Installing Windows Server has become a critical task for system administrators, IT professionals, homelab enthusiasts, cloud engineers and enterprise teams. Whether you are preparing a brand new server, deploying a virtual machine or performing an in-place upgrade, the accuracy of the Windows Server installation process directly affects performance, security and long term stability.
This Windows Server installation and Configuration step by step guide covers everything you need from creating the Windows Server installation media to troubleshooting installation failures and preparing your server for production use. It includes version specific instructions for Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2022 and the new Windows Server 2025 releases.
What Is Windows Server?
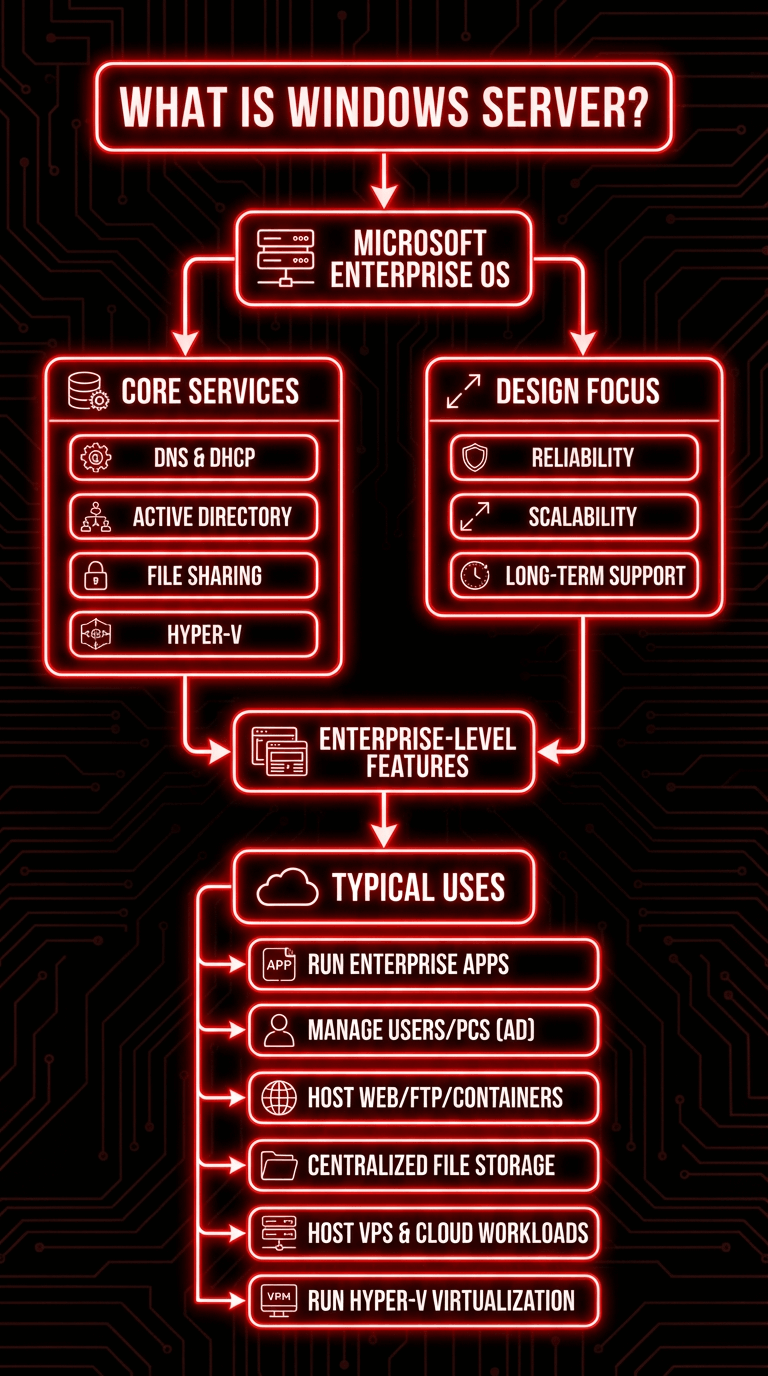
Windows Server is Microsoft’s enterprise operating system used to manage networks, host applications, run virtual machines and provide essential services such as DNS, DHCP, Active Directory, Hyper V and file sharing. While Windows Server shares many visual elements with Windows desktop systems like Windows 10, it is designed for reliability, scalability and long term enterprise level support.
Understanding What is Windows Server is essential before installing it because choosing the right edition and installation type affects resource usage, performance and available features.
Typical Windows Server uses include:
- Running enterprise applications
- Managing users and computers through Active Directory
- Hosting web servers, FTP servers or container environments
- Building centralized file storage systems
- Hosting Windows Server VPS or cloud based workloads
- Running Hyper V virtualization
Windows Server Editions Overview
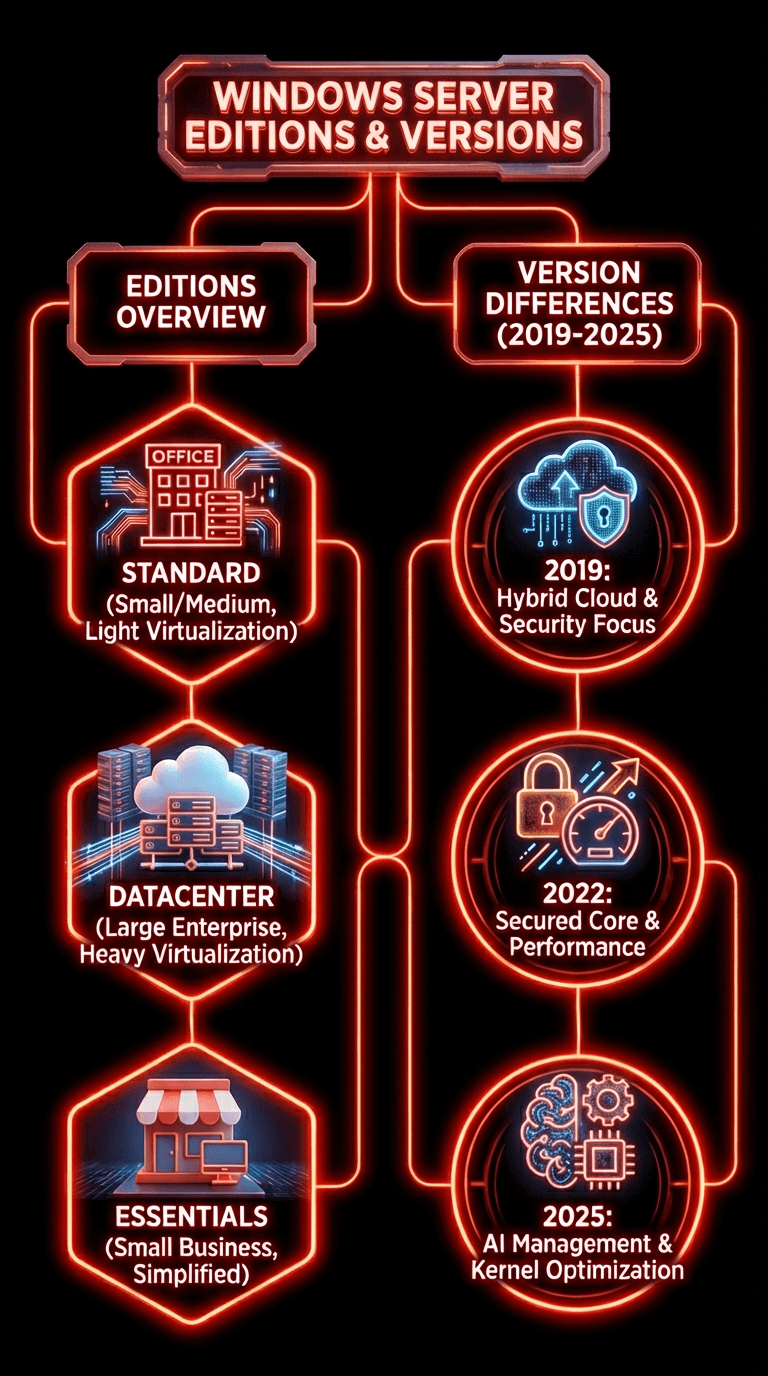
Windows Server usually ships in several editions:
Windows Server Standard
Suitable for small and medium businesses that run physical or lightly virtualized environments.
Windows Server Datacenter
Designed for heavy virtualization, cloud deployments and large scale enterprise infrastructures.
Windows Server Essentials
Simplified server for small businesses with limited IT capacity.
Windows Server 2019, 2022 and 2025 Differences
- 2019 focuses on hybrid cloud and security
- 2022 adds secured core server and improved performance
- 2025 introduces AI based management improvements and updated kernel optimizations
Windows Server Installation Requirements
Before starting the Windows Server installation process, verify that your hardware meets Microsoft’s official minimum requirements. Failing to meet these specifications is a common cause of the error “Windows Server installation has failed” and also affects long term server stability.
Hardware Requirements for Windows Server Installation
|
Component |
Minimum Requirement |
Recommended for Stability |
|
Processor |
1.4 GHz 64 bit processor compatible with x64 architecture |
2.0 GHz multi core CPU with virtualization support |
|
RAM |
2 GB |
8 GB or more for virtualization or roles |
|
Storage |
32 GB minimum |
100 GB SSD for better performance |
|
Network |
Gigabit Ethernet adapter |
Dual NIC or bonded configuration |
|
Firmware |
UEFI or BIOS |
UEFI with Secure Boot support |
|
File System |
NTFS or ReFS |
NTFS for general setups, ReFS for Storage Spaces |
Important Notes:
- Windows Server requires a 64 bit CPU and will not install on 32 bit hardware.
- Using UEFI instead of BIOS helps avoid installation errors, especially on new servers.
- For Windows server installation windows 10 environments where Windows Server Hyper V is used on Windows 10 machines, ensure virtualization extensions are enabled.
Preparing Windows Server Installation Media
The Windows Server installation media is the core element required to boot the system and begin deployment. Creating it properly allows you to avoid issues such as corrupted ISOs, missing system files or the common message “Windows Server installation has failed”.
Download Windows Server ISO
You can download official ISO files from Microsoft’s evaluation center or through volume licensing. Make sure you select the correct version:
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server 2022
- Windows Server 2025
Create Windows Server Installation Media
Creating installation media is the most important preparation step. You can prepare it using:
- Rufus (recommended for USB drives)
- Windows USB and DVD Tool
- Media Creation Tool for supported versions
- Hyper V or VMware virtual ISO mount
Windows Server Installation USB
A Windows server installation usb is the simplest way to perform both physical and virtual server deployments. It is also required for many situations such as installing Windows Server 2022 on bare metal hardware or running Windows server installation windows 10 Hyper V environments.
How to Create a Bootable Windows Server USB Using Rufus
1. Insert a USB flash drive with at least 8 GB capacity.
2. Open Rufus.
3. Under Device, select your USB drive.
4. Select the Windows Server ISO file.
5. Choose partition scheme:
- GPT for UEFI
- MBR for BIOS
6. Click Start and wait for the process to complete.
This method works for every version including Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2022 and Windows Server 2025.
If you want to deploy Windows Server inside Windows 10, this process is also required because Windows server installation windows 10 using a virtual machine still depends on the same ISO file.
Windows Server Installation Step by Step Full Walkthrough
This Windows Server installation and Configuration step by step guide works for all modern versions including 2019, 2022 and 2025.
Step 1: Boot From USB, DVD or ISO
Insert your Windows server installation usb or mount your ISO in a virtual machine. Restart the system and open the boot menu. Select:
- USB device
- Optical drive
- Virtual ISO mount
If your system does not boot, ensure that Secure Boot, UEFI mode or virtualization settings are correct.
Step 2: Choose Language, Time and Keyboard
Select your regional preferences. These can be changed later but it is recommended to choose correct settings to avoid format issues.
Step 3: Select Windows Server Edition
You will now see options like:
- Windows Server 2019 Standard
- Windows Server 2019 Datacenter
- Windows Server 2022 Standard
- Windows Server 2025 Datacenter Azure Edition
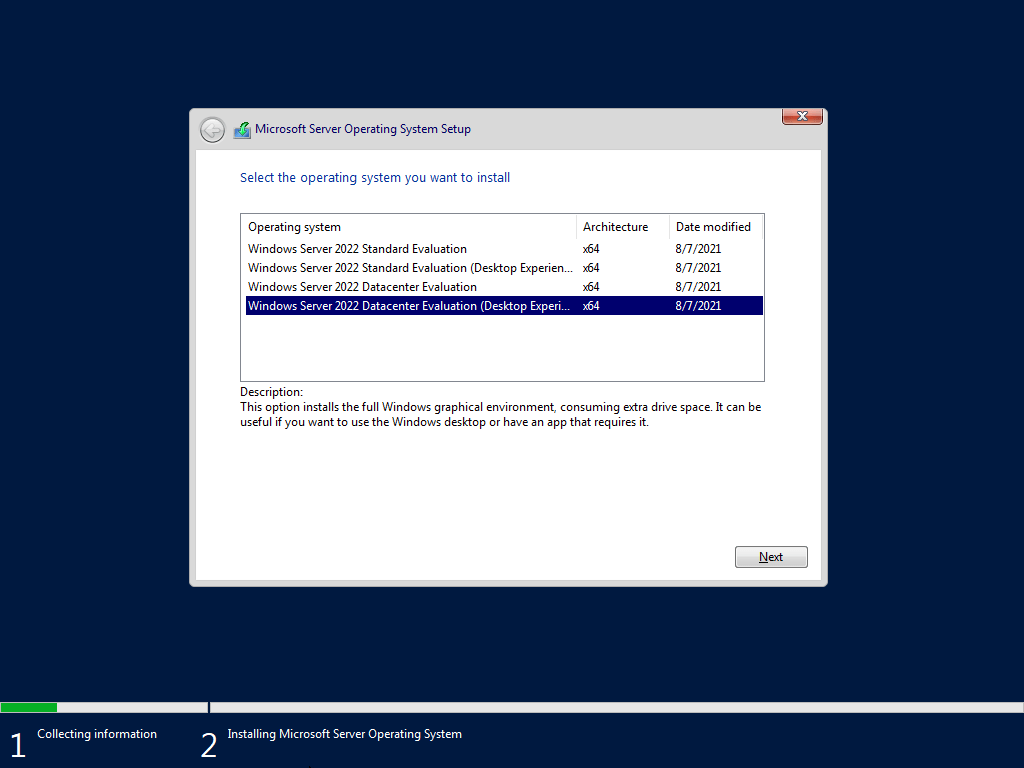
Or other similar options.
Your choice will determine available features, licensing and virtualization capacity.
If you need help evaluating versions, refer to Best Windows Server Versions.
Step 4: Custom Installation vs Upgrade Installation
A Custom installation formats the system drive and is recommended for:
- New servers
- Virtual machines
- Cloud installations
- Replacing old configurations
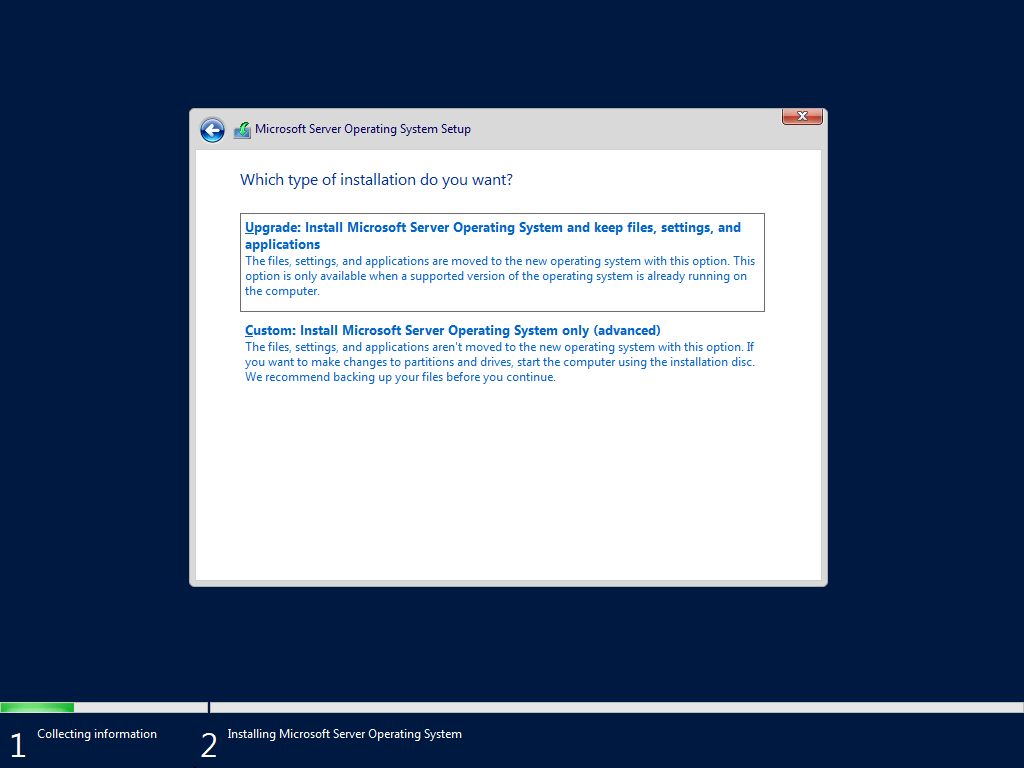
Upgrade installation keeps existing data but can fail if old roles or drivers create conflicts. Many installation errors such as “Windows Server installation has failed 2025” occur during upgrade attempts.
Step 5: Configure Disk Partitions
This is where many users encounter issues like:
- MBR or GPT mismatches
- Incorrect boot partition format
- Unsupported RAID controller
- Corrupted drive tables
Recommended partition setup:
- 100 MB EFI System Partition
- 16 MB MSR partition
- Primary NTFS partition
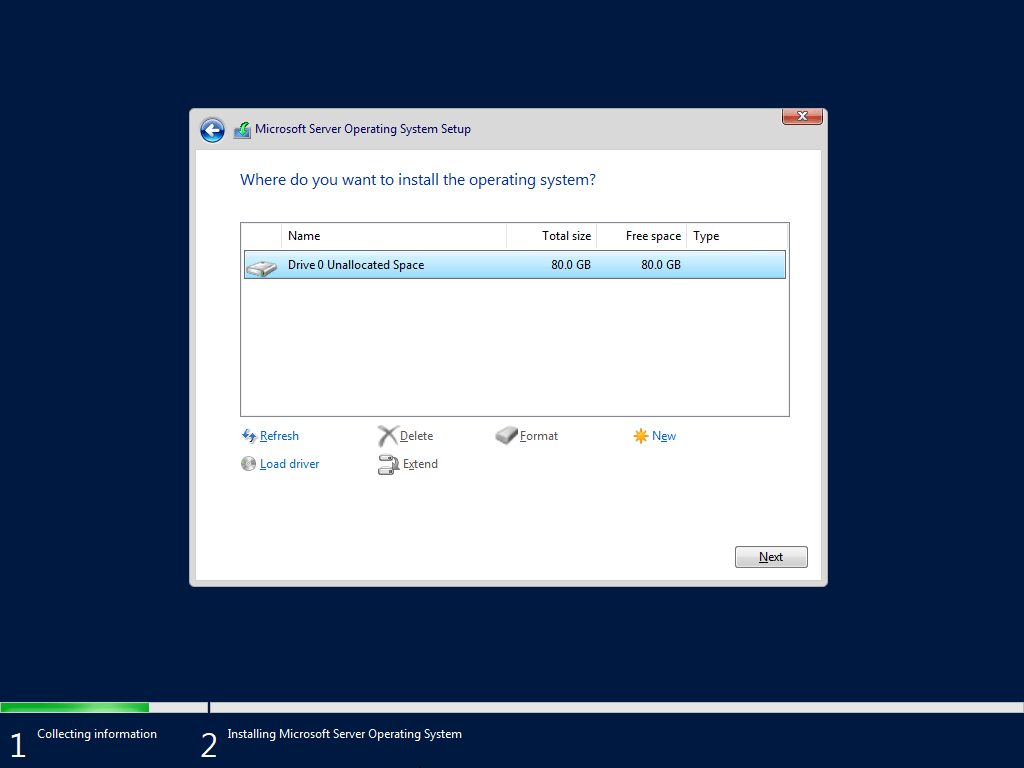
This stage is also where users must understand what is the default file system for Windows Server installation, which is NTFS for almost all scenarios.
Step 6: Copying Files and First Reboot
The installation media copies system files and prepares Windows Server for the first boot. Do not interrupt the process. At this step, using high speed SSD storage can reduce installation time.
Step 7: Administrator Password Configuration
Once the system reboots, enter the initial Administrator password. This password should follow security guidelines because Windows Server environments often handle sensitive business operations.
How to Configure the Administrator Password
- Wait for the installation to finish and the server to restart automatically.
- When prompted, enter a strong password that follows recommended security rules.
- Confirm the password.
- Click Finish to complete this stage.
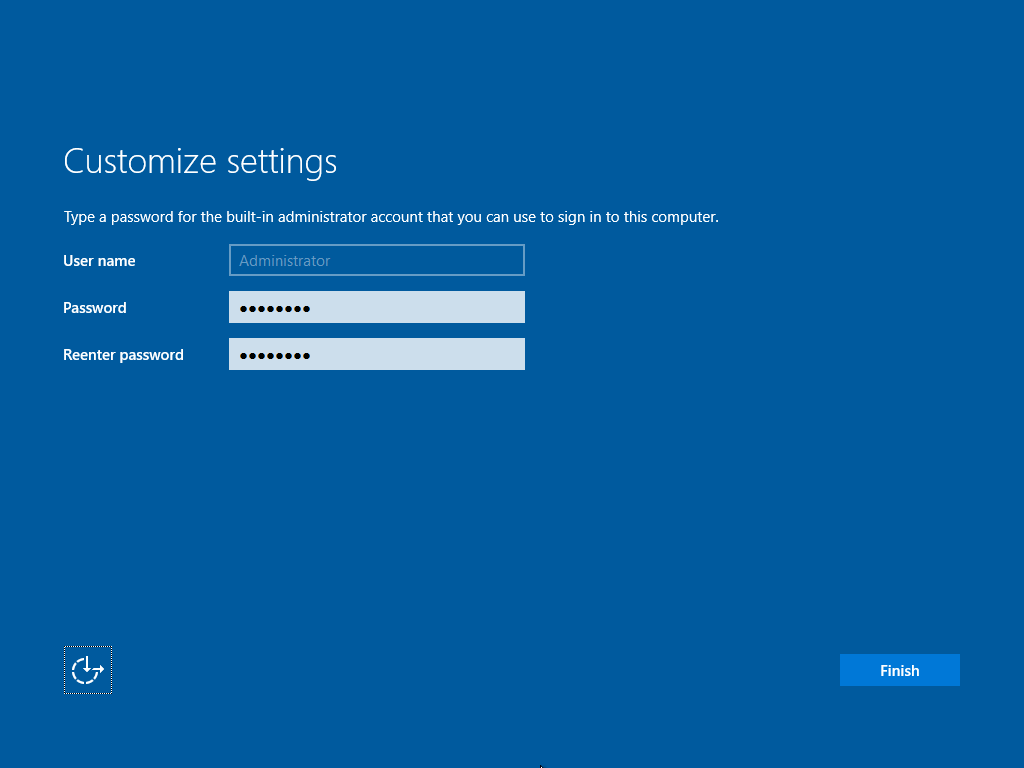
This completes the base setup. You now have a clean Windows Server installation and can proceed to Windows server installation and configuration step-by-step tasks such as IP setup, domain joining, and role installation.
Windows Server 2019 Installation
Many users still search for How to install Windows Server 2019 because it remains one of the most stable and widely deployed versions.
How to Install Windows Server 2019
The process is almost identical to modern versions such as 2022 and 2025. These steps include:
- Create a bootable USB using your preferred tool. This satisfies the Google suggestion for Windows server installation usb.
- Boot your system from the USB.
- Choose language, time, and keyboard settings.
- Select the appropriate Windows Server 2019 edition.
- Choose Custom installation if installing on a clean disk.
- Create or select partitions.
- Continue until installation completes.
- Set the Administrator password.
How to Install Windows Server 2019 From USB
This is one of the most commonly searched terms. Follow these steps:
- Download the ISO from Microsoft.
- Use Rufus to create a bootable Windows Server 2019 USB.
- Ensure your system is set to boot from USB.
- Start installation and follow the Wizard.
These steps ensure you meet the exact requirements for How to install Windows Server 2019 from USB.
Server Roles After Installation
You can now install roles such as:
- DNS Server
- Active Directory Domain Services
- DHCP Server
- Hyper V
- File and Storage Services
If you want a deeper guide on installing DNS, refer to the article Install a DNS Server in Windows Server for a complete configuration walkthrough.
Windows Server 2022 And 2025 Installation
These newer versions introduce improved security and performance features. Although the installation steps remain similar, there are some differences.
Important Installation Differences
- More strict secure boot requirements
- Additional driver requirements for network and storage controllers
- Optional SMB over QUIC support
- Advanced virtualization and containerization updates
Driver Requirements
Windows Server 2022 and 2025 require:
- Updated NIC drivers
- Updated RAID and storage drivers
- TPM 2.0 enabled for certain security features
For more information, read Windows Server 2025 Features.
Windows Server Installation Has Failed 2025
This is an increasingly common issue users face when installing the newest version. Causes include:
- Corrupt ISO file
- Unsupported RAID configuration
- MBR or GPT mismatch
- Missing drivers
- Secure Boot requirements not met
Automate Windows Server Installation
Automating your installation process saves time across multiple servers and ensures consistency.
Unattended Installation
Automation uses an XML-based configuration file called unattend.xml. You can specify:
- Product key
- Edition selection
- Disk partition rules
- Administrator password
- Network settings
- Domain join settings
Using Answer Files (unattend.xml)
To create answer files:
- Install Windows ADK (Assessment and Deployment Kit).
- Open Windows System Image Manager.
- Load your Windows Server image.
- Generate the answer file.
- Save as unattend.xml and place it in the root of the installation media.
Deployment Through WDS
Windows Deployment Services allows:
- PXE boot installation
- Centralized image management
- Automated deployments
This is ideal for enterprise-scale rollouts.
Windows Server Installation Types
|
Installation Type |
Description |
When to Use |
Desktop Experience |
Full GUI |
Beginners Or Admins |
|
Server Core |
Command based minimal environment |
Cloud, datacenters, secure environments |
No |
No |
Skilled admins |
|
Desktop Experience |
Full graphical interface |
General servers, small businesses |
Yes |
Yes |
Beginners and admins |
|
Nano Server |
Extremely lightweight and remote managed |
Containers, microservices, IoT |
No |
No |
Advanced users |
Notes:
- Server Core offers better performance, fewer attack vectors, and lower resource consumption.
- Desktop Experience offers convenience but uses more RAM/CPU.
- Nano Server is completely remote-managed and cannot run traditional server roles.
Post Installation Configuration (Core Admin Tasks)
Once the installation finishes, you must configure the system. These are necessary Windows server installation and configuration step-by-step tasks.
Configure IP And Networking
- Open Settings or Server Manager
- Assign static IP
- Configure DNS
- Test connectivity using ping
Rename Server And Join Domain
- Open System Properties
- Change computer name
- Enter domain credentials
- Restart the server
Joining a domain is essential for enterprise deployments.
Enable Roles And Features
Use Server Manager or PowerShell.
You can follow the article Installing Windows Server’s Features and Roles through PowerShell for advanced automation.
Windows Update Configuration
Always update the server before production use:
- Open Windows Update
- Download updates
- Restart if required
Repair Windows Server Installation
If the system becomes corrupted, you can repair Windows Server installation using the following tools.
Startup Repair
Boot from USB or ISO and select Repair your computer.
Safe Mode
Use Safe Mode to troubleshoot faulty drivers.
SFC And DISM
Use commands:
sfc /scannow
dism /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth
These are essential for system recovery.
Read more: Windows Server Migration Tools
Fixing Windows Server Installation Has Failed
Below is the required troubleshooting section.
Common Causes
- Corrupt installation media
- Wrong disk format
- Secure Boot or TPM errors
- RAID driver missing
- BIOS configuration problems
- MBR or GPT mismatch
Troubleshooting Checklist Table
|
Issue |
Cause |
Solution |
|
Installation stops at 0 percent |
Corrupt ISO |
Redownload ISO |
|
Setup cannot find disk |
Missing driver |
Install RAID or NVMe drivers |
|
Secure Boot error |
BIOS mode mismatch |
Check UEFI settings |
|
Installation loops |
Wrong boot order |
Adjust BIOS |
|
Windows server installation has failed 2025 error |
Compatibility problem |
Switch to UEFI and GPT |
Windows Server Installation Checklist
A thorough installation checklist helps avoid common mistakes and ensures a stable environment:
✔ Ensure BIOS/UEFI mode is correct
Confirm that the system is configured for either Legacy BIOS or UEFI. For modern deployments, UEFI is strongly recommended as it supports Secure Boot, faster boot times, and GPT disks.
✔ Verify storage partitions
Ensure your disk layout includes system, recovery, and data partitions as needed. Using SSD or NVMe storage is ideal for improving OS performance and virtualization workloads.
✔ Confirm all drivers are available
Before installation, download NIC drivers, RAID/SAS controller drivers, and chipset packages. Missing storage drivers are a common cause of the “Windows server installation has failed” error during setup.
✔ Check network connectivity
Assign a static IP address after installation, verify DNS reachability, and ensure the machine can access the internet or domain controllers.
✔ Create user accounts and roles
Prepare administrative credentials, service accounts, and least-privileged roles according to your security policy.
✔ Configure updates
Enable automatic updates or configure WSUS policies to ensure the server receives security patches and cumulative updates.
✔ Install server roles and features
Roles such as DNS, DHCP, AD DS, Hyper-V, File Server, or IIS should be installed based on your deployment plan.
Use Server Manager or PowerShell to verify configuration.
✔ Verify backups
Before deploying into production, configure Windows Server Backup or third-party backup tools to protect system state and important data.
✔ Document configuration
Record server name, IP address, installed roles, firewall rules, and administrative accounts. Clear documentation prevents errors during maintenance and recovery.
Conclusion
Windows Server installation is a critical process for any IT environment. By following this detailed step-by-step guide, using proper Windows Server installation media, and applying reliable configuration practices, you can deploy stable and secure servers for 2019, 2022, and 2025 versions.
If you want to take the next step and run Windows servers on high performance infrastructure, you can explore Windows Server VPS from MonoVM. These plans offer fast deployment, global data centers, optimized performance, and 24/7 expert support.
Your server installation journey does not end here. With the right tools, documented procedures, and the support of a reliable hosting provider, you can maintain secure and efficient operations across all deployments.

An experienced tech and developer blog writer, specializing in VPS hosting and server technologies. Fueled by a passion for innovation, I break down complex technical concepts into digestible content, simplifying tech for everyone.