List of content you will read in this article:
The reasons for reinstalling Ubuntu can vary, but common scenarios include system slowdowns, software conflicts, or the desire to clean up your system after prolonged usage. Reinstalling Ubuntu can breathe new life into your computer, resolving lingering issues and ensuring a smooth, optimized experience. In this comprehensive guide, we will take you through the process of reinstalling Ubuntu step by step.
Prerequisites to Reinstall Ubuntu
Backup Your Data
The first and most critical step is to safeguard your important data. Reinstalling Ubuntu will erase everything on your current installation, so make sure you have a backup of your documents, photos, and any other essential files. Consider using an external drive or cloud storage for added security.
Create a Bootable Ubuntu USB
You'll need a bootable USB drive with the Ubuntu installation media. Visit the official Ubuntu website, download the latest version, and follow the instructions to create a bootable USB. This will be your lifeline during the reinstallation process.
Check System Requirements
Ensure that your computer meets the system requirements for the Ubuntu version you plan to install. This includes checking processor specifications, RAM, and storage capacity. Running an operating system on insufficient hardware can lead to performance issues.
Document Your System Configuration
Take note of your current system configuration, including hardware specifications and any custom settings you've applied. This information will be useful when reconfiguring your system post-reinstallation.
Verify Internet Connectivity
Having a stable internet connection is essential for a smooth reinstallation process. This ensures that you can download the latest updates and drivers during the installation, keeping your system up to date from the start.
When Should You Reinstall Ubuntu?
Determining the right time to reinstall Ubuntu is crucial for maintaining a healthy and optimized system. Here are scenarios where reinstalling Ubuntu might be the best course of action:
- Persistent Issues:
If you're facing recurring problems, such as frequent crashes, software glitches, or unresponsive applications, reinstalling Ubuntu can provide a fresh start, resolving these issues.
- Major System Upgrades:
When a significant Ubuntu version update is released, reinstalling ensures a clean transition. It allows you to benefit from new features and improvements without potential conflicts from the previous installation.
- Security Concerns:
If your system has been compromised or you suspect a security breach, a reinstall is a reliable way to eliminate any potential threats and establish a secure computing environment.
- Optimization and Performance Boost:
Over time, your system may accumulate unnecessary files and settings, leading to a decline in performance. Reinstalling Ubuntu can revitalize your system, providing a performance boost.
- Customization Overload:
If you've extensively customized your Ubuntu system and find it challenging to troubleshoot issues, a clean reinstall allows you to start anew, applying customizations more selectively.
Tutorial Reinstall Ubuntu Linux Step by Step
Ensure a smooth Ubuntu reinstallation process by adhering to the steps outlined below. Prioritize creating a backup as your initial step before embarking on the system reinstallation journey.
Make a Backup
While reinstalling Ubuntu typically doesn't harm personal files, it's essential to err on the side of caution. Back up your data before proceeding. Employ an external drive or USB to safeguard crucial files that you wouldn't want to lose.
Post reinstallation, ensure the preservation of the following:
- The /home directory containing your files and settings.
- The entries in the boot menu, particularly if multiple operating systems are present.
Download Ubuntu
Navigate to the official Ubuntu downloads page. Select your desired version for reinstallation and initiate the download by clicking the designated button.
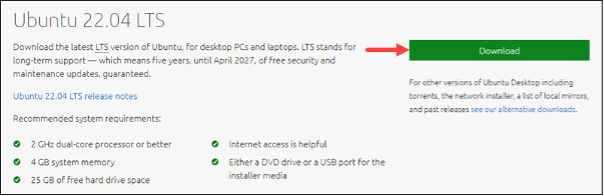
Allow time for the ISO image to complete its download process.
Use Startup Disk Creator tool to Create live USB in Ubuntu
Before you proceed to reinstall Ubuntu, ensure you have the following:
- A USB stick/flash drive with a capacity of 4GB or larger.
- The Ubuntu ISO file was downloaded in the previous step.
Creating a Bootable USB in Ubuntu
If you still have access to your Ubuntu system, utilize the Startup Disk Creator tool that comes pre-installed.
Follow these steps to create a bootable USB on Ubuntu:
- Insert a USB stick into an available port with a capacity of 4GB or more.
- Open the app drawer by clicking the Show Applications button.
- In the search field, type "startup disk creator" and select the corresponding application.

- Within the tool, pick the target USB drive in the Disk to use section. Click the Other... button to load the ISO image in the Source disc image (.iso) section.
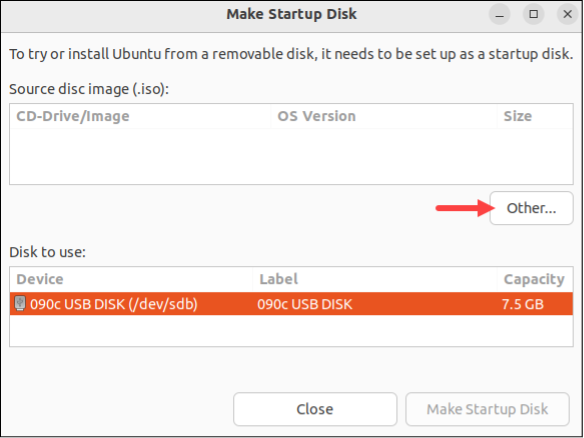
- Select the "Make Startup Disk" button to initiate the creation of the Live USB.
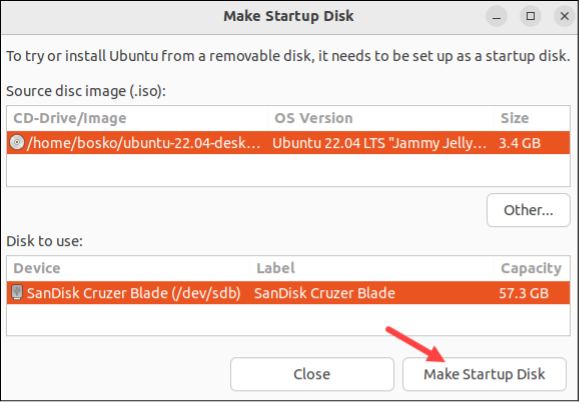
- When prompted, click Yes to confirm.
- Enter the administrator password and click Authenticate to proceed with writing to the device.
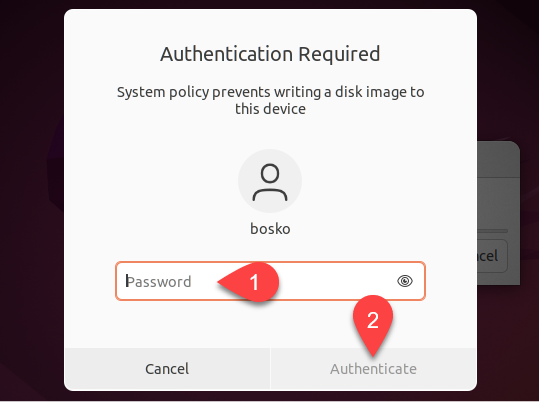
- Allow the tool to finish writing the image to the USB. Upon completion, an info message will appear, indicating the successful installation. Click Quit to close the dialog box and proceed with the subsequent steps for reinstalling Ubuntu.
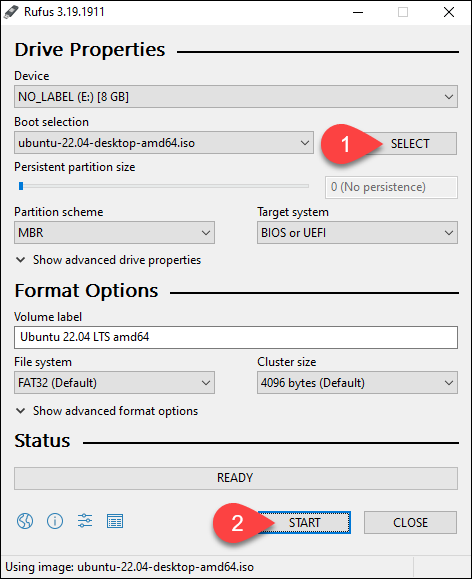
Create Live USB in Windows
If you're using Windows, employ Rufus or another third-party tool to fashion a bootable USB drive. For Rufus, adhere to the steps outlined below:
- Plug your USB stick into an available USB port.
- Visit the official Rufus website and scroll down to the Downloads section. Download the latest Rufus version by clicking the provided link.

- Execute the downloaded file. During the initial launch, Rufus may prompt you to opt for regular online updates. Choose your preferred option. Rufus will automatically identify the connected USB drive.
- Click the SELECT button and locate the downloaded Ubuntu ISO image.
- Initiate the process by clicking START to format the USB drive and commence writing the image to the device.
Reinstall Ubuntu
Ensure the USB drive remains connected as you proceed to restart the machine. During the post screen, use the F2/F10/F12 key, depending on your machine's brand, to access the BIOS settings. In the BIOS, confirm that Removable Devices/USB is prioritized at the top of the Boot order list. Save the changes and exit the BIOS.
- The system will restart and boot from the live USB. Follow the steps outlined below for the Ubuntu reinstallation:
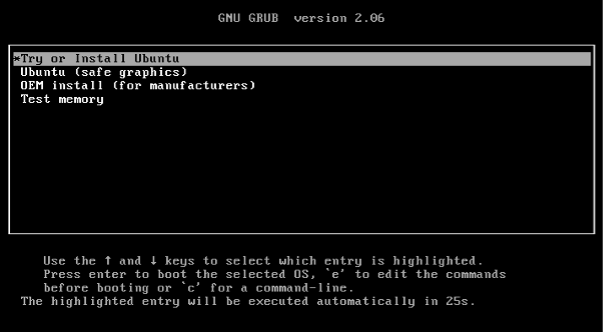
- Navigate to the GNU Grub menu and choose the Try or Install Ubuntu option, then press Enter.
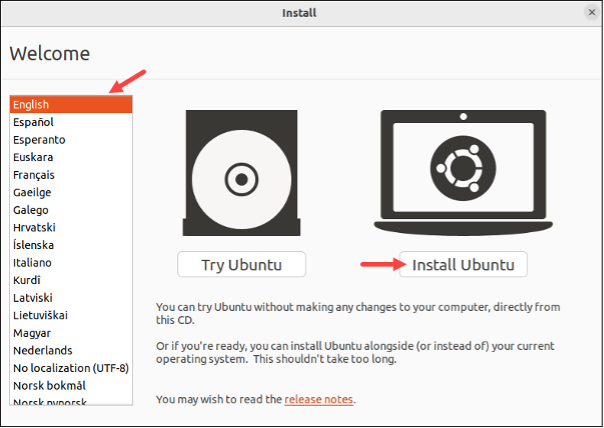
- On the Welcome screen, select your preferred language and choose the Install Ubuntu option.
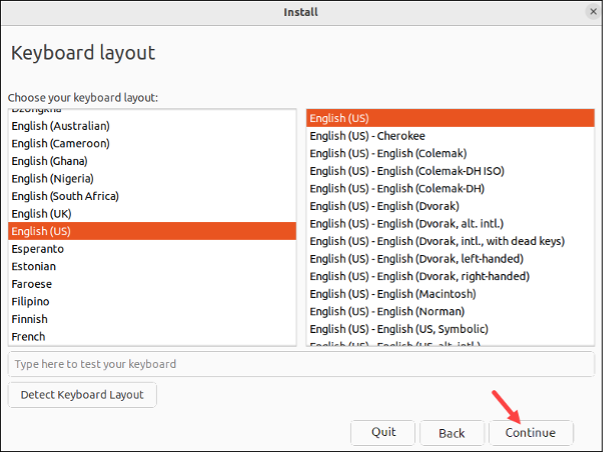
- Pick your keyboard layout and click Continue.
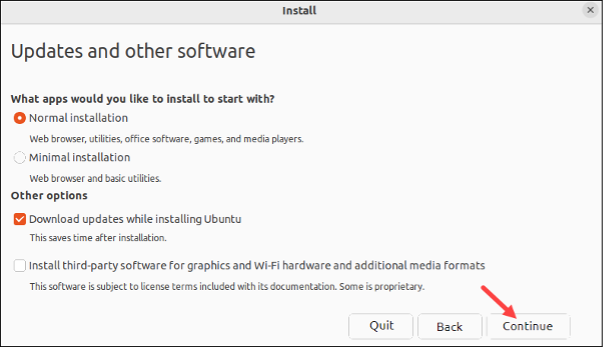
- Depending on your preferences, select either the Normal or Minimal installation type. Optionally, in the Other options section, tick the boxes to download updates during installation and install third-party software for graphics and Wi-Fi devices. Click Continue.
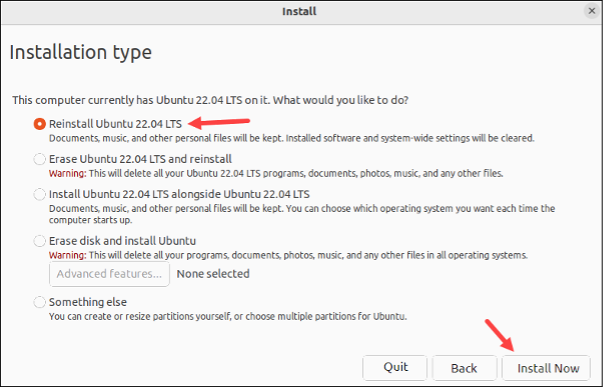
- On the Installation type screen, choose the Reinstall Ubuntu option to retain personal files. Alternatively, opt for Erase Ubuntu and reinstall to format the hard drive and initiate a fresh Ubuntu installation. Click the Install Now button to initiate the installation.
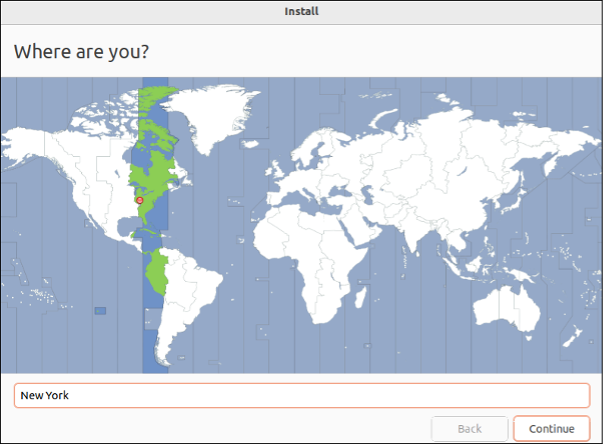
- Set your time zone and click Continue.
- Generate a username and password, then click Continue.
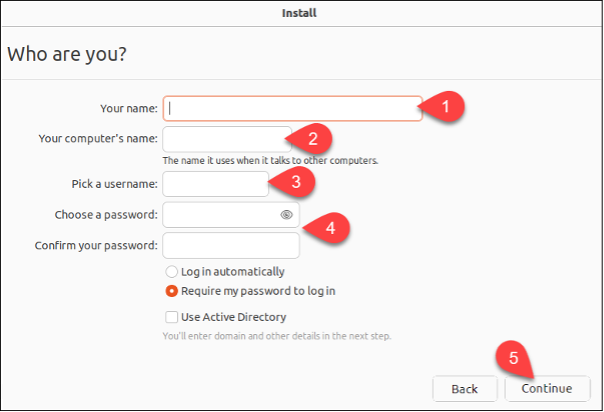
- Allow the installation to complete, then remove the USB drive and proceed to boot into the system.
What is the difference between update and reinstall Ubuntu?
- Update Ubuntu:
Updating Ubuntu involves applying the latest software patches, security fixes, and feature enhancements to your existing installation. This process is like giving your system a tune-up, ensuring it stays current and secure. Updates are incremental and generally retain your applications and user data.
- Reinstall Ubuntu:
On the other hand, reinstalling Ubuntu means wiping the existing installation and starting fresh with a clean slate. Unlike updates, this process involves a complete overhaul of the operating system. It's recommended when facing persistent issues, major upgrades, or the need for a performance boost. However, it requires backing up your data and reinstalling applications afterward.
Final Words
In conclusion, Ubuntu offers a robust, user-friendly, and open-source computing environment that can cater to a wide range of users. Reinstalling Ubuntu is a valuable step to rejuvenate your system and keep it running at its best. We hope this guide has been informative and that you continue to enjoy the Ubuntu experience while exploring the limitless possibilities it offers. Happy computing!

Hello, everyone, my name is Lisa. I'm a passionate electrical engineering student with a keen interest in technology. I'm fascinated by the intersection of engineering principles and technological advancements, and I'm eager to contribute to the field by applying my knowledge and skills to solve real-world problems.