List of content you will read in this article:
- 1. 1. Use the systeminfo command to get system information
- 2. 2. Use the tasklist command to see the list of running processes in Windows
- 3. 3. Use the taskkill command to stop a process
- 4. How to Determine Whether a System Can Run the 64-bit Solaris Operating Environment
- 5. How to Determine Whether a System Has 64-bit Solaris Capabilities Enabled
- 6. How to Display System and Software Release Information
- 7. How to Display General System Information
- 8. How to Display a System's Host ID Number
- 9. How to Display a System's Installed Memory
- 10. How to Display the Date and Time
- 11. Conclusion
- 12. FAQ
With CMD commands, you can explore an unexplored area of computer knowledge. If you've ever wondered how to access and acquire vital system information, “CMD commands computer information” is for you. In this blog post, we'll walk you through the process of using CMD commands computer information examples, from basic commands to complex techniques.
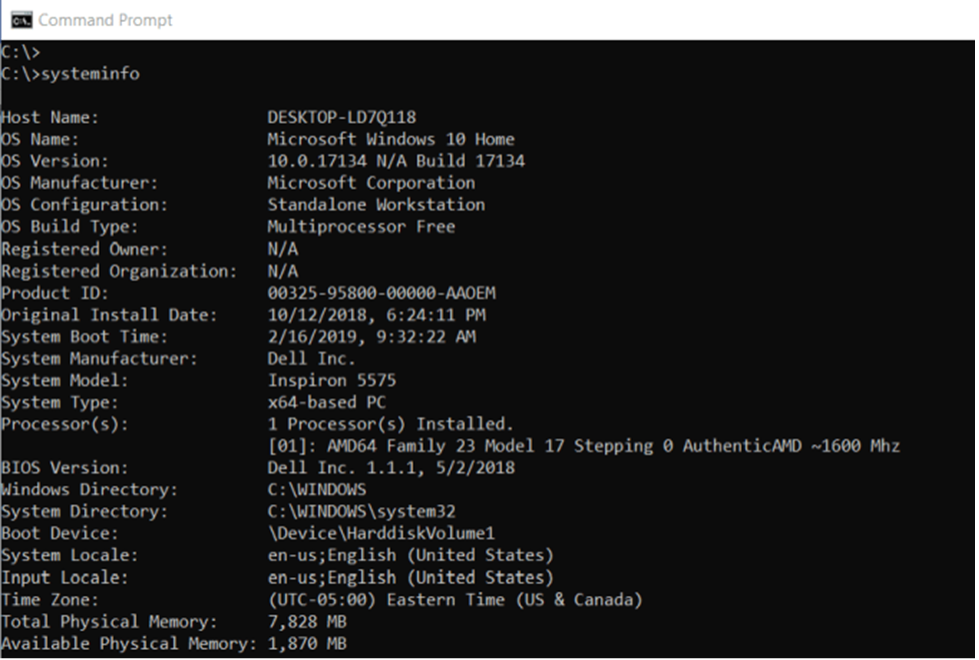
1. Use the systeminfo command to get system information
One of the cmd commands computer information windows 7 is systeminfo! The systeminfo command can be used efficiently to gather extensive system information and gain insights into many areas of your computer's settings. Explore essential Windows commands here.
When the command completes, you will be shown information such as the operating system version, hardware characteristics, installed hotfixes, network setup, and much more.
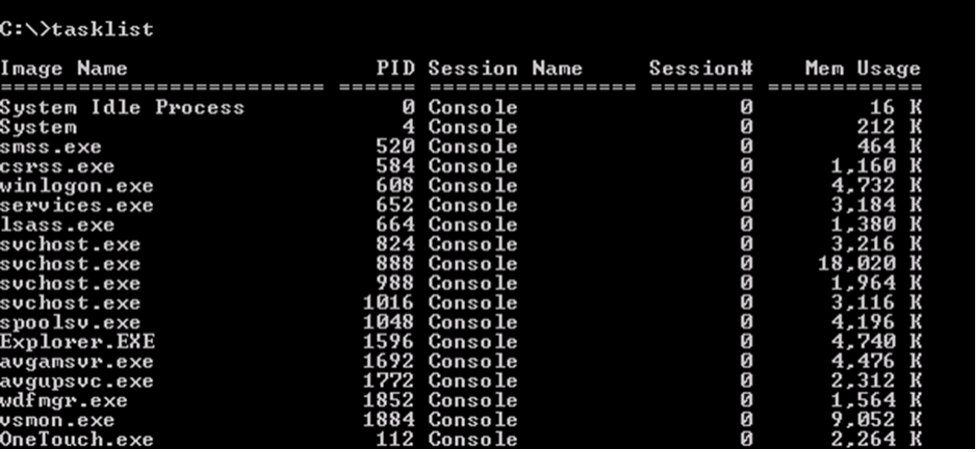
2. Use the tasklist command to see the list of running processes in Windows
You can use the tasklist command to get an overview of the processes that are currently executing on your Windows system. It can be useful for troubleshooting, resource monitoring, and identifying any unwanted or suspicious processes.
When the command completes, you will see a list of running processes. Each process's Process ID (PID), Session Name, Session Number, Memory Usage, and Image Name are presented.
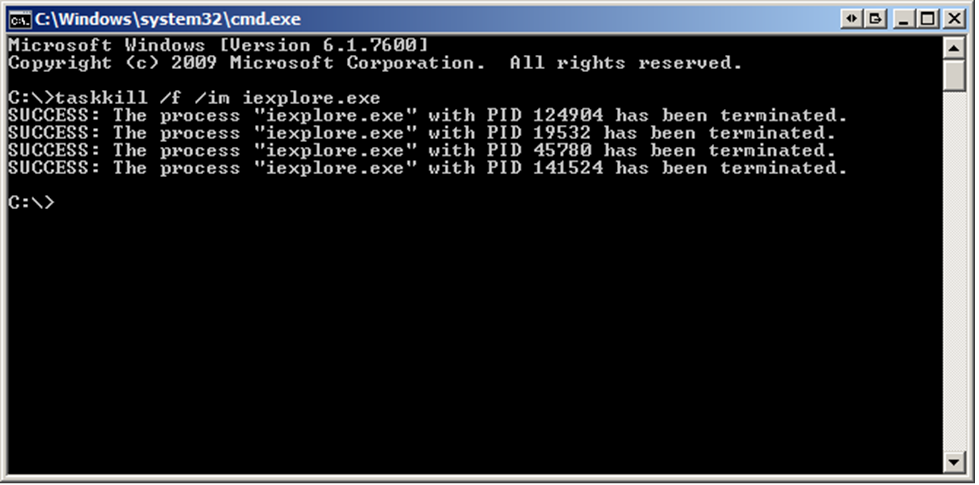
3. Use the taskkill command to stop a process
One of the other cmd commands computer information windows 11 is taskkill! To terminate a specific process, type "taskkill /PID PID>" (replace PID> with the real Process ID) in the Command Prompt window. To stop a process by its name, use "taskkill /IM process_name>" (replace process_name> with the name of the process).
If the process is still operating and can be properly ended, you will receive a notice confirming that it has been terminated.
How to Determine Whether a System Can Run the 64-bit Solaris Operating Environment
Check to see if the machine is running a supported version of Solaris and if it is the 64-bit variation. In the Solaris terminal, run the "isainfo -kv" command. If the output shows "64-bit sparcv9 kernel modules" or "64-bit amd64 kernel modules," the system may run the 64-bit Solaris operating environment.
How to Determine Whether a System Has 64-bit Solaris Capabilities Enabled
Check the CPU architecture to see if a system has 64-bit Solaris capabilities enabled. To do so, type "isainfo -b" into the terminal and hit Enter. This command will display your system's processor architecture.
- If the output is "64," the system is equipped with 64-bit Solaris capabilities.
- If the output is "32," it signifies that the system lacks 64-bit Solaris capabilities and is operating in 32-bit mode.
Examples
Example 1: Checking the "isalist" File

In this example, examining the contents of the "/etc/isalist" file reveals the presence of "amd64", confirming that the system has 64-bit Solaris capabilities enabled.
Example 2: Checking the "isalist" File for SPARC Architecture

In this example, examining the contents of the "/etc/isalist" file reveals the presence of "sparcv9", confirming that the system has 64-bit Solaris capabilities enabled for the SPARC architecture.
How to Display System and Software Release Information
You can use cmd commands computer information windows 10 to display system and software release information. The "showrev -a" command is specific to the Solaris operating system. It is used to display detailed information about the system and software release on a Solaris system. This command is excellent for gaining a complete overview of a Solaris machine's system setup and software versions.
Example
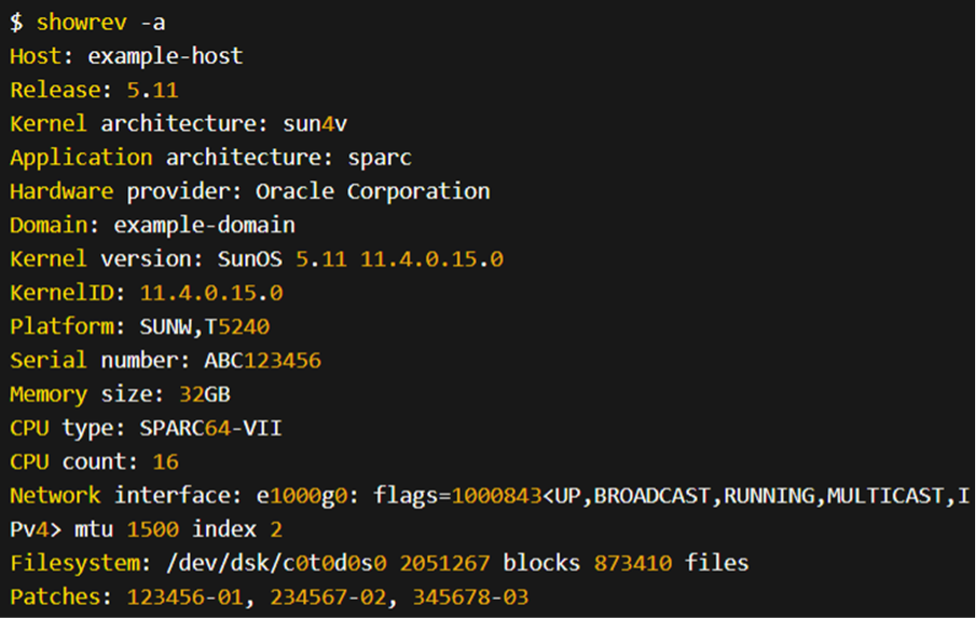
When you run this command, it will provide a comprehensive output that includes information such as:
- Solaris release version
- Kernel revision
- System hardware architecture
- Installed patches and their versions
- Software packages and their versions
- Network interfaces and their configurations
- Filesystem information
- Memory and CPU details
- System firmware version
- System serial number
- System uptime
How to Display General System Information
Use the "uname" command to display general system information. Type "uname" on the terminal or command prompt, followed by any optional flags. "-a" is the most widely used flag, and it displays all accessible information.
The command should be written as follows: -a uname
The output of the program will show system information such as the operating system, kernel version, machine architecture, and more.
Example

In this example, the output from the "uname -a" command provides the following information:
- Operating System: Linux
- Hostname: myhost
- Kernel Version: 5.10.0-10-generic
- Kernel Release Information: #10-Ubuntu SMP Mon Sep 20 21:31:20 UTC 2021
- Machine Architecture: x86_64 (This is repeated three times, representing the hardware architecture for the system, user space, and compiler used to build the kernel.)
- Kernel Type: GNU/Linux (This indicates that the Linux kernel is used with GNU utilities.)
How to Display a System's Host ID Number
The "hostid" command can be used to display a system's host ID number. A host ID is a one-of-a-kind identifier assigned to a system. The result will show the host ID number once you run the program.
Please keep in mind that the "hostid" command may not be accessible on all operating systems and may have various parameters or behaviors depending on the platform.
Example

In this example, the host ID number is "0123456789ab". Note that the actual host ID value will vary based on your system.
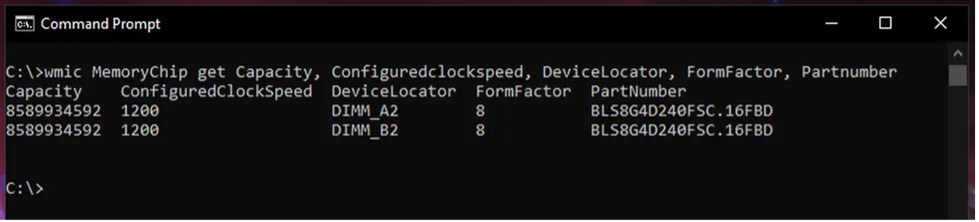
How to Display a System's Installed Memory
The following command can be used to display a system's installed RAM on Windows using the command line:
wmic memorychip get Capacity
The command will obtain and display the capacity of each memory chip installed in your system in bytes. It should be noted that this operation will return the capacity of each memory chip individually.
Example

In this example, the system has two memory chips installed, each with a capacity of 8,589,934,592 bytes (which is equivalent to 8 GB).
You can sum up the capacities displayed by the command to determine the total installed memory of your system.
How to Display the Date and Time
You can display the date and time using cmd commands computer information. The following command can be used to display the date and time from the command line:
echo %date% %time%
The command will display the current date and time in the format that your system has set.
Example
In this example, the command displays the current date as "Mon" (Monday), the date as "12/11/2023" (December 11, 2023), and the time as "2:34:56.78" (2:34 AM and 56.78 seconds).
Conclusion
Using the command-line interface, CMD commands provide a powerful and quick means to acquire important computer information. Users can access a variety of information about their operating system, network setup, CPU, RAM, and installed software with programs such as "systeminfo," "ipconfig," and "wmic." This information can be extremely useful for troubleshooting, system optimization, and obtaining a better understanding of your computer's hardware and software components.

Hello, everyone, my name is Lisa. I'm a passionate electrical engineering student with a keen interest in technology. I'm fascinated by the intersection of engineering principles and technological advancements, and I'm eager to contribute to the field by applying my knowledge and skills to solve real-world problems.