List of content you will read in this article:
Fiber optics is a medium that is used to transmit light pulses over a long distance through glass or plastic strands. These strands are like real fibers, and they play a very important role in data networking systems and telecommunication services. This fiber optic technology will soon become the only backbone of broadband. There are many reasons to justify this claim, and it is not only because of its reach, speed, and availability. The optics technology perfectly aligns with modern-day applications, and one such communication facility offered by this type of technology is fiber Internet.
Major companies, including Google and Verizon, are taking part in this movement of fiber optics technology. These companies take advantage of gigabit internet speeds for their FIOS and Google Fiber services, respectively. There are many more sectors using fiber optics like defence and Medica. This article will cover some major aspects surrounding fiber options and share some of the best use cases.
What is Fibre Optics?
Fiber optic technology involves a series of cables combined together to help transmit data across large distances in minimum time. The optic cables involved in the data transmission are made of either tiny glass or plastic. In both cases, the particle carries the data in the form of light beams. Now, when the light beams reach the recipient, the light pulses automatically translate to binary values. The computer does the conversion to binary, so we cannot visually witness that part.
The reason for choosing such optic cables for large-distance transmission is because they have faster data transfer rates. Users will also have an advantage in using fiber optics because it is less susceptible to noise and interference. Other alternatives used in the market are copper and telephone lines, but both come nowhere near fiber optic cables in terms of speed and transmission performance.
Construction of Fibre Optic Cables
We know that fiber optic technology uses certain cables to complete data transmission. Now, let us see how those fiber cables are formed and what parts are present in their construction.
The two main parts of an optical fiber are core and cladding. The core of a fiber optic is the cable's innermost part, and it is the main medium used to transmit light pulses. The second part is cladding, and this part is the thicker layer of the same core material.
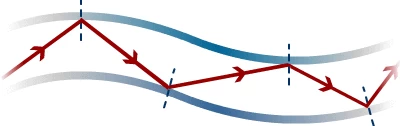
Both these parts undergo the same phenomenon called total internal reflection. The cladding and core make sure to keep the light inside the cable, and TIR helps facilitate the process by allowing the light to hit at a certain angle that makes it reflect into the cable.
When the light makes its way to the other side of the network, it follows a binary system for conversion, and light pulses become ones and zeroes. It has been recorded that these light pulses can go for sixty miles before we see any signs of degradations.
How does Fibre Optics work?
Even in the 60s, people used to execute long-distance telephone calls using fiber optic technology at the speed of light. If, at that time, it was used for communication, then now it has advanced to new levels of telecommunications that is capable of running 25,000 calls for each strand of optical cable. The basic or fundamental principle surrounding fiber optics' workings is sending coded data in light and converting the same into binary values for the computer to read.
We also got to pay attention to total internal reflection and how it plays a role in not letting the light escape out of the cable. The reflection properties are observed within the transparent parts of optical cables, and the pattern in which the light pulses travel is also unique. A zig-zag pattern is run through the entire cable till the light reaches the other side of the network.
Types of Fibres Optics
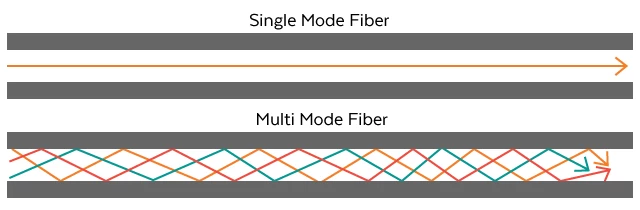
When we talk about optic cables carrying light, it is done in a path called mode, and light follows this path when travelling down the fiber. With fiber optic technology, one can use multiple paths to send across the data, so there will be different fiber optic cables. Take a look at some of the main fiber optic cables available in the marketplace:
Single Mode
One of the simplest structures in communication and transmission technology is single-mode fiber. The core is relatively thinner than other cables, and the path followed is a simple, straight down the cable without making any patterns. Real-world scenarios using single-mode optical cables are CATV, Internet, and telephone communication.
Multimode
This is a different fiber optic compared to single-mode, and it is because of many reasons. The core for multimode fiber is significantly larger than single-mode, and it is proven that the diameter allows not one but multiple light pulses to make their way to the other end of the cable. As it involves multiple light pulses, multimode transmission has a higher possibility of facing signal loss. The light used to create cable pulses comes from LEDs.
Main Use Cases of Fibre Optics
We often forget how important fiber optic technology is in our lives because we depend on it for so many applications. The laser signals can be roaming under the pavement, and we will not even have an idea about it. To know more about fiber optics' real-life applications, we have to dive deep into each sector and see how it is facilitating their development.
Computer Networks
Computer networks take full advantage of long-distance data transmission done by optical cables. With less loss signal and higher bandwidth, computer networks will perform at a high-efficiency rate. It can increase efficiency, but it can significantly reduce costs to maintain and operate networking computers. Another noteworthy point to be made on fiber optics impact on computer networks is it brought cloud computing to reality. As fiber optic cables transmit data at an insanely high speed, people get a better internet connection and will be more online. These cables also facilitate Skype calls over the internet, so computer networks have increased application by integrating fiber optic technology over conventional DSL broadband.
Broadcasting
Fiber optics is the future of broadcasting. In earlier days, radio and TV received less attention because it required people to install antennas to get transmission signals from the broadcasting station. Now, none of that is in existence, and fiber optic cables took over every broadcasting company. Fiber optics will eventually make coaxial cables of no use because we are no longer in the analogue world of communication. The digital world demands more, and it is fiber optics that have the functionality to deliver. The offering is higher for optic cables, and they need fewer signal boosters for amplification purposes. We will witness a complete change in the broadband system using only fiber optic technology to telecast shows and television programs with little to no interference.
Medicine
The first-ever use case of fiber optics in medicine was to help doctors create equipment advanced enough to pierce through the body's skin without having to cut it wide open. And this idea came through in the 1960-70s. Now, the doctors have so many instruments in place to help during a medical exam or operation. The latest trend that is attracting medical professionals is a lab on a fiber. With thin strands of fiber optics sent into the patient's body, the doctor can study whichever body part they want to examine. The symptoms or details of illness can be deduced by changing certain parameters related to fiber optic cables. Doctors can vary the intensity of light and change the wavelength up and down to get the patient's body's required properties.
Military
Missile launch sites and radar tracking stations make the most out of fiber optic technology. Military bases require something that is easy to carry and inexpensive, so fiber cables perfectly fit that description and help them against electromagnetic interference. Another huge advantage of using fiber optics in the military is that they don't need excessive protection or insulation because they are immune to any natural attack.
Here’s a table comparing the distances and speeds of the types of fiber optic cables
|
Cable Type |
Fiber Cable Distance |
||||||
|
Fast Ethernet 100BA Se-FX |
1Gb Ethernet 1000BASE-SX |
1Gb Ethernet 1000BASE-LX |
10GB Base SE-SR |
40Gb Base SR4 |
100Gb Base SR10 |
||
|
Single mode fiber |
OS2 |
200m |
5000m |
5000m |
10km |
- |
- |
|
Multimode fiber |
OM1 |
200m |
275m |
550m (mode conditioning patch cable required) |
- |
- |
- |
|
OM2 |
200m |
550m |
- |
- |
- |
||
|
OM3 |
200m |
550m |
300m |
100m |
100m |
||
|
OM4 |
200m |
550m |
400m |
150m |
150m |
||
|
OM5 |
200m |
550m |
300m |
400m |
400m |
||
Advantages of Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables have numerous advantages over traditional copper cabling. Here’s just a few of them:
- Higher Capacity: The current most widely used copper cable standard, Cat5e supports a bandwidth of up to 1Gbps, however, fiber optic cables can have bandwidths of up to 100Gbps.
- Fewer Signal Boosters: Since light can travel much farther distances down the cable without losing its strength, it minimizes the need for repeaters.
- Less Interference: A copper cable requires special shielding to avoid electromagnetic interference, which works well most of the times, however, it is not sufficient when many cables are strung together. The physical properties of glass in fiber optic cables prevent such issues.
What is Dark Fiber?
Although sounding sinister, it simply refers to the fiber optic cables that have been installed but are not currently in use. Extremely large quantities of fiber optic cabling have been laid since the 1980s onward, with the worldwide total being more than a hundred million kilometres and some of them still lie unused today. It is generally believed that most networks contain a third to half of the dark fiber.
Conclusion
We know it's been a decade since fiber optics first arrived, but our technology is slowly catching up to create more real-life applications and use it to its full potential. We will get faster, and our data will always be safe when these cables are in full use in the future. And the best part about fiber cables is that they are everywhere, and companies can readily acquire them in large quantities.
The only thing we need to focus on is the development and more services based on fiber optics like Monovm's Cloud VPS solution. If that happens over the next five-ten years, we will see more use cases in other fields.
