List of content you will read in this article:
Linux servers are based on a command-line interface by default, however, some might want to use them with a visual interface. In these cases, we can install an application that provides a GUI (i.e. Graphical User Interface). One of such applications is named GNOME and you can follow the steps outlined below to get it on your machine.
What is GNOME?
GNOME (i.e., GNU Network Object Model Environment) is a graphical user interface and set of computer desktop applications for users of the Linux computer operating system. It's intended to make a Linux operating system easy to use for non-programmers and generally corresponds to the Windows desktop interface and its most common set of applications. In fact, GNOME allows the user to select one of several desktop appearances. With GNOME, the user interface can, for example, be made to look like Windows 98 or like Mac OS. In addition, GNOME includes a set of the same type of applications found in the Windows Office 97 product: a word processor, a spreadsheet program, a database manager, a presentation developer, a Web browser, and an e-mail program.
GNOME Features
Now that you know what GNOME is, here are some of its greatest features:
Easy to Use
While the default Linux command line interface holds some challenges for its users and requires decent knowledge to operate, a GUI like GNOME allows even complete beginners to efficiently navigate the OS and utilize most of its tools.
Vide Choice Variety
GNOME is available in many forms on some distributions, such as GNOME Classic, GNOME on Xorg, etc. While they may all look similar on the surface, they use different X servers and are built with different toolkits.
Efficient
The dash and application viewer allows the user to open and utilize all the installed software from one place.
How to Install GNOME on CentOS?
Please note: our Linux server is running CentOS 7 and the following codes might vary for other distributions.
Step 1: At first, we should update CentOS:
Yum update -y
Step 2: After completion, install Gnome with the following command:
sudo yum groupinstall -y "GNOME Desktop"
Please note: to install this package, you must have at least 2.2Gb of free space.
Step 3: Now, reboot the server after the installation is complete.
Step 4: Install VNC server to have remote access to the server:
sudo yum install -y tigervnc-server
Step 5: Now, we want to configure the VNC server for the client. In this case, we should copy the generic VNC service unit file under /etc/system/system.
sudo cp /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@.service /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@:4.service
Please note: to make multiple connections with multiple clients, you should define users and make a copy of the file for each user. Also, you should change the port of each user. We defined port 5904 for our user with vncserver@:4.service in the previous command.
Step 6: Open the copied file to change the configuration with vi command.
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@:4.service
Step 7: Go to the [Service] section and replace username and screen resolution with default values:
[Service]
Type=forking# Clean any existing files in /tmp/.X11-unix environmentExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'ExecStart=/sbin/runuser -l root -c "/usr/bin/vncserver %i -geometry 1280x1024" PIDFile=/home/root/.vnc/%H%i.pid
Step 8: Then save the file and exit. Run the following command to reload daemon and the user will be enabled during boot time.
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadsudo systemctl enable vncserver@:4.service
Step 9: Now we should add the ports to the firewall.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=5904/tcp
Step 10: Then, reload the firewall:
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Step 11: In this step, we should start the VNC server. Run the below command and set a password to the VNC server.
Vncserver
The output should look something like this:
You will require a password to access your desktops.
Password:
Verify:
Step 12: Now restart the VNC server and reload the services:
vncserversudo systemctl daemon-reloadsudo systemctl restart vncserver@:4.service
Step 13: Open VNC viewer from your PC and type the server IP followed by port and click on Connect.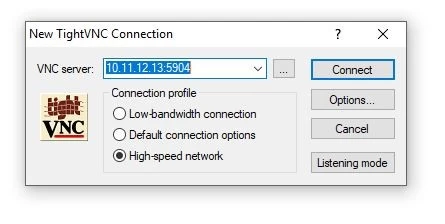
Step 14: Enter the password we set previously:
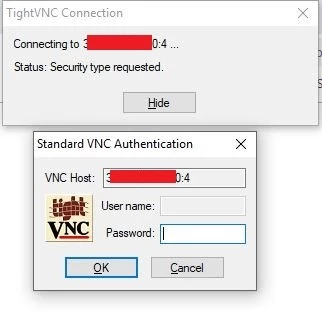
And that is it! You should now be able to see the welcome screen:
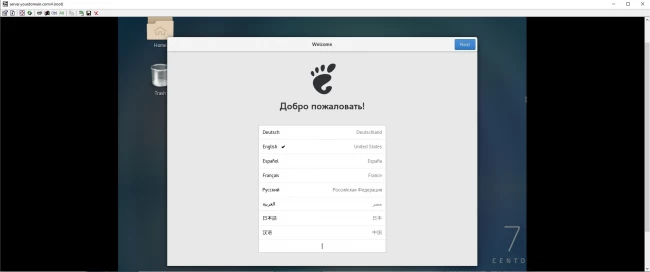
Conclusion
While mastering the Linux command-line interface is the way to go if you wish to become a professional sysadmin or want to find a career in server management, for daily use a GUI such as GNOME is simply more convenient. We hope that this step-by-step tutorial helped you in installing GNOME on CentOS.

I’m Oliver k. I have MS degree in Computer Engineering. For nearly 5 years that I have been working on web programing and also in last 2 years I have worked on windows and Linux VPS. This is my honor to share my experiences with a new community.