the aforementioned steps successfully, finalize the settings and mop up, meaning use the new port rather than the previous one.
Step 4: Configure the SSH daemon, open /etc/ssh/sshd_config delete/comment out the Port 22 in it.
Now you have told SSHD not to listen on port 22, which is the default port.
Step 5: It is time to finalize the firewall configuration:
firewall-cmd --add-port YOUR_PORT_HERE/tcp --permanent
firewall-cmd --reload
Step 6: After that, type the following commands:
systemctl restart sshd.service
firewall-cmd --remove-service ssh --permanent
firewall-cmd --reload
If you face the following error when restarting the SSHD:
job for sshd.service failed because the control process exited with error code. See "systemctl status sshd.service" and "journalctl -xe" for details.
Run journalctl –xe by the command:
journalctl –xe
Upon execution of the command you will get an output like this:
server1 kernel: type=1400 audit(1537086072.510:4): avc: denied { name_bind } for pid=1074 comm="sshd" src=6378 scontext=system_u:system_r:sshd_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 tcontext=system_u:object_r:unres
server1 sshd[1074]: error: Bind to port 6378 on 0.0.0.0 failed: Permission denied.
server1 sshd[1074]: error: Bind to port 6378 on :: failed: Permission denied.
server1 kernel: type=1400 audit(1537086072.515:5): avc: denied { name_bind } for pid=1074 comm="sshd" src=6378 scontext=system_u:system_r:sshd_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 tcontext=system_u:object_r:unres
server1 sshd[1074]: fatal: Cannot bind any address.
server1 systemd[1]: sshd.service: main process exited, code=exited, status=255/n/a
server1 systemd[1]: Failed to start OpenSSH server daemon.
Step 6: You have to run the following commands to set the changes for the system:
semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp 3456
Step 7: Now, you can verify that SELinux has allowed SSHD to listen on the two ports:
semanage port -l | grep ssh
ssh_port_t tcp 3456, 22
Step 8: Next, type this command:
yum whatprovides semanage
The output should look like this:
policycoreutils-python-2.5-22.el7.x86_64 : SELinux policy core python utilities
Repo : base
Matched from:
Filename : /usr/sbin/semanage
Step 9: Now, install policycoreutils.
yum install -y policycoreutils-python
Step 10: Finally, check that you can log in to a server through a new SSH port with the following command:
ssh -p 3456 root@server1
How to Change SSH Port in CentOS 8
Step 1: First you need to check the status of SSH Service in CentOS 8 using systemctl command:
systemctl status sshd.service
After executing the aforementioned command, you will a get message like this:
â sshd.service - OpenSSH server daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2020-08-08 17:59:18 PKT; 2s ago
Docs: man:sshd(8)
man:sshd_config(5)
Main PID: 1564 (sshd)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 5916)
Memory: 1.2M
CGroup: /system.slice/sshd.service
ââ1564 /usr/sbin/sshd -D -oCiphers=aes256-gcm@openssh.com,chacha20-poly1305@openssh.com,aes256-ctr,aes256-cbc,>
Aug 08 17:59:18 centos-8.centlinux.com systemd[1]: Starting OpenSSH server daemon...
Aug 08 17:59:18 centos-8.centlinux.com sshd[1564]: Server listening on 0.0.0.0 port 22.
Aug 08 17:59:18 centos-8.centlinux.com sshd[1564]: Server listening on :: port 22.
Aug 08 17:59:18 centos-8.centlinux.com systemd[1]: Started OpenSSH server daemon.
We can tweak /etc/ssh/sshd_config file to customize SSH service according to our requirements. There is no Port directive in this file, and the SSH service uses the default ssh port number 22.
Step 2: Add a Port directive in sshd_config file using the echo command.
echo "Port 50" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Step 3: SELinux configuration does not allow any service to run on a non-default port. Configure SElinux to enable SSH to use port 50/tcp.
Step 4: Use semanage command to add port 50/tcp to type ssh_port_t:
semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp 50
Firewall Settings
Step 1: Now, you will need to list allowed ports or services in the firewall.
firewall-cmd --list-all
Once you execute the above command, you will see the following:
public (active)
target: default
icmp-block-inversion: no
interfaces: ens33
sources:
services: cockpit dhcpv6-client ssh
ports:
protocols:
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
source-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:
You can also type systemctl firewalld instead of the above-executed command.
Step 2: Now, block this SSH service and allow a new SSH port in the firewall.
firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-service=ssh
success
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=50/tcp
success
firewall-cmd --reload
success
Step 3: After that, type the following command to restart the service:
systemctl restart sshd
Step 4: You will also need to verify the status of SSH Service by typing:
systemctl status sshd.service
After executing the command, you will get the message like this:
â sshd.service - OpenSSH server daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2020-08-08 18:13:37 PKT; 14s ago
Docs: man:sshd(8)
man:sshd_config(5)
Main PID: 10376 (sshd)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 5916)
Memory: 1.2M
CGroup: /system.slice/sshd.service
ââ10376 /usr/sbin/sshd -D -oCiphers=aes256-gcm@openssh.com,chacha20-poly1305@openssh.com,aes256-ctr,aes256-cbc>
Aug 08 18:13:37 centos-8.centlinux.com systemd[1]: Stopped OpenSSH server daemon.
Aug 08 18:13:37 centos-8.centlinux.com systemd[1]: Starting OpenSSH server daemon...
Aug 08 18:13:37 centos-8.centlinux.com sshd[10376]: Server listening on 0.0.0.0 port 50.
Aug 08 18:13:37 centos-8.centlinux.com sshd[10376]: Server listening on :: port 50.
Aug 08 18:13:37 centos-8.centlinux.com systemd[1]: Started OpenSSH server daemon.
Step 5: Now, type the following command to access SSH service using ssh and sftp commands from the default ssh port:
ssh root@centos-8.xyz.com
You will get the output like this after executing the aforementioned command. This output will show that the Firewall is not allowing traffic through port 22.
ssh: connect to host centos-8.centlinux.com port 22: Connection refused
sftp root@centos-8.centlinux.com
ssh: connect to host centos-8.centlinux.com port 22: Connection refused
Connection closed
Connection closed
Step 6: Now, you can access the SSH service using the ssh command:
ssh root@centos-8.centlinux.com -p 50
Output:
The authenticity of host '[centos-8.centlinux.com]:50 ([192.168.116.206]:50)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:skGj4xg0w+jIQtrfF8AOdfItgcXUQQu+bWUFfvws1Hk.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added '[centos-8.centlinux.com]:50,[192.168.116.206]:50' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
root@centos-8.centlinux.com's password:
Last login: Sat Aug 8 17:59:01 2020
[root@centos-8 ~]#
Similarly, execute the following commands for sftp:
sftp -P 50 root@centos-8.centlinux.com
root@centos-8.centlinux.com's password:
Connected to root@centos-8.centlinux.com.
sftp>
Conclusion
Congratulations, you made it to the end. If you are looking to set up your very own SSD-based CentOS VPS, then you can do so easily with Monovm. As we have mentioned earlier, it is good to change the SSH port on the servers as it offers additional security for the system. We have included a step-by-step procedure how to do exactly that on the three latest versions of CentOS.
People Are Aalso Reading:

I'm fascinated by the IT world and how the 1's and 0's work. While I venture into the world of Technology, I try to share what I know in the simplest way with you. Not a fan of coffee, a travel addict, and a self-accredited 'master chef'.